This is an automatically translated article.
The article is professionally consulted by MSc Vo Thien Ngon - Urologist, Department of General Surgery, Vinmec Danang International General Hospital.
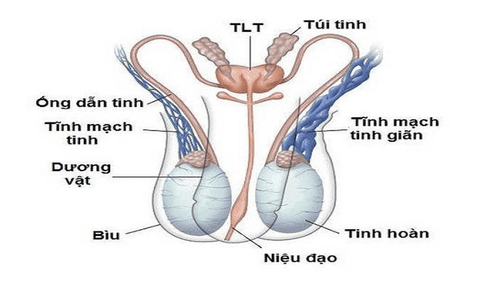
Testicular tumor occurs when the testicle rotates around the spermatic cord (testicular stalk) blocking the blood vessels that feed the testicle. About half of cases of testicular torsion occur during sleep. Testicular tumors are uncommon but most often malignant and usually appear in men aged 15-35 years.
1. Symptoms of testicular tumor
The typical symptom of testicular tumor is
Sudden, severe and increasing pain in one testicle, especially at night. Accompanied by nausea, pain may spread to the groin, pelvic cavity. Examination revealed: testicles are enlarged, lying high and the axis is transversely rotated; If the testicle is pulled low, the patient will experience increased pain. If it is an undescended testicle, you will feel pain in the inguinal canal, there is a bulge in this area, pain is pressed, and the scrotum is on the same side without palpating the testicle. The loss of scrotal skin reflex is a valuable symptom for the diagnosis of testicular tumor. Testicular tumor is a gynecological emergency. Without emergency treatment (within 4-6 hours of the onset of pain) the testicles will become ischemic and necrotic. Testicular tumors are most common between the ages of 10 and 20. However, it can occur in men of any age.
One third of patients had previously experienced similar acute scrotal pain but did not last long and then resolved on its own. This is the reason why patients subjectively do not go to the hospital early because they think the pain can go away on its own like last time.
However, acute scrotal pain can also be caused by other causes such as epididymitis, testicular torsion... but the diagnosis of testicular torsion must be thought of first in order to have timely treatment.

2. Causes of testicular tumor
There are many diseases that cause acute testicular tumor such as: testicular torsion, testicular torsion, epididymitis, orchitis, testicular trauma, in which, testicular torsion is the most dangerous because it can cause damage irreversible testicular injury. Therefore, in testicular tumor, physician and patient must be monitored urgently until testicular torsion is ruled out.
4. Treatment of testicular tumors

The most common testicular tumor is Yolk sac tumor. Tumors usually respond well to treatment with radical orchiectomy. Cases of Yolk sac tumor that have metastasized to abdominal lymph nodes need additional chemotherapy. Chemotherapy in this case is very effective. Most cases of testicular tumors can be completely cured.
However, in order to know specifically and accurately the prognosis of each case, you should directly meet the doctor who treated your child to ask in detail about the treatment results and follow-up plan like. This depends a lot on the pathology results (resulting in the type of cells in your baby's testicular tumor) and the stage of the disease.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.