This is an automatically translated article.
The article is written by Master, Doctor Ma Van Tham - Head of Pediatrics - Neonatology Department - Vinmec Phu Quoc International General Hospital.Early life wheezing is a common disorder, with about 50% of children having an episode of wheezing within the first year of life. Recurrent wheezing is estimated to occur in one-third of preschool-aged children and can cause significant morbidity, reduced quality of life, and increased frequency of health care services. and economic costs.
1. Overview
Wheezing is a high-pitched whistling sound that occurs when the small airways are narrowed due to bronchospasm, mucosal thickening due to inflammation, edema, excessive secretions, or foreign bodies. Wheezing also has a variety of tones when the airways are narrow to varying degrees, as in asthma. Monophonic wheezing is produced in the larger airways during expiration such as the trachea or distal bronchi.Wheezing is very common in infants and children under 5 years of age. More than 30% of children under 3 years of age have at least one episode of wheezing, about 50% of children under 5 years of age have at least one episode of wheezing. About half of all children who develop wheezing before age 3 will not have a recurrence by age 6.

Thở khò khè rất hay gặp ở trẻ nhũ nhi và trẻ dưới 5 tuổi.
2. Pathogenesis
Young children tend to be more prone to wheezing because of anatomical factors related to the lungs, chest wall, and immunological and molecular influences than older children.Ventilation is affected by airway radius and lung elasticity. Airway resistance is inversely proportional to the fourth power of airway radius. In children younger than 5 years of age, a small peripheral airway may contribute up to 50% of total airway resistance. Further narrowing of the airways may result in subsequent airflow limitation and consequent wheezing.
Newborn's chest is soft, the pressure inside the thoracic cavity at the end of expiration is not enough to open the airways maximally, causing a relative narrowing of the airways. Restriction of airflow in young children is also due to differences in tracheal cartilage composition and airway smooth muscle tone, leading to increased airway resistance compared with older children. All of these mechanisms combine to make the airways more prone to collapse in young children, increased airway resistance, and subsequent wheezing. Many of these factors grow rapidly and change rapidly during the first year of life.
Immune and molecular influences may contribute to an increased tendency to wheeze in young children. Compared with older children and adults, young children tend to have more lymphocytes and neutrophils than mast cells and eosinophils in the bronchial lavage. A variety of inflammatory mediators have also been implicated in wheezing, such as histamine and leukotrienes. During the fetal or neonatal period, lung structure and function is affected by factors including fetal nutrition and fetal exposure to maternal drug use or exposure to secondhand smoke. happen.
3. Children's wheezing patterns by age
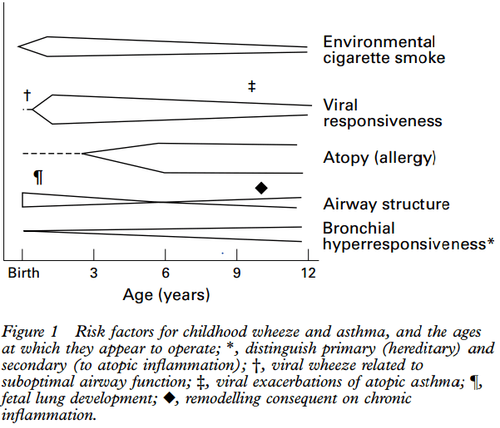
Một số yếu tố nguy cơ gây khò khè ở trẻ.
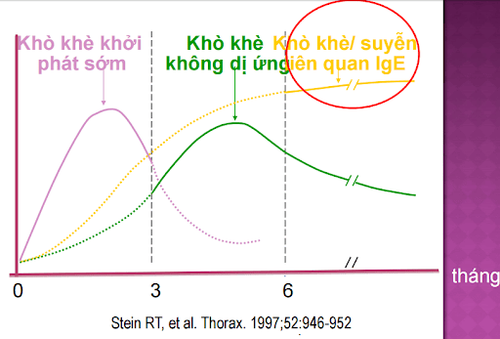
Sự thay đổi kiểu hình khò khè của trẻ theo độ tuổi.
To avoid wheezing, parents should add some supportive foods containing lysine, essential micro-minerals and vitamins such as zinc, chromium, selenium, B vitamins,... Helps to fully meet the needs of nutrients while supporting the immune system, enhancing resistance, reducing the risk of upper respiratory tract infections, bronchitis, flu.
Lysine is very necessary for the development of children, Lysine promotes the production of digestive enzymes to stimulate children to eat better and digest easily and effectively, increase food metabolism, maximize absorption of nutrients. Nutrition from food.Strengthening lysine for babies helps the body create antibodies, develop resistance to help reduce cough, thin phlegm in children.
Parents can learn more:
Why do you need to supplement Lysine for your baby?
Please regularly visit Vinmec.com website and update useful information to take care of your baby and family.