This is an automatically translated article.
Research shows that 1 out of every 1,000 children is born with clubfoot. This disease does not cause pain to children, but if not diagnosed and treated in time, it will cause many complications when the child grows up such as severe imbalance, difficulty in standing and walking.1. What is congenital clubfoot?
Clubfoot is a foot deformity that occurs during pregnancy. Includes forefoot tilt, internal rotation, and downward traction; The heel is pulled inward, and some muscles and ligaments are shortened and contracted.This malformation usually occurs on both sides, if it occurs on one side, it is more common to see the left side than the right side.
Definitive treatment of clubfoot in children is extremely difficult, but if diagnosed and treated early, the possibility of functional recovery for children is very high.
Trắc nghiệm: Bạn có biết nên khám thai lần đầu vào lúc nào không?
Việc khám thai lần đầu mang ý nghĩa rất quan trọng, giúp bạn xác định chính xác mình có mang thai hay không? Thai nhi đã vào buồng tử cung hay chưa?... Vì vậy, nếu chưa biết khám thai lần đầu vào lúc nào, trả lời nhanh 5 câu hỏi trắc nghiệm sau sẽ giúp bạn có câu trả lời.2. Causes of congenital clubfoot
Currently, the main cause of congenital clubfoot in children is unknown. May be caused by:Genetic abnormalities: If a family has one child with clubfoot, the chance of having another child with clubfoot is about 3-4%. If the father and/or mother have clubfoot, the chances of having a child with clubfoot are also very high. Abnormal fetal foot position. Chromosomal mutations: Children with congenital multi-joint stiffness (club feet, club hands, knee stiffness, elbow stiffness, shoulder stiffness, hip dislocation...). Congenital structural abnormalities of the foot. Abnormalities in the nerves that supply the feet. The baby has hypoxia or lack of amniotic fluid when the mother is pregnant. Environmental factors such as cigarette smoke, industrial dust, infections, viral infections during pregnancy can also cause birth defects.
Trẻ bị thiểu dưỡng khí hoặc thiếu nước ối khi người mẹ mang thai có thể là nguyên nhân dẫn đến dị tật bàn chân khoèo
3. Symptoms of congenital clubfoot
Signs to detect a child with congenital clubfoot deformities include:Closed and tilted in the forefoot, midfoot. Feet in spade position (Flat flexion). Curved outer edge of foot. Skin folds on the back of the foot are obvious. Skin folds in the middle of the foot are obvious. The space between the medial ankle and the clavicle was not palpable. Short big toe. Leg muscles may atrophy or become paralyzed. Using your hands can not bring the foot to the intermediate position. Other malformations may be associated such as hip dislocation, knee stiffness, patellar dislocation, elbow stiffness, club hand.
4. How to cure congenital clubfoot?
4.1 Treatment principles Early intervention immediately after birth. Comprehensive congenital clubfoot rehabilitation intervention: orthopedic cast, stretching exercises, orthopedic brace. Routine re-examination every 6 months after the end of the cast to assess progress. 4.2 Early intervention goals Gradual correction of foot deformity (rotation and intra-foot tilt) to medial. Stretches contracted muscles and ligaments. Maintain the foot in the intermediate position after the cast. Improves correct back gait. 4.3 Rehabilitation techniques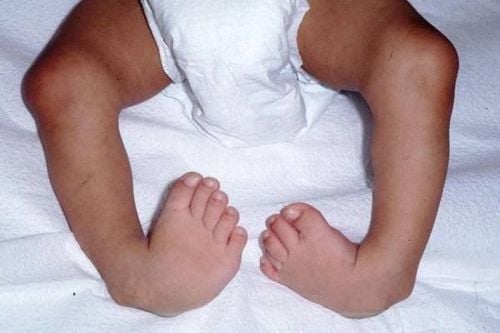
Dị tật bàn chân khoèo có thể được điều trị bằng phương pháp Ponseti
Indications: children with congenital clubfoot < 12 months.
