This is an automatically translated article.
The article was professionally consulted by Specialist Doctor I Huynh Kim Long - Emergency Resuscitation Doctor - Emergency Resuscitation Department - Vinmec Danang International HospitalViral hepatitis is one of the notable infectious diseases worldwide as well as in Vietnam. In particular, hepatitis C (also known as HCV) is the leading cause of liver transplantation in the United States. Vietnamese people are 3 to 4 times more likely to be positive for hepatitis C than other ethnic groups.
1. About Hepatitis C
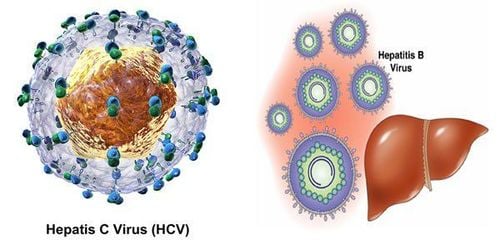
Hepatitis C is a virus that tends to invade liver cells, causing hepatitis. Hepatitis C was only discovered in 1989, so testing for hepatitis C has only become available in recent years. Hepatitis C circulates in the blood, so hepatitis C is transmitted mainly through blood and is also detected through blood tests. Hepatitis caused by HCV has an incubation period of 30-120 days, with an average of 2 months. The main routes of transmission of the virus are from:
Recipients of blood or blood products infected with the virus, although blood donor selection measures are being applied, hepatitis C can still pass through the net and be infected. transmitted to the receiver. Sharing needles contaminated with the hepatitis C virus Healthcare workers can become infected with the hepatitis C virus by coming into contact with samples containing the virus during their work. There is a risk of contracting the virus through sex, but it is rarer than hepatitis B. Mother-to-child transmission is possible, but the incidence is low. Other causes: tattooing, piercing ears with unsterilized equipment can transmit the C virus. Hepatitis C infection is unknown: accounts for 30-40% of cases.
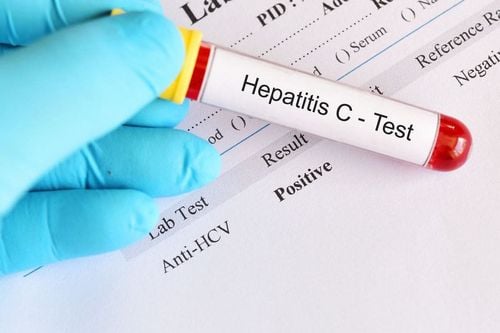
2. Hepatitis C . Test
2.1 Blood test A blood test is the only way to confirm hepatitis C. When the hepatitis C virus infects the body, the immune system produces an antibody called HCV-Ab (antibody). Hepatitis C). However, this antibody is too weak to kill the hepatitis C bacteria. So if you have hepatitis C antibody (HCV-Ab) positive, it means you have hepatitis C. You should consult your doctor as soon as possible about testing and treatment options, even if you have no symptoms at all. Anti-hepatitis C antibodies are positive in most cases:
ELISA techniques to detect HCV-specific antibodies. Diagnostic methods by molecular biology techniques. PCR technique allows detection by selective amplification of some very small nucleotide acids that cannot be detected by conventional techniques.
2.2 Specialized liver examination In hepatitis C, elevated liver enzymes also indicate that liver cells are being destroyed. Liver function can be disturbed depending on the severity and duration of the disease. Therefore, after confirming that there is a hepatitis process, the doctor will advise the patient to conduct further tests with other tests:
Tests to evaluate liver function. Liver ultrasound: study the structure of the liver and surrounding organs, look for signs of cirrhosis or other abnormalities. Liver biopsy: this is a test that allows doctors to look at liver cells under a microscope, determine the degree of inflammation, diagnose the stage of the disease, and evaluate the effectiveness of treatment. HCV RNA test: directly detects the virus in the blood, and identifies the subgroup to choose a reasonable regimen. This test is also used to predict good response to treatment. If you know or suspect that you are infected with the HCV virus, get a blood test quickly to confirm the disease. Once confirmed, you should let those who may be in contact with your blood and body fluids know: sexual partners, family members, doctors, dentists, and general medical staff to prevent infection. transmit hepatitis C virus to those around.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.