This is an automatically translated article.
Surgery to remove complex maxillofacial tumors in difficult-to-intervention positions is performed according to standard procedures. This method brings new life to the patient.
1. Types of tumors in the maxillofacial region
There are many types of tumors in the human body. Tumors can be found in the mouth or jaw. The rate of tumors in the maxillofacial region compared to the whole body is 5-10%. These include both benign and malignant tumors.
Benign tumors are well-defined, unchanged, slow growing, do not invade nearby tissues and do not metastasize to other places. Malignant (cancer) has no clear boundary, invades surrounding tissues, wreaks havoc on the body, and metastasizes to other organs. To distinguish between benign and malignant tumors most accurately, surgery is needed to take samples of the tumor for testing (biopsy).
Benign maxillofacial tumors include:
Hemangiomas: Presence of dark red or brown birthmarks on cheeks, lips, forehead, tongue, floor of mouth,... Hemangiomas are mainly congenital, are benign, can last a lifetime. This is a common tumor, accounting for about 10% of diseases in the maxillofacial region. Surgery to remove hemangiomas is very difficult because the bleeding is profuse and difficult to control. The main treatment method is to use a laser to block the blood vessels feeding the tumor, shrink, and atrophy the tumor; Lymphoma: Red, dark purple, present in many places in the mouth, mainly the tongue and floor of the mouth. Treatment of lymphoma includes surgery or laser burning; Fibroids, neurofibromas: Appears in many places of the face, mainly on the face, cheeks, forehead,... Lipomas: Usually in the skin of the face, the lining of the lips, cheeks and floor of the mouth. Lipoma has a yellow, hard, fat-like nucleus with clear boundaries. This type of tumor is usually treated with surgery and has a low recurrence rate; Osteosarcoma and bony prominence: Mainly facial bone tumors in the lower jaw area, causing facial deformities. When the tumor grows large, surgery is needed. Osteoma can be combined with fibroma to form a mixed bone and fibrous tumor, present in the skull and chin bones; Parotid gland tumor: Common in the cheek area close to the ear, where the maxillary salivary gland is located. This is a benign tumor, but after surgery, it can recur and develop into a malignant tumor. Surgery for parotid adenomas is often difficult because it can cause injury to the VII nerve, causing facial paralysis; Papilloma: Appears in the cleft palate and floor of the mouth. If papillae on the floor of the mouth will push the tongue, making chewing difficult. Papillomas are usually treated with surgery and are less likely to recur; Yeast tumor: Usually appearing in the lower jaw, it is a benign tumor but easy to recur. Enamel tumours inflate the lower jaw bone, destroy the bone marrow inside and hollow out the bone, making it easier to break teeth and fractures of the jaw. The treatment of yeast tumors is mainly surgical options. When surgical curettage of the tumor, the inside of the tumor is as soft as mud, and if the tumor is not removed, it is easy to recur.
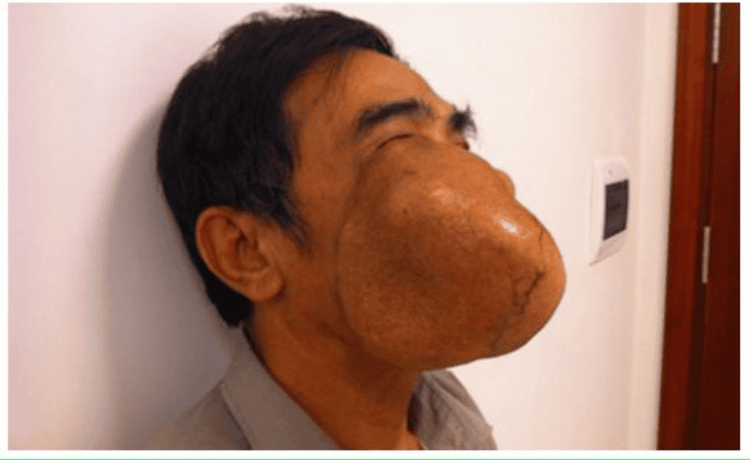
U men răng gây căng phồng trong xương hàm
2. Complicated facial tumor removal surgery
Common maxillofacial tumors include skin cancer, hemangioma, melanoma, hemangioma, parotid gland tumor, pox tumor, submandibular gland tumor,... Tumor was determined to be complex and difficult to operate when located in a complex location such as invading blood vessels, nerves or located in organs such as lips, eyelids, nose, ear lobes,...
