This is an automatically translated article.
The article is professionally consulted with Master, Doctor Le Nhat Nguyen - Doctor of Obstetrics and Gynecology - Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology - Vinmec Danang International General Hospital.Polycystic ovary syndrome in the long term has the potential to increase the risk of a number of diseases such as heart disease, diabetes, endometrial cancer, high blood pressure...
1. Causes of Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome
So far, it is not clear what causes polycystic ovary syndrome, but the disease has some symptoms such as:
Abdominal obesity. Menstrual cycle disorder due to irregular or irregular menstrual cycle, amenorrhea, oligomenorrhea, polymenorrhea, menorrhagia. More severe cases can be uterine bleeding. Insulin resistance, accompanied by other metabolic disorders, leads to diseases such as high blood pressure, dyslipidemia. Hirsutism, which often develops in places such as the cheeks, chin, neck, mid-chest, and below the navel. Acne. Hair loss, baldness.
2. Diagnostic criteria for polycystic ovary
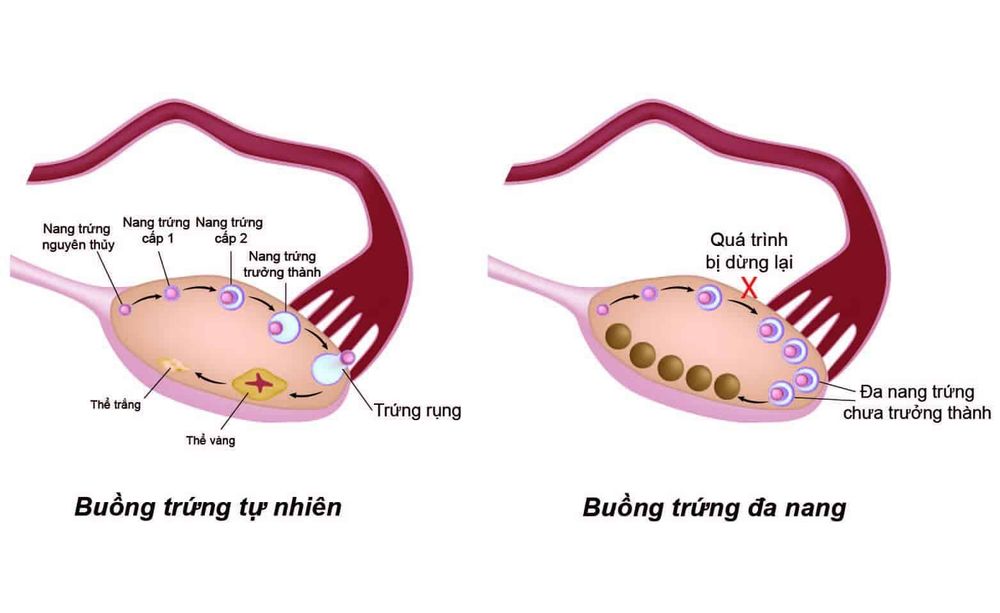
According to European standards, the image of polycystic ovaries on ultrasound is considered the "gold standard" to diagnose the disease. About 90% of women with amenorrhea are found to have polycystic ovaries on ultrasound. In addition, in Vietnam, it is combined with one or more other accompanying symptoms. Based on ESHRE ASRM Rotterdam Consensus 2003, the criteria are agreed upon:Menstrual cycle is sparse or amenorrhea, menstrual cycle > 35 days or amenorrhea > 6 months. Hyperandrogen causes hirsutism and acne. Image of polycystic ovaries on ultrasound: When ultrasound day 2 - 5 of the menstrual cycle or day 3 of the artificial cycle, there are 12 follicles with size from 2 to 9mm, ovarian volume increases > 10cm3 and expressed in at least one ovary. When 2/3 of the above criteria are met, the diagnosis is polycystic ovary syndrome.
3. Treatment of polycystic ovary syndrome
Currently, the specific treatment of polycystic ovary syndrome does not have a specific modality and varies according to the purpose of treatment, whether it is symptomatic treatment of hyperandrogenism or treatment of infertility.3.1 Cases where infertility treatment is not required
It is possible to use some hormonal drugs to reduce symptoms of the syndrome such as irregular menstrual cycles, hirsutism ... or prevent some risks that may appear long-term. However, when the medication is stopped, symptoms may return.3.2 Infertility treatment cases
Because polycystic ovary syndrome causes ovulation disorders, failure to ovulate, leading to infertility, the goal of treatment is to induce ovulation. There are many treatments to induce ovulation.Lose weight for people with obesity, to lose fat, reduce insulin resistance; Use of drugs that stimulate follicular development; Reduces androgen levels in the blood, improves the menstrual cycle, thereby increasing the chances of pregnancy. Alternatively, laparoscopic scintigraphy can be performed on the surface of the ovary. This is a new technique and has a high rate of inducing ovulation, regular menstrual cycles, and post-operative ovulation. After ovariectomy, the patient has a better response to ovarian stimulators. Ovarian ultrasound to detect polycystic ovaries on ultrasound is the main standard for the diagnosis of polycystic ovary.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.