Children with congenital clubfoot on both sides. Children with congenital clubfoot on one side. Children with clubfoot have multi-joint stiffness, hip dislocation... Contraindications:
Children with large spinal cord hernia (with hernia sac) Children with congenital brittle bones (glass man) Ponseti cast technique is used proceed as follows:
Maximum inclination and rotation of the foot. Gradually adjust the toes to rotate outwards. Gradually raise the soles of the feet to the dorsal side. Transfer the sole of the foot to the outside with the outside edge of the foot higher than the inside edge 4.3.2 Bandage or tie method Place the child on his or her back, knees bent. Wrap the padding around your feet, knees, and thighs. Wrap the tape over the cushion from the outer edge of the foot, up the instep, down the sole, over the knee to the other side (inner thigh, lower leg). Wrap the second tape around the lower leg to keep the first one. Note:
Every 2-3 days, add a new layer of tape on top of the old one. After 7 days remove all adhesive tape and padding. On the 8th day reapply a new time as described above. Daily exercises to exercise feet in ice for children: passive stretching exercises at the ankle-foot joint. 4.3.3 Orthopedic brace Polypropylene under-knee brace and outer shoe or slippers: indicated immediately after cast removal. Check splint periodically every 2 months. Routine monitoring and evaluation up to 3 years of age. 4.3.4 Therapeutic movement Exercise 1: Massage the toe, instep (dorsal flexor) and lower leg (twin, slipper).
Exercise 2: Passive stretching exercise at the ankle-foot joint: Do in order from the back of the foot to the front of the foot and ankle joint.
Steps to take:
Step 1: Gently pull the heel bone down (stretching the Asin tendon). Step 2: Gently pull the calcaneus outward (to correct the medial forefoot). Step 3: Gently pull the front of the foot forward. Step 4: Gently push the talus posteriorly and gently pull the forefoot outwards to correct the forefoot flexion and medial tilt. Step 5: Gently pull the heel bone down and push the front of the foot up to correct the ankle flexion position. Step 6: Adjust the incline in the foot with a 3-point adjustment: the heel pulls out, the forefoot pulls out, and the middle part of the outer edge of the foot pushes in. Passive stretching exercise at the ankle - foot joint: Practice while not in a cast between sessions and before the cast.
5. Follow-up and re-examination

Nếu các ngón chân sưng, tím, đau, cần tháo bột ngay tránh hoại tử
Gathering a team of leading pediatricians: including leading experts with high professional qualifications (professors, associate professors, doctorates, masters), experienced, worked at major hospitals such as Bach Mai, 108.. Doctors All are well-trained, professional, with a mind - range, understanding young psychology. In addition to domestic pediatric specialists, the Department of Pediatrics also has the participation of foreign experts (Japan, Singapore, Australia, USA) who are always pioneers in applying the latest and most effective treatment regimens. . Comprehensive services: In the field of Pediatrics, Vinmec provides a series of continuous medical examination and treatment services from Newborn to Pediatric and Vaccine,... according to international standards to help parents take care of their baby's health from birth to childhood. from birth to adulthood Specialized techniques: Vinmec has successfully deployed many specialized techniques to make the treatment of difficult diseases in Pediatrics more effective: neurosurgery - skull surgery, stem cell transplantation. blood in cancer treatment. Professional care: In addition to understanding children's psychology, Vinmec also pays special attention to the children's play space, helping them to have fun and get used to the hospital's environment, cooperate in treatment, improve the efficiency of medical treatment. To register for examination and treatment with Pediatricians at Vinmec International General Hospital, please click the "Contact Us" button on the website or register online HERE.
SEE MORE:
"Blow" clubfoot for a 3-year-old girl who can walk normally Mai Ngoc Lan – The clubfoot girl will soon be able to run and jump to her childhood! How long does it take for a fibula fracture to heal?