2.1 Indications/contraindications
Indications
Tumor areas maxillofacial is cancerous in nature or suspected to be cancerous; Large tumor causing obstruction, affecting the function of organs or lacking in aesthetics. Contraindications
U has no indication for surgery; Elderly and frail patients, heart failure, severe kidney failure, poor health are not able to withstand the effects of major surgery.
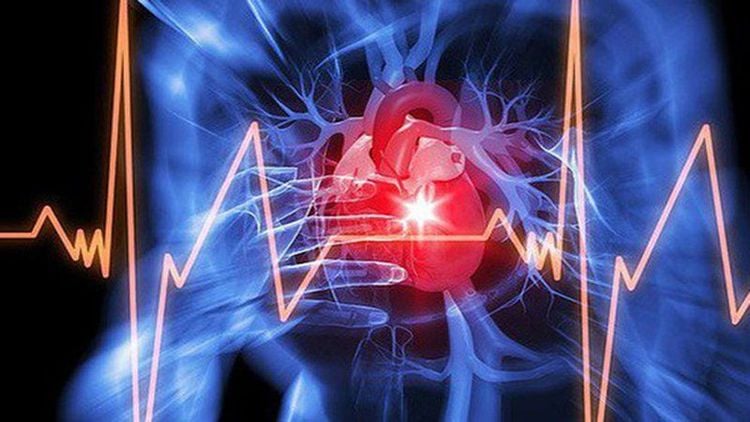
Chống chỉ định với bệnh nhân suy tim
2.2 Surgical procedure
Preparation
Performer: Dentist - jaw - face; Means: Software surgical kit, anesthetized means, endotracheal tube; Patient: Be explained about the purpose and procedure of the procedure and should strictly follow the doctor's instructions before and after surgery; Medical records: According to the regulations of the Ministry of Health, it is necessary to describe the tumor, size and co-morbidities, if any such as cardiovascular disease, diabetes,... Implementation
Anesthesia: Intubation anesthesia ; Patient position: Prepare a position suitable for each type of maxillofacial tumor and the location of the tumor; Skin incision: Incision around the tumor or on the tumor (depending on the type of tumor) and if it is cancer, the incision must be wide according to the principles of cancer surgery; Tumor dissection and resection: Dissect the tumor out of the surrounding healthy tissue, especially nerves - blood vessels; remove the tumor after the dissection is complete; perform hemostasis; Close the incision according to anatomical layers, creating a flap of skin to cover.
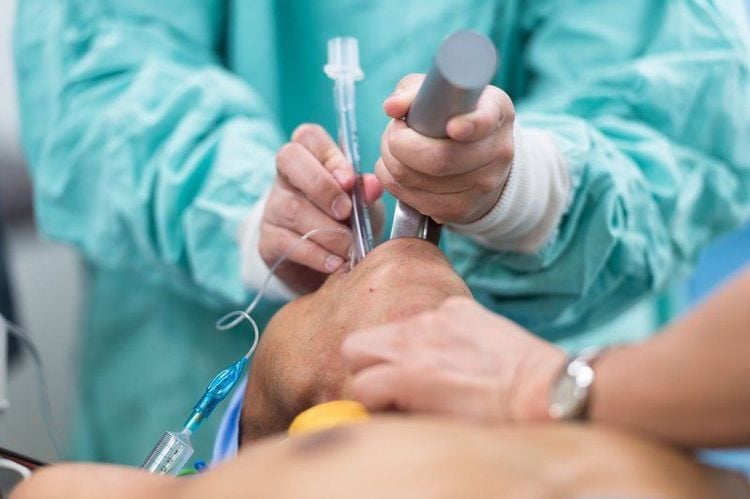
Người bệnh được gây mê nội khí quản
Monitoring of complications
After surgery of complex maxillofacial tumors, the patient may bleed (bleeding from the skin edge, blood vessels are invaded during surgery). The treatment is to cut the thread to stop the bleeding. With other complications, the right treatment according to the protocol depending on each specific case.
When being assigned to perform complex maxillofacial surgery, patients need to follow all instructions of the doctor to ensure the best treatment effect and avoid possible complications.
Patients can go to Vinmec International General Hospital for examination and treatment. There is a team of musculoskeletal specialists who are well-trained, experienced and professional; system of modern equipment, meeting international standards; Professional service quality, high efficiency in diagnosis and treatment.
For detailed advice on malignant tumors in the maxillofacial region, please come directly to Vinmec medical system or register online HERE.
MORE:
Malignant bone tumors: Causes, symptoms, diagnosis and treatment Oral cancer: Causes, symptoms, diagnosis and treatment How is bone cancer diagnosed?