This is an automatically translated article.
The article is professionally consulted by Master, Doctor Hoang Thanh Nga - Ophthalmologist - Department of Medical Examination and Internal Medicine - Vinmec Ha Long International General Hospital.
Macular degeneration (AMD) is one of the most common middle-aged diseases that cause serious vision problems. If age-related macular degeneration is not detected and treated at an early stage, the disease can affect the patient's daily life and cause serious health complications.
1. What is macular degeneration (AMD)?
Macular degeneration (AMD) is an age-related eye condition that usually affects people aged 60 years and older. AMD progression is often very slow, making it difficult for patients to notice changes in vision. Macular degeneration usually occurs in the macula, the central part of the retina. With AMD, the patient will have impaired vision, possibly even vision loss in both eyes, leading to some vision problems.1.1. Types of macular degeneration Dry (atrophic) macular degeneration: More common than wet (about 90%). Dry AMD occurs due to an increase in retinal waste products, or drusen, that cause the light-sensitive layer of cells in the macula to thin, which over time leads to tissue death, causing blurred vision. or loss of central vision. In addition, dry macular degeneration if not treated early can develop into wet macular degeneration - a much more severe form of AMD. Wet macular degeneration (exudative): Less common than dry AMD (only about 10%), but it causes extremely serious effects on the patient's vision. Wet AMD occurs when abnormal blood vessels form under the retina. Blood and other fluids then leak from the blood vessels, causing scarring in the macula. This condition will cause central vision to be distorted or lost, patients may misidentify straight lines as wavy lines.
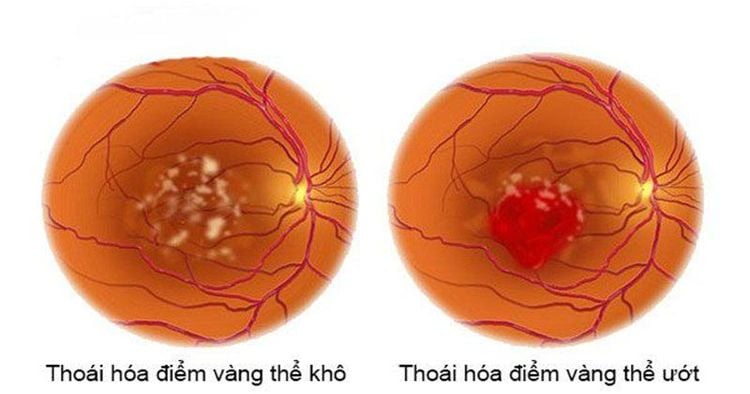
Có 2 loại thoái hóa điểm vàng
1.2. Symptoms of Macular Degeneration (AMD) Age-related macular degeneration (AMD) can cause some of the following symptoms:
Impaired vision Feeling difficult to read, drive a car due to reduced quality of vision resolution. Distorted vision, for example, when looking at faces or lines, wavy lines appear. When looking at the center of the image will feel dark, blurry or unclear. Eyes have difficulty adapting to working in low light Color vision disorder Dazzling Diplopia One or both eyes 1.3. Risk factors for macular degeneration (AMD) Several factors can increase your risk of developing macular degeneration (AMD), including:
Gender: Women are more likely to develop AMD than women. with men. Age: people in middle age (from 50 years old and above) are a high-risk group for macular degeneration. Lifestyle: People who regularly smoke, are sedentary will have a high risk of AMD. Heredity: Parents with macular degeneration can also pass it on to their children. Diet: An unhealthy diet such as low in vegetables, high in fat will make the body not receive enough nutrients and antioxidants to protect healthy eyes. Medical condition: People with chronic diseases such as high blood pressure, obesity will have a higher risk of developing macular degeneration than others.
