This is an automatically translated article.
The article was written by Doctor Tran Truong Giang - ICU Doctor - Intensive Care Department - Vinmec Times City International General Hospital.Extracorporeal membrane oxygenation (ECMO) is a technique where your blood is pumped outside of your body to a heart-lung machine to remove CO2 and return oxygenated blood to your body's tissues. Blood flows from the right side of the heart to the membrane oxygenator in the cardiopulmonary machine, which is then warmed and sent back to the body. This method allows blood to pass through the heart and lungs, allowing these organs to rest and heal. ECMO is used in critical situations, when your heart and lungs need support to heal. It can be used to treat COVID-19, ARDS and other infections.
1. Overview
Extracorporeal membrane oxygenation is a technique that temporarily supports cardiopulmonary function by an artificial cardiopulmonary system.The patient is connected to the extracorporeal circulatory system including the blood oxygenation membrane through the blood pump system. This system will support the lungs and/or heart during recovery or preparation for a heart-lung transplant.
ECMO therapy (artificial lung) is a technique performed by taking blood from the central vein, passing through the oxygen exchange membrane and then returning to another central vein through a pump system to support the lungs during the time. severe damage.
2. Designation
ECMO technique is indicated for patients with severe but reversible acute respiratory failure.Patient was defined as severe respiratory failure when Murray score ≥ 3 or decompensated CO2 elevation with pH < 7.2.
Murray score is calculated based on 4 parameters as follows: PaO2/FiO2: ≥ 300 = 0 points, 225 – 299 = 1 point, 175 – 224 = 2 points, 100 – 174 = 3 points, 30 cm H2O) and/ or FiO2 > 0.8 over 7 days.

Bệnh nhân suy hô hấp nặng nhưng có khả năng phục hồi sẽ được chỉ định ECMO.
3. Contraindications
Intracranial hemorrhage. Any contraindication related to the continuous use of heparin.4. Conduct ECMO . technique
Record check: Review indications and contraindications and the family's commitment to consent to ECMO Check the patient: vital functions to see if the procedure can be performed. Implementation of the technique Step 1: Intravascular access Place the cannula according to the venous-venous configuration.Bloodline: The cannula that takes blood out of the body is usually located in the right femoral vein. Ultrasound is required to bring the tip of the cannula located at the intersection of the inferior vena cava into the right atrium.
Return blood line: Right internal jugular vein. Ultrasonography is required to bring the tip of the cannula to the junction of the superior vena cava and the right atrium.
The technique can be placed by guidewire or by venipuncture.
Step 2: Connect the extracorporeal circulatory system to the catheter. Step 3: Adjust parameters Blood rate adjustment:
Blood speed is adjusted in order to achieve maximum blood oxygenation and maintain hemodynamic stability.
Normally, the initial blood rate is about 50 ml/kg/min and can range from 50 to 100 ml/kg/min.
Adjust the amount of oxygen:
In the first stage, use 100% oxygen. Then, the oxygen rate will be adjusted according to the clinical response and blood gas of the patient.
Pay attention to maintain hemoglobin level > 10 g/l.
Anticoagulation: Continuous heparin infusion during ECMO, adjust heparin to maintain ACT parameters from 160-200 seconds.
For patients at risk of bleeding, maintain ACT from 170 - 190 seconds.
Set ventilator parameters: Ventilator parameters are set to volume or pressure to help the lungs rest and avoid further lung damage or oxygen poisoning: Plateau pressure (Pplateau) remains below 30cm H2O and FiO2 ≤ 0.5
Step 4: End When the gas exchange function of the lungs recovers, conduct a trial of gradually reducing ECMO support for the patient.
Maintain the same blood rate, gradually reduce the ECMO oxygen concentration to 20% and monitor the patient for several hours. If blood pressure is stable and blood gas is good, stop the technique.
Note: After stopping the pump, the amount of blood in the extracorporeal circulatory system is not returned to the patient directly through the catheter, but must be put into a blood bag and then retransfused to the patient by the route of the catheter. normal veins.
5. Follow up
Monitor vital signs in general: Pulse, blood pressure, SpO2, urine,... Monitor indicators of blood oxygenation level: Maintain central venous oxygen saturation (ScvO2) or mixed venous blood saturation (SvO2) remained at 75% to 80%. Arterial blood oxygen saturation is maintained between 85% and 100%. Monitor for signs of ischemia in the lower extremities on the right side to place blood in, brain ischemia in the upper half of the body including the brain and upper extremities. Monitor for signs of bleeding, hemolysis, infection, pulmonary embolism,... related to ECMO.6. Handling accidents and complications
Bleeding:Bleeding complications due to continuous anticoagulant heparin and thrombocytopenia. Precautions: Monitor and maintain ACT readings for 170 - 190 seconds in high-risk patients with platelet counts above 100,000/mm3. Pulmonary embolism:
Pulmonary embolism can occur because a blood clot created in the extracorporeal circulatory system enters the body and causes a pulmonary embolism. Precaution: Administer heparin anticoagulation continuously and maintain ACT for 210 – 230 seconds. Observation of manifestations of blood clot formation in the extracorporeal circulatory system, including routine observation of junctions, monitoring of transmembrane pressure (of oxygenated membranes).
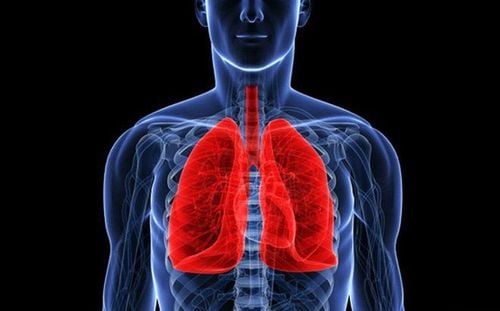
Người bệnh có thể bị tắc mạch phổi khi dùng ECMO.
Bleeding: Check for causes and treatment. Infections: Treat infections. ECMO is a medical method that requires highly qualified doctors and technicians to perform. ECMO technique is considered a lifesaving technique for severe pneumonia and acute myocarditis that do not respond to conventional treatments and need more time to recover. ECMO is also a bridge for seriously ill patients waiting for a heart or lung transplant.
ECMO has been deployed at Vinmec International General Hospital system. In particular, the ICU department - Vinmec Times City International General Hospital has implemented ECMO technique to treat patients with severe respiratory failure (ARDS) due to pneumonia and severe heart failure since 4 years with a successful success rate. high work. Doctors at Vinmec Times City International General Hospital have been well-trained in ECMO techniques in the US and India, enough to respond to all serious situations. In 2018, Vinmec Times City International Hospital was certified as a member center of the world ELSO. Vinmec Times City International General Hospital is currently equipped with 3 most advanced ECMO machines, enough to support 3 patients at the same time.
To register for examination and treatment at Vinmec International General Hospital, you can contact Vinmec Health System nationwide, or register online HERE.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.