This is an automatically translated article.
The article was professionally consulted with MSc Vo Thien Ngon - Urologist, Department of General Surgery, Vinmec Da Nang International Hospital.Urethral trauma is a common surgical emergency in men. If not detected and treated promptly and properly, the injury will leave many serious complications for the urinary and genitals.
1. Causes of urethral trauma
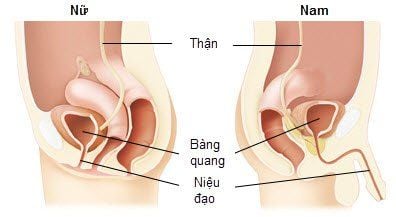
The urethra is the small tube that carries urine from the bladder to the outside of the body. In men, the urethra is also the tube that carries semen during ejaculation.The urethra in men is 14-16 cm long. Physiologically, the male urethra is divided into two parts, the posterior urethra and the anterior urethra. In which, the anterior urethra is 10-12cm long, also called spongy urethra because it is surrounded by spongy objects. The urethra before injury will cause a lot of bleeding. The posterior urethra is 4.5-5cm long, including the prostatic urethra and the membranous urethra. The posterior urethra is vulnerable to pelvic trauma.
The urethra in women is a tube about 3-5cm long that goes from the inner urethral orifice in the bladder neck to the external urethral orifice in the vulva, elastic, can dilate up to 1cm.
Injury to the urethra is a common surgical emergency in men, rarely in women. If trauma to the female urethra occurs, it is usually very severe.
Common causes of male urethral trauma are:
Anterior urethral trauma: due to a direct fall of the patient sitting on a hard object, the traumatic force directly affects the urethra and causes injury. . The main causes are occupational accidents and traffic accidents.
Posterior urethral trauma : mainly due to indirect trauma, often as a complication of pelvic fracture. When the pelvis is ruptured, the posterior urethra passes through the medial perineal fascia, the urethra is pulled when the pelvis is injured. This is considered a multi-injury, often caused by traffic accidents or occupational accidents. Urethroscopy and dilatation can also cause posterior urethral injury. Injuries to the male urethra are common in men aged 20-50 years old because this is the working age and often participates in traffic. The rate of injury involving both anterior and posterior urethra in men is 30-50%. 50-70% of patients with urethral trauma experience shock due to pain, blood loss, and associated lesions.
2. Symptoms of urethral trauma in men
In addition to systemic symptoms such as shock due to pain, blood loss; infection when the patient is late. Anterior urethral trauma and posterior urethral trauma have different characteristic symptoms such as:
2.1. Symptoms of anterior urethral trauma
After an accident that leads to injury, the patient has sharp pain, which can be so painful that he faints or can't sit up and walk. Bleeding from the mouth more or less. Perineum hematoma bruised butterfly shape large or small. The hematoma may extend to the groin and anteriorly, with the scrotum distended. Patients with urinary retention due to disruption of urethral circulation. Urinary retention may appear immediately after the injury or appear late. After the trauma, the patient can still urinate a few times before experiencing urinary retention, usually due to urethral perforation, edema or blood clot occlusion.

2.2. Symptoms of posterior urethral trauma
Patient is in moderate or severe shock with symptoms of tachycardia and hypotension. Deep hematoma due to pelvic injury usually presents late. A pale green hematoma usually appears in the groin, inner thighs, and perianal area. When the pelvis is injured, it is necessary to think about the possibility that the patient has a posterior urethral injury, especially when the patient has urethral bleeding, urinary retention, hematoma, etc.
3. Treatment of urethral trauma
Injury to the male urethra, if not treated promptly and properly, will leave many serious complications in both urinary and genital. The principle of treatment is to prevent infection with systemic and local antibiotics. Early detection and timely treatment of lesions, at the same time stop bleeding and release hematoma, drain urine and restore urethral circulation.
3.1. Methods of restoring urethral circulation
Non-surgical:
Apply to patients with simple urethral tamponade. The doctor appoints a urethral catheter and saves the catheter for 7-10 days. Apply cold compresses and ice packs to the perineal area. Give the patient topical and systemic antibiotics. After removing the catheter, dilate the urethra. Patients need to periodically re-examine by appointment to detect early complications of urethral stricture. Surgery:
1 stage surgery: the surgical team will proceed to treat the combined lesions. Injuries to the urethra, if possible, will be drained of the bladder, sutured, placed the urethral barrel on a plastic barrel or foley for the urethra to heal itself. 2-stroke surgery: indicated for patients with severe shock who do not allow prolonged surgery. In phase 1, the patient will have a suprapubic bladder drainage. Stage 2, the doctor will conduct a urethroplasty, this is done after 7 days-1 month when the patient has recovered.
3.2. Specific treatment of urethral trauma
Urethral contusion:
If the patient comes early, it will be treated by placing a foley catheter through the urethra, saving the catheter for 7 days. Hand-held compression bandage, combined with ice and antibiotic use.
For the late patient, perform local compression, suprapubic bladder drainage and perineal hematoma. Give the patient systemic antibiotics.
Urethral rupture:
Treatment steps include:
Drainage of the bladder above the pubic bone, collection of perineal hematoma. Place the urethral catheter closed, withdraw after 3-4 weeks, and periodically dilate the urethra after the catheter is removed. Urethral reconstruction surgery to restore circulation (part 2). Urethral flexion:
With a male urethral injury, the patient will be drained of the bladder above the pubic bone, combined with the urethral tube. The urethral catheter will be removed after 3-4 weeks. The patient must be re-examined to dilate the urethra periodically after the tube is removed. If the urethral reconstruction surgery is not performed in the 2nd period.
Injury to the urethra if not given emergency treatment and early treatment can leave dangerous complications, especially urethral trauma in men. Therefore, when experiencing urethral trauma, it is necessary to quickly move the patient to medical centers for examination and treatment.
Vinmec International General Hospital is the place to gather many good urologists, experienced in examining, treating and emergencying many complicated urological diseases, bringing efficiency and stable health to patients. patient. Especially with modern facilities, meeting international standards, sterile space will bring optimal efficiency for customers using services at Vinmec.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.