This is an automatically translated article.
Yondelis belongs to a group of drugs indicated in the treatment of certain cancers. The drug blocks the growth and spread of cancer-causing cells. To better understand what is Yondelis drug? What are the uses of Yondelis? What features should be paid attention to when using? The following article will help you better understand the drug Yondalis.
1. The effect of the drug Yondelis
Yondelis is a medicine used to treat patients with liposarcoma or leiomyosarcoma. Yondelis (trabectedin) is a medicine used to treat certain types of cancer that cannot be treated with surgery, or whose cancer has spread to other areas of the body.
This is a chemotherapy drug that works by slowing the growth of cancer cells. Please note that patients should only use drugs to treat other diseases when prescribed by a doctor.
2. Usage and dosage of Yondelis
Adults: Soft tissue sarcoma
Recommended dose: 1.5 mg/m2 body surface area, IV infusion over 24 hours. Repeat dose every 3 weeks.
Ovarian cancer
Recommended dose: 1.1 mg/m2 body surface area, immediately after PLD injection at a dose of 30 mg/m2. Inject every 3 weeks.
To minimize the risk of PLD infusion reactions, the initial infusion rate should not be greater than 1 mg/min. If there is no reaction to the infusion, the next dose of PLD can be infused in about 1 hour.
All patients should receive corticosteroids (eg, 20 mg intravenous dexamethasone) 30 minutes before PLD (in combination therapy) or trabectedin (in monotherapy) to prevent vomiting and protect the liver. Use additional antiemetics if needed.
To be able to use trabectedin, the patient must meet the following criteria:
Absolute neutrophil count (ANC) not less than 1,500/mm3. Platelet count not less than 100,000/mm3. Bilirubin is not greater than the upper limit of normal (ULN). Alkaline phosphatase not less than 2.5 x ULN (consider hepatic isoenzyme 5-nucleotidase or gamma glutamyl transpeptidase (GGT), if elevation may be due to bone). Albumin not more than 25 g/l. Alanine aminotransferase (ALT) and Aspartate aminotransferase (AST) not less than 2.5 x ULN. Creatinine clearance not more than 30 ml/min (monotherapy), serum creatinine not less than 1.5 mg/dl (≤ 132.6 μmol/l) or creatinine clearance not more than 60 ml/min (therapy combination). Creatine phosphokinase (CPK) not less than 2.5 x ULN. Hemoglobin is not more than 9g/dl. Patients need to meet the above criteria before starting a new treatment cycle. Otherwise, treatment must be delayed until the requirements are met.
Monitor hematological indicators of bilirubin - alkaline phosphatase, aminotransferase -CPK weekly for the first two cycles, and at least once in subsequent cycles.
The same dose should be given for all cycles, provided that grade 3 - 4 toxicity is not observed and the patient meets the criteria as outlined above.
Adjust dosage during patient treatment.
If any of the following occurs at any point between cycles, a dose reduction according to Table 1 (table 1 below) is required for subsequent cycles:
Neutropenia count not more than 500/mm3 for more than 5 days or associated with fever or infection. Thrombocytopenia less than 25,000/mm3. Increased bilirubin greater than ULN or alkaline phosphatase greater than 2.5 x ULN. Elevated aminotransferases (AST or ALT) not more than 2.5 x ULN (monotherapy) or less than 5 x ULN (combination therapy), still not reversible on day 21. Any other grade 3 or 4 adverse reactions (such as nausea, vomiting, fatigue). Once the dose of the drug has been reduced due to toxicity, the doctor recommends not to increase the dose in subsequent cycles. If any toxicity reappears in subsequent cycles, further reductions can be made at the following dose.
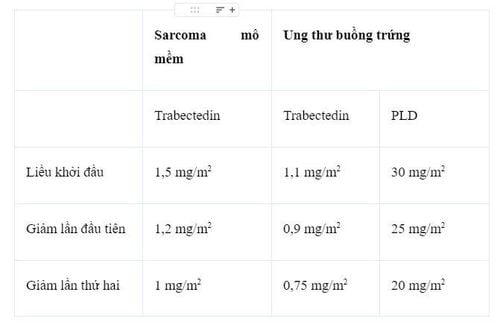
Bảng 1. Bảng điều chỉnh lại liều trabectedin (đơn trị trong sarcoma mô mềm (STS) hoặc kết hợp đối với ung thư buồng trứng) và PLD.
In the event that further dose reduction is required, consider discontinuing treatment.
Duration of treatment
The number of cycles of trabectedin treatment is not limited. The patient continues to take the drug as long as the patient still has good results after treatment.
