This is an automatically translated article.
Vaginal tears are common during labor and vaginal delivery, especially in women giving birth to their first child. This tear stretches the vagina, making it easier for the baby to pass through the birth canal.1. Vaginal tear overview
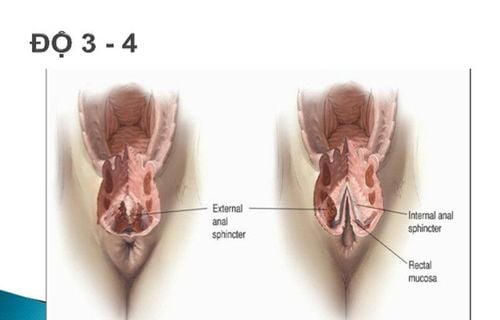
Vaginal tear, often accompanied by perineal tear, is a condition that occurs after a woman gives birth normally with an episiotomy, or gives birth through supportive procedures such as forceps, suction... Other factors also causes vaginal tearing including:Pregnant women are overweight; Rapid labor; prolonged labor; The breech position with the head facing up creates a lot of pressure; When the mother gives birth for the first time, the vaginal muscle tissue has not been able to adapt and stretch wide enough. Vaginal tearing, if not detected and treated promptly, can lead to acