This is an automatically translated article.
The article was professionally consulted by Dr. Nguyen Luong Tan - Head of Cardiology Department - Cardiovascular Center - Vinmec Central Park International General Hospital.Congenital heart disease is a malformation of the heart and large blood vessels caused by abnormalities in the fetus during the 2nd and 3rd months of pregnancy, at the time when large blood vessels are formed from the primitive heart ducts. The prevalence in the world is 1/1000 children. In which, transposition of the great arteries, also known as transposition of the great arteries, accounts for a high percentage (8%) of congenital heart diseases.
1. Causes of congenital heart defects
The heart is a hollow muscle, divided into right and left halves, consisting of four chambers: right ventricle, right atrium, left ventricle, and left atrium. The two ventricles are separated by the interventricular septum, the two atria are separated by the interventricular septum. The heart has the function of both sucking and pushing blood to the organs for metabolism.The fetus receives blood from the mother through the umbilical vein. Blood from the umbilical vein of the fetus to the inferior vena cava flows to the right atrium, from here the blood passes through the foramen ovale (the hole located in the atrial septum connecting the two atria) to the left atrium and into the left ventricle. Blood into the aorta carries oxygen to the organs in the upper part of the fetus. Then, the blood flows from the superior vena cava to the right atrium, to the right ventricle, to the main pulmonary artery.
Because the fetus is not breathing, the lungs are not active, only 10% of the blood enters the lungs, the remaining 90% of the blood through the ductus arteriosus enters the descending aorta to nourish the organs in the lower body of the fetus. pregnant. Because pulmonary capillary pressure is higher than arterial vascular pressure, blood from the right atrium passes through the left atrium, from the pulmonary artery via the ductus arteriosus to the aorta.
After the baby is born there is a change in the circulation. The blood flowing under high pressure from the left ventricle is pumped by the heart to the aorta, bringing oxygen-rich blood to all tissues, and then the blood follows the great veins to the vena cava, pouring blood into the atria. right. The right atrium contracts to pump blood into the right ventricle through the pulmonary artery, to the pulmonary capillaries where oxygen is exchanged and carbon dioxide becomes oxygen-rich blood, through the 4 pulmonary veins back to the left ventricle. This is a closed cycle.
Congenital heart disease is the result of abnormal fetal development, which can be caused by environmental factors as well as genetic factors. According to research, the rate of chromosomal abnormalities and gene mutations accounts for about 10% of children with congenital heart disease.
Environmental factors such as chemicals, viral infections, drugs, ... also participate in the formation of structural abnormalities of the heart. In addition, poor nutrition, drinking alcohol during pregnancy, pregnant women over 40 years old... are also factors that increase the risk of disease.
Tim bẩm sinh là hậu quả của sự phát triển thai nhi bất thường
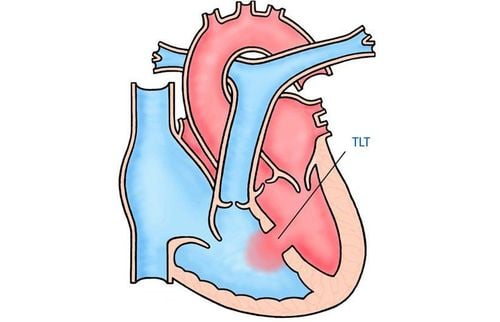
2. Congenital heart defects transposition of the great arteries
As mentioned above, the average person has a closed circulatory system. But with transposition of the great arteries, the blood does not circulate in the body like that, but separates and forms two non-connecting closed circulations.Circulation 1: Blood from the left ventricle to the pulmonary artery to the pulmonary vein returns to the left atrium to the left ventricle. Second circulation: Blood from the right ventricle through the aorta and vena cava to the right atrium. People with two separate double circulation, the human body does not have enough oxygen to deliver to the tissues to function, if not detected early, the patient can die early. Therefore, there must be passages (also known as shunts) between the two circulations to supply oxygen to the body.
Shunt helps to connect two circulations including:
Bronchial artery circulation. Ventricular septal defect: is a congenital heart abnormality that is very common in transposition of the great arteries and helps the baby to survive after birth thanks to the good mixing of arterial and venous blood in the ventricles. The ductus arteriosus: In the fetus, the ductus arteriosus connects the pulmonary artery and the isthmus of the aorta. After birth, the blood through the ductus arteriosus gradually decreases, so the ductus arteriosus gradually closes. The ductus arteriosus is completely closed within 2 months of birth. Therefore, to make the ductus arteriosus not close to form a communication route between the two circulations, the patient will be infused with Prostaglandin, the baby will live for a few more days and be taken to surgery. Foramen ovale: As mentioned above, the foramen ovale is the communication site between the two atria. From there, the disease can meet 3 cases:
Cases with large ductus arteriosus and small oval foramen: In this case, the patient is prone to pulmonary edema. Because the ductus arteriosus is large, more blood flows to the left atrium leading to the left ventricle. The left ventricle can't stand causing blood stasis receding and the patient will have pulmonary edema. After determining the patient's condition, the medical staff will perform the Raskin procedure (using an instrument to increase the size of the foramen ovale) to create a larger oval hole, more blood will go to the right atrium. reduces left atrial pressure. Case of large ductus arteriosus and large bulbous foramen: This is the most ideal case. In case the ductus arteriosus is closed and the foramen ovale is large: It is necessary to maintain a hemoglobin level of 15 to 18g/l for caesarean section.
Chuyển vị đại động mạch là bệnh lý nguy hiểm, cần chẩn đoán và điều trị kịp thời
The disease can be detected during pregnancy by trans-abdominal ultrasound, so pregnant women should be consulted during pregnancy to detect the disease early for the fetus, when the diagnosis is suspected. Maternal transposition of the great artery should be hospitalized and delivered near or at a hospital that can perform Raskin interventions or surgical repair of transposition of the great arteries.
To protect the health of pregnant women and babies during pregnancy, Vinmec International General Hospital provides a package of maternity services as a solution to help pregnant women feel secure because of the companionship of the medical team. doctor throughout pregnancy. When choosing Maternity Package, pregnant women can:
The pregnancy process is monitored by a team of highly qualified doctors Regular check-ups, early detection of abnormalities The package pregnancy helps to facilitate Convenience for childbirth Newborns receive comprehensive care Thanks to good medical services, the hospital is always appreciated and becomes the choice of many couples.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.