This is an automatically translated article.
The article is professionally consulted by Master, Doctor Nguyen Thanh Nam - Radiologist - Department of Diagnostic Imaging - Vinmec Danang International General Hospital. The doctor has over 10 years of experience in the field of Diagnostic Imaging.Liver cancer is one of the most common cancers in the world. Most cancers are incurable because they are often detected at a late stage.
1. What is liver cancer?
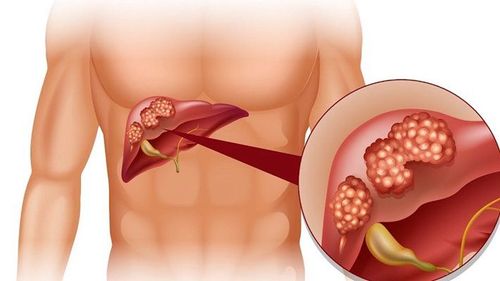
Liver cancer is a malignant tumor in the liver. Most liver cancer is secondary or metastatic, which means it started elsewhere in the body.The liver is considered the most important organ of the body, keeping essential functions such as filtering blood circulating through the body, metabolizing nutrients and drugs absorbed from the digestive tract. The liver performs many other important functions, such as removing toxins and other chemical waste products from the blood and excreting them.
Because the liver is made up of several different types of cells, several types of tumors can form there. Some of these are benign (noncancerous), and some are malignant (may spread to other parts of the body- metastases). Common benign liver tumors include:
Hemangiomas Localized nodular hyperplasia Benign hepatocellular adenomas Liver cysts Liver cysts 2 types of liver cancer:
Primary liver cancer : a cancer that starts in liver. Some common primary cancers include: Hepatocellular carcinoma (most common) Hepatoblastoma (rare) Vascular sarcoma (rare) Cholangiocarcinoma (less common) ) Secondary cancer: also known as metastatic cancer, ie cancer has spread from other parts of the body to the liver.
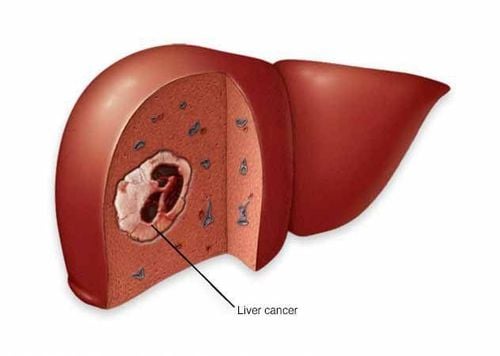
2. Causes of liver cancer
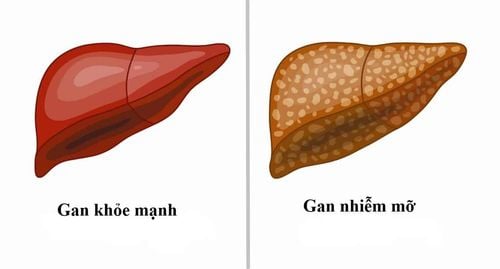
Primary liver cancer (hepatocellular carcinoma) tends to occur in people whose liver has been damaged by birth defects, alcohol abuse, or chronic infections with diseases such as hepatitis B and C. , hemochromatosis (an inherited disease caused by too much iron in the liver) and cirrhosis.More than half of people diagnosed with primary liver cancer have cirrhosis - often due to alcohol abuse. Hepatitis B and C and hemochromatosis can cause permanent damage and liver failure. Liver cancer can also be linked to obesity and fatty liver disease.
Risk factors for liver cancer may include:
Gender: Men are more likely to get hepatocellular carcinoma than women. Weight: Obesity can increase the risk of hepatocellular carcinoma. Race: Asians and Pacific Islanders are more susceptible to liver cancer than Europeans Steroid use to increase muscle strength History of diabetes Genetic diseases: Diseases that disrupt metabolism normal in the body increases the risk of liver cancer.
3. Symptoms of liver cancer
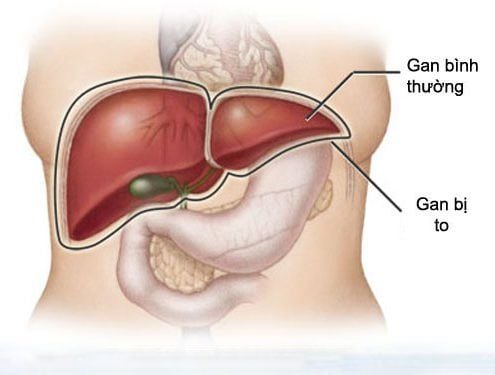
Liver cancer is often difficult to identify in its early stages because it has few signs and symptoms. Symptoms will appear only as the tumor grows and becomes larger than before. We can recognize liver cancer through the following signs and symptoms:Abdominal bloating, loss of appetite, weight loss Jaundice, yellow eyes Epigastric pain Enlarged liver, enlarged spleen Ascites Silver color stools, yellow urine dark.
4. Determine the degree of liver cancer
Once liver cancer is diagnosed, your doctor will determine the extent (stage) of the cancer. Imaging techniques such as ultrasound, CT, and MRI help determine the size and location of the tumor and assess the extent of its spread. Imaging techniques used to stage liver cancer include CT, MRI, and bone scintigraphy or PET/CT.Liver cancer has 4 stages:
Stage I: Single tumor has not invaded any blood vessels. Stage II: A single tumor has invaded nearby blood vessels, or there may be multiple small tumors in the liver. Stage III: Multiple large tumors, or one large tumor has invaded the main vein of the liver or invaded nearby tissues, such as the gallbladder. Stage IV: Cancer has spread outside the liver to other parts of the body.
5. Treatment of liver cancer
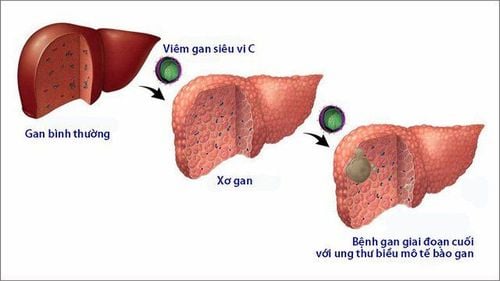
Tumor removal surgery Liver transplant surgery Local treatment: is a method to kill the tumor directly using different techniques. Local treatment options for liver cancer include: heating, freezing the tumor, injecting alcohol into the tumor, injecting chemotherapy drugs into the liver tumor, and injecting Y-90 radioactive microspheres into the liver tumor. through the arteries. Radiation Therapy Targeted Drug Therapy Immunotherapy Chemotherapy.
6. Palliative care for patients with liver cancer
Palliative care is specialized medical care that focuses on relieving pain and other symptoms of a serious illness. Palliative care professionals work with patients, families, and other physicians to support the continuum of care. Palliative care may be used while undergoing other cancer treatments, such as surgery, chemotherapy, or radiation.When palliative care is used along with all other appropriate treatments, people with cancer can feel better and live longer.
Vinmec International General Hospital has provided customers with a package of screening and early detection of liver cancer to screen for liver cancer pathology for people at high risk of diseases such as alcohol abuse, cirrhosis of the liver. , have a family history of liver cancer, cirrhosis, hepatitis B virus infection, chronic hepatitis C,...
Service selection Package for screening and early detection of liver cancer, the patient will be Examining, consulting and performing tests, diagnostic imaging to evaluate liver function, liver diseases and liver cancer screening.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.
Articles refer to sources: Mayoclinic.org, Webmd.com