This is an automatically translated article.
Articles written by Master. Resident Doctor. Tran Duc Tuan - Department of Diagnostic Imaging, Vinmec Central Park Hospital.
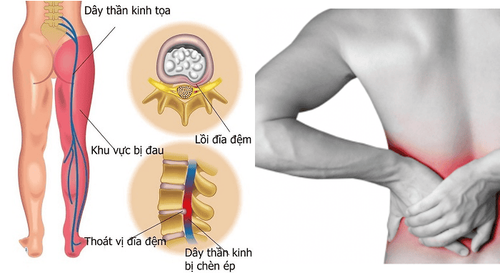
Treatment of low back pain - sciatica caused by DR currently has many methods. Medical treatment alone or a combination of physical therapy and acupuncture. Surgical treatment helps to solve the cause, relieve pain quickly, but this method can damage many anatomical structures, greatly affect health, and still have certain complication rates.
1. Lumbar spine and discs
The spine is the main pillar of the body that goes from the underside of the occipital bone to the top of the coccyx. The spine consists of 33-35 vertebrae overlapping each other, divided into 5 segments, each segment has a curvature and its own characteristics suitable for the function of that segment. From top to bottom: 7 cervical vertebrae, 12 thoracic vertebrae, 5 lumbar vertebrae, 5 sacral vertebrae and the last 4-6 vertebrae fused to form the coccyx.
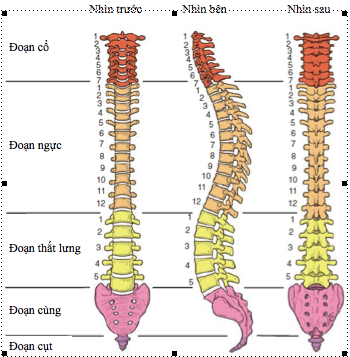
The lumbar spine together with the pelvis create continuity with the lower extremities to help participate in movement. The lumbar spine (CSTL) is composed of many functional units called motor segments. The motor segment includes: 1 disc, 2 upper and lower vertebral bodies and 1 spinal canal.
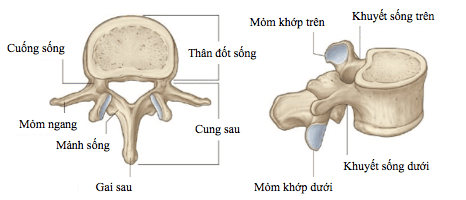
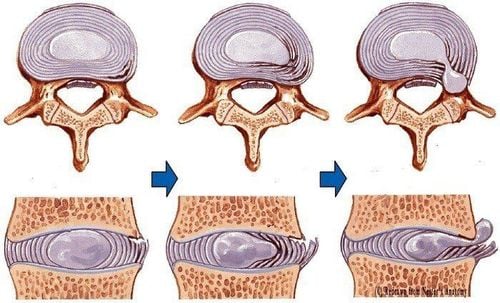
Each disc is composed of a central nucleus containing gelatin, the periphery consisting of many concentric fibrocartilage rings. The mucinous nucleus of the disc is very fragile compared to the annulus. It does not have a fibrous structure for good positioning and becomes increasingly dense as people get older causing herniated discs (DVT).
In the CSTL segment, the posterior and posterior lateral parts are composed of a few fine fibers, so here the thickness of the loop is thinner than elsewhere. This is the weakest point of the annulus, which is easily broken, causing posterior lateral hernia.
2. Pathogenesis of spinal disc herniation
Functionally, discs ensure a tight connection between the vertebral bodies, play the role of shock absorption and support the weight of the body along the longitudinal axis of the spine. In addition, it is also involved in spinal motor function.
When the disc is normal, if there is a load acting on the spine along the longitudinal axis, the nucleus pulposus flattens, the annulus fibers bulge. That load is evenly distributed in all directions creating equal pressures on the annulus and medial cartilage plates, so the load transmitted to the vertebra below is greatly reduced. DVT is a consequence of the degenerative process, occurring in the components of the spine, first in the discs, then in the facet joints, vertebral bodies, and ligaments. The degenerative process progresses with age and usually develops in multiple intervertebral compartments.
