This is an automatically translated article.
Blood clots are the leading cause of stroke with an 80% rate. A blood clot forms and blocks a blood vessel in the brain, or important blood vessels (mostly in the heart) that feed the brain. From there, causing serious consequences such as vision loss, difficulty speaking, especially hemiplegia.1. What is a thrombosis (blood clot)?
Thrombosis is the process of gathering blood to the torn blood vessels and stopping the bleeding, when a person bleeds, the clotting process will be activated.
Initially, platelets are summoned to the injured area to create a node around the wound. They are then held together by fibrin fibers produced during the activation of clotting factors. The platelets that come first release chemicals that attract other platelets to form a more stable clot and stop bleeding.
Proteins in the body have a role in determining when to stop the clotting process when it is large enough. When the wound is healed, the fibrin fibers dissolve on their own and the platelets return to normal blood tissue.
2. What is a brain stroke?
A stroke is a brain injury that occurs when the blood supply to the brain is interrupted or significantly reduced, leading to a lack of oxygen and nutrients in the brain and the process of self-destruction of brain cells. Because of these serious harms, a stroke is considered a medical emergency that requires prompt diagnosis and treatment.
3. Blood clots - The leading cause of brain stroke
Up to 80% of strokes are caused by blood clots. A blood clot that forms in a blood vessel will block blood flow, causing brain ischemia. When brain cells die, symptoms such as loss of balance, dizziness, dizziness, severe headache, decreased vision, even hemiplegia, difficulty speaking...will occur. There are 2 types. Brain stroke due to blood clot formation (ischemic stroke):Thrombotic stroke: Due to the existence of a blood clot (thrombus) that forms in an artery in the neck or brain. That is, a blood clot forms directly in the brain. These arteries can have fatty deposits called plaques that over time block blood vessels that limit or completely stop blood flow.
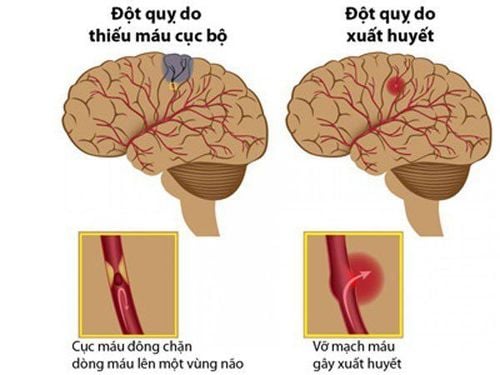
Do sự tồn tại của cục máu đông (huyết khối) được hình thành trong động mạch ở cổ hoặc nã
Embolic stroke: Due to the existence of blood clots that form in other parts of the body (usually the heart) and travel to the brain. A common manifestation is an irregular rhythm in the upper two chambers of the heart (atrial fibrillation), which can cause blood clots to form.
4. What are the signs and symptoms of thrombosis (blood clots)?
When a blood clot occurs in a vein, the area will be red, painful, swollen, and possibly warmer than normal areas. Sometimes the injured area is swollen and blue due to a large blood clot.
If blood clotting occurs in the arteries, the condition becomes more serious. Blood flows through the arteries to perform biological functions such as breathing, so if a blood clot blocks it, it can cause sweating, shortness of breath, sometimes nausea, chest pain or increased blood pressure. undigested.
In general, blood not reaching the brain causes confusion, loss of vision or speech.
5. What factors increase the risk of forming a blood clot that causes a stroke?
Controllable risks include:
High blood pressure: High blood pressure is the leading cause of stroke due to the formation of blood clots that cause stroke. Because high blood pressure can increase the risk of stroke 2-6 times, controlling blood pressure with medication can significantly reduce the risk. Smoking: Smoking doubles the risk of stroke caused by a blood vessel blockage. Smoking can damage the walls of blood vessels, increase hardening of the arteries, make the heart work harder, and raise blood pressure. Passive smoking also increases the risk of stroke. If you stop smoking today, within 2-5 years, your risk of stroke will drop to that of someone who has never smoked. High cholesterol and being overweight: A cholesterol level <= 200 is best for adults. Excess cholesterol can build up on the artery walls and lead to blockage of these vessels. Being overweight also increases your risk of developing high blood pressure, paving the way for other risk factors for stroke. A sedentary lifestyle can increase the risk of stroke. Taking cholesterol-lowering statin drugs may reduce the risk of stroke. Uncontrollable risks include:
Age: Stroke risk doubles every 10 years from age 55. Gender: Men have a slightly higher risk of stroke than women. Family history: Your risk of having a stroke is higher if someone in your family has had a stroke. Diabetes: Poorly controlled diabetes can cause circulatory problems that increase the risk of stroke. Cardiovascular disease: Having a heart attack can increase your risk of stroke. An additional risk factor is a heart abnormality called atrial fibrillation (AF). In people with AF, the left atrium can beat rapidly and uncontrollably up to 400 times a minute, which is many times higher than normal 60-100 times/minute. If left untreated, AF can increase the risk of stroke four to six times. Recurrent stroke: A person with a history of stroke has an increased risk of having a recurrent stroke. This high risk is highest within the first few months, lasts approximately 5 years, and decreases over time. Transient ischemic attack: Transient ischemic attack (TIA) increases the risk of having a stroke. Medications, including aspirin, can help prevent future strokes.
6. What living habits help limit the formation of blood clots in the brain?
Increase physical activity Keep cholesterol levels stable with a healthy diet low in saturated fat, cholesterol and salt. Daily blood pressure control

Kiểm soát huyết áp hàng ngày
Make weight loss Keep blood sugar stable Do not smoke, abstain from alcohol. Avoid stress, staying up late and overwork. In cerebrovascular accident, emergency and prompt treatment are very important. If the golden period is over, the patient's likelihood of complications may be higher. The technique of treating cerebral artery thrombosis has been applied at Vinmec International Hospital in order to increase the chances of treating patients with cerebral infarction in particular and thromboembolic diseases in general.
The technique is indicated for patients:
Subarachnoid hemorrhage due to ruptured cerebral aneurysm Infarction due to large cerebral artery occlusion. Brain hemorrhage due to brain vascular malformations The outstanding advantage of that method is the use of magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) 3.0 and a 640-segment CT scanner for interventional techniques to remove cerebral artery thrombosis.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.