There are no reports of cumulative toxicity in patients who have received multiple cycles of treatment.
Children: Trabectedin should not be used in children under 18 years of age with sarcoma.
Others: Elderly
No specific studies in older people have been performed.
Hepatic impairment
Particular care is required and dose adjustment may be required in patients with hepatic impairment because plasma concentrations of trabectedin are increased, leading to an increased risk of hepatotoxicity.
Renal failure
Has not been studied in patients with renal failure, so trabectedin is not indicated for these patients. No dose adjustment is required in patients with mild or moderate renal impairment.
3. Contraindications of the drug Yondelis
Hypersensitivity to the active ingredient trabectedin. Have a serious or uncontrolled infection. Women who are breastfeeding. Vaccinating yellow fever vaccine. What drugs can interact with Yondelis? Medicines that may interact with Yondelis® such as statins (atorvastatin, simvastatin).
Other drugs that may affect the way Yondelis® work such as azole antifungals (such as fluconazole, ketoconazole), macrolide antibiotics (such as clarithromycin), HIV drugs (such as ritonavir), rifamycins (such as rifabutin) and an certain medicines used to treat seizures (such as carbamazepine, phenobarbital, primidone) and others.
To avoid drug interactions, it is best to write a list of all the medicines you are taking (including prescription, nonprescription, herbal and dietary supplements) and show them to your doctor or pharmacist. . To ensure safety when taking medicine, do not arbitrarily take the drug, stop or change the dose of the drug without the permission of your doctor.
4. Notes when using Yondelis
Before using the drug for treatment, the patient should tell the doctor or pharmacist if:
The patient is allergic to any of the ingredients of the drug. The patient has or has ever had medical conditions such as low blood cell counts, liver disease, kidney disease, infection. To reduce your risk of getting scratched, bruised, or injured, use caution with sharp objects like razors and avoid activities like contact sports. Before surgery, tell your doctor or dentist about all the products you use (including prescription drugs, over-the-counter medicines, and herbal products). This medicine must not be used during pregnancy, as it may harm the unborn baby. If you become pregnant, tell your doctor right away. It is not known whether this medicine passes into breast milk. Therefore, breast-feeding is not recommended while using this medicine and for 3 months after treatment. This medicine can make the patient feel tired or weak, when taken with alcohol or marijuana can make you more tired. Patients should not drive, use machines, or do anything that requires alertness.
How should Yondalis be used? Yondelis is given as an intravenous infusion over 24 hours. To help avoid irritation at the site of the infusion, Yondelis is given into a large vein through an IV line called a central venous line.
Yondelis is usually taken every 3 weeks.
The specialist may reduce the dose or slow the dose if there are certain side effects. If there are any serious side effects, treatment may be discontinued.
Before each treatment, steroid medication will be given to help reduce the risk of certain side effects. Your doctor will decide how long to continue treatment, or possibly to do certain tests while you are being treated to check for side effects, and to see how they respond.
5. Yondelis side effects
Yondelis can cause serious side effects, including:
Severe infections caused by a decrease in white blood cells. A decrease in white blood cell counts is common in Yondelis, but it can also cause severe infection or death. Your doctor may need to reduce your dose, slow down, or stop your treatment if your white blood cell count is too low or if you have a serious infection. Call your doctor right away if you have a fever or other signs of infection. Severe muscle problems (rhabdomyolysis). Yondelis can cause muscle problems that can be severe and lead to death. Tell your doctor right away if you have severe muscle pain or weakness. Liver problems, including liver failure. Tell a specialist if you notice the following symptoms: Yellowing of the skin and whites of the eyes; pain in the right side of the abdomen; nausea; vomit; not feeling well; problems with concentration; mistake; sleepy; heart muscle problems, including heart failure.
Some of these reactions are severe and may require discontinuation of treatment to treat the allergic reaction. Signs of an allergic reaction may include: difficulty breathing, chest tightness, wheezing, swollen lips, or skin rash. Tell your doctor if you bruise easily or bleed; changes in liver and kidney function.
6. How to store Yondalis . medicine
Should be stored at room temperature, away from moisture and light. Do not store in the bathroom or in the freezer. You should keep in mind that each medicine may have different storage methods. Therefore, you should carefully read the storage instructions on the packaging or ask the pharmacist. Keep medicine out of reach of children and pets.
Do not throw medicine down the toilet or plumbing unless asked to do so. Instead, dispose of medication properly when it is past its expiration date or cannot be used. You can consult your pharmacist or local waste disposal company about how to safely dispose of your medication.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.