In the pathology of herniated disc, the nucleus pulposus degenerates displaced from the physiological position. If the swelling of the mucinous nucleus is maintained to a certain extent, and the annulus has ruptured much, herniation of the mucinous nucleus will occur. If the nucleus pulposus is severely degenerated, the annulus is compressed and flattens, exceeding the limit of the bony body and the height of the disc is reduced. From there, it will cause a disc-root conflict on the path of the nerve or cause mechanical compression and aseptic epidural inflammation, causing the nerve and nerve roots to become inflamed, leading to neuropathic pain.
3. Treatment of low back pain – sciatica
Corticosteroid dialysis injection is one of the conservative treatment methods mentioned in the world literature and there are many reports confirming the clinical efficacy as well as the safety of the method.
The method has many advantages such as: can relieve pain quickly, minimally invasive technique, drugs are concentrated at the pain site to help reduce the equivalent dose of oral drugs as well as limit systemic effects, ....
Currently, there are 3 main injection methods commonly used: epidural injection, selective nerve root injection and posterior trochanteric injection. In which epidural injection is indicated for low back pain secondary to spinal stenosis, disc herniation with or without radicular pain or low back pain of unknown cause. Posterior trochanteric joint injection is used in the case of back pain caused by osteoarthritis of the posterior trochanter or trauma. Nerve root selective dialysis injection is widely indicated in the treatment and diagnosis of acute or chronic rheumatic low back pain.
The risks from steroids themselves are rare and much less than the side effects of oral steroids.
4. Technical steps
The patient underwent interventional procedures under the guidance of a computerized tomography machine (CLVT) performed by doctors and technicians of the Department of Imaging. The technique is carried out according to a basic procedure as follows:
Step 1: Prepare the patient and interventional instruments
Explain to the patient and family clearly the treatment goals, procedure and complications may occur during the procedure. The patient's family member wrote a written commitment agreeing to carry out the procedure. The patient lies prone on the computed tomography table. Place an intravenous line. Disinfect the site of the procedure, spread sterile. Prepare the kit for the procedure. Step 2: Locate the dialysis injection site
Scan to locate the intervertebral vertebrae under CT, take slices through the vertebral layer – disc damage, depending on the location to be injected, the desired slice will be selected. entry point and skin entry
Figure 5. Positioning the vertebrae – discs perform the procedure on CT
Step 3: Percutaneous microneedling
Insert a very fine needle into the desired position, approach under the direction guidance of the CVT.
Figure 6: Insert the needle under the guidance of the CT
Step 4: Inject the drug
Aspirate the needle slowly before injecting to see if it punctures the blood vessel or not.
Inject the contrast agent to accurately check the desired injection range and exclude blood vessels. If the position is correct, pump a mixture of Corticosteroids mixed with Lidocaine.
Figure 7: Inject the drug into the desired position
Step 5: Withdraw the puncture needle, end the actual procedure
Withdraw the needle. After withdrawing the needle: re-sterilize and cover the injection site with medical tape. Clean up tools.
Step 6: Post-treatment monitoring and evaluation
After the procedure: the patient can sit up and walk gently, monitor the patient's bleeding and reaction for at least 30 minutes after the injection . Instruct the patient after the procedure: do not let water seep in, do not rub the medicine. After 24 hours, remove the bandage and shower as usual. Pain at the injection site may occur within the first 12-24 hours, which should subside within 48 hours of injection. When discharged from the hospital, patients will be followed up after 2 weeks, 1 month, 3 months to evaluate the effectiveness of treatment. With the new trend of medicine leaning towards non-surgical percutaneous interventions, dialysis injection to relieve lumbar spine pain - sciatica due to disc herniation is a method that is increasingly being applied to patients. advantages for rapid pain relief immediately after injection, limited effects of systemic drugs and minimal invasiveness as well as short intervention time, no hospital stay.
At Vinmec Central Park Hospital, we also perform many other analgesic interventions such as pain relief in acute/chronic shingles, trigeminal ganglion block (Gasserian) in pain related to facial nerve, plexus blockade in pain caused by cancer, pain after surgery... For advice on examination and treatment, please contact the hotline number of Vinmec Central Park Hospital.
Customers can directly go to Vinmec Health system nationwide to visit or contact the hotline for support.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.