This is an automatically translated article.
The article was professionally consulted by Specialist Doctor II Le Thanh Cam - Department of Pediatrics - Neonatology, Vinmec Da Nang International General Hospital.Middle ear infection or middle ear infection is a fairly common disease that occurs in children. Children 1-2 years old are most at risk of infection. The disease often appears in the rainy season, the weather changes. Due to the subjective not being treated in time, there have been many cases of otitis media causing deafness, death due to complications of meningitis or brain hemorrhage,...
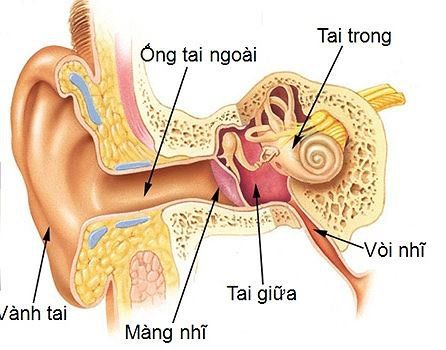
1. What is otitis media?
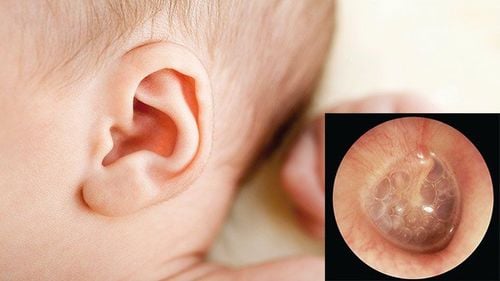
If you have otitis media without timely treatment, it will lead to very dangerous acute mastoid otitis. Once the disease is severe, it is easy to cause complications of tympanic membrane perforation, hearing loss, tympanic membrane fibrosis, facial nerve palsy, mastoiditis. The most dangerous is when complications occur in the brain such as meningitis, brain abscess, epidural abscess, ... easily causing death in children.
2. Causes and signs of otitis media
The cause of otitis media is an infection of the nasopharynx by bacteria or viruses. In addition, blocked eustachian tubes, often caused by warts, tumors in the nasopharynx, caused by purulent rhinosinusitis are also causes of the disease. There are cases of diseases caused by respiratory infections, allergens, reflux disease, polluted air, and cold weather are also causes of otitis media today.
When suffering from otitis media, the patient will have symptoms such as:
At first, there is ear pain, then watery ears and decreased hearing. In addition, there are other uncommon signs such as tinnitus, dizziness (usually detected in older children), fever, swelling behind the ears, loss of appetite and trouble sleeping,... To detect the disease, adults and children need the help of a doctor in diagnosis such as using an otoscope with magnifying glass (Otoscope); Oto-Endoscope and otoscope.

3. How to treat otitis media
There are many ways to treat otitis media, in which, medical treatment is the most applied. Oral antibiotics are the drugs of choice, and antibiotic selection is based on knowledge of the bacteria commonly seen in otitis media. The most accurate is based on antibiotic results of ear culture.
Treatment time for otitis media takes place at least 8 days. If the eardrum shows no signs of perforation, ear drops should be used, not irrigation. If the eardrum is perforated, the ear can be instilled in the first 3-4 days (non-toxic to the ear) to prevent the formation of pustules that block the drainage and then rinse with physiological saline or hydrogen peroxide. In addition, it is possible to open the tube, pump the eustachian tube.
Some cases of ear infection but antibiotic treatment is not effective will have to make an incision in the eardrum to insert the Diablo tympanic catheter. If otitis media is accompanied by signs of upper respiratory tract infection due to obstruction by enlarged tonsils, tonsillitis should be removed. In cases where the patient develops more serious complications and medical treatment does not bring satisfactory results, a tympanic cavity surgery may be necessary.
Otitis media can be completely cured and does not cause dangerous complications if parents detect early signs of the disease and have a scientific treatment plan as well as a doctor's supervision.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.