2. Treatment of age-related macular degeneration
Although age-related macular degeneration (AMD) cannot be completely cured, there are treatments available to help slow the progression of the disease and prevent further damage. damage to vision caused by disease. Treatment options will depend on each person's age and medical condition. Here are some effective treatments for patients with macular degeneration (AMD):
2.1. Anti-VEGF Therapy VEGF therapy is commonly used for cases of wet macular degeneration. A person's body normally makes a protein called vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF). It has the ability to stimulate the creation of new blood vessels and provide the necessary amount of oxygen for tissues to function properly. However, if the amount of VEGF in the body increases too much, it will lead to rapid proliferation of blood vessels in the retina and leakage of fluids, causing macular degeneration. Because wet macular degeneration is a problem involving abnormal blood vessels, doctors can treat it with anti-VEGF drugs. This medication is injected directly into the patient's eye (also known as an intraocular injection), which inhibits the growth of new blood vessels and improves vision. VEGF usually has four main drugs, including: Aflibercept (Eylea), Bevacizumab (Avastin), Brolucizumab (Beovu), and Ranibizumab (Lucentis).
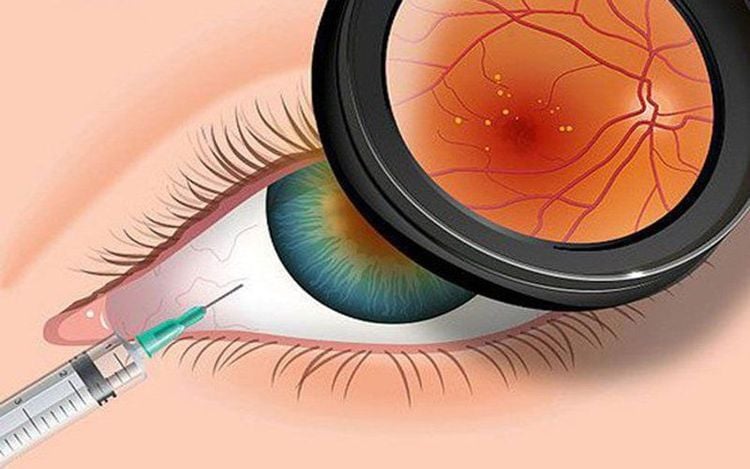
Thuốc kháng VEGF được tiêm trực tiếp vào mắt bệnh nhân
2.2. Photodynamic therapy In photodynamic therapy, your doctor will use a laser in combination with verteporfin, a mild photosensitive drug, to treat macular degeneration (usually for the wet form). At the start of photodynamic therapy, a medical professional will inject medication into a vein in the patient's arm. The medicine then travels to the abnormal blood vessels in the eye and stays there. Next, the doctor will make drops to numb the eye and shine a laser light into the patient's eye. At that time, the laser will interact with the drug and activate the effect of the drug. This therapy helps create clots in the blood vessels and closes them, preventing fluids from leaking out.
2.3. Laser surgery This method is also known as laser photocoagulation, but it is rarely recommended by doctors to treat macular degeneration (AMD). The main goal of laser surgery is similar to photodynamic therapy - to stop leaking blood vessels. After the eye has been numbed, the doctor will use a laser to burn parts of the macula, helping to "seal" the leaky blood vessels.
In addition to the above age-related macular degeneration treatments, doctors also recommend that patients with macular degeneration use the AREDS formula to support the treatment of the disease. This formula stands for "Age-Related Eye Disease Study". Research has shown that certain combinations of vitamins and nutrients are effective in treating both dry and wet forms of macular degeneration. In AREDS includes zinc and antioxidants such as: 400 IU vitamin E, 500 milligrams vitamin C, 80 milligrams zinc oxide, 15 milligrams beta-carotene, 2 milligrams cupric oxide
However, later studies have controlled Edit the formula, name it AREDS2. This formula contains the following ingredients: 500 milligrams of vitamin C, 400 IU of vitamin E, 80 or 25 milligrams of zinc oxide, 10 milligrams of lutein, 2 milligrams of zeaxanthin, 2 milligrams of cupric oxide.
Since age-related macular degeneration still has no cure, prevention of macular degeneration is very important. To prevent macular degeneration, you should follow a nutritious diet, eat lots of fish and omega-rich foods, eat rich in fresh fruits, dark green leafy vegetables, supplement vitamins, minerals and nutrients. Antioxidant. When going out in the sun, wear sunglasses to protect your eyes. At the same time, you should adjust your habits when using electronic devices to ensure eyesight.
Customers can directly go to Vinmec Health system nationwide to visit or contact the hotline here for support.
Reference source: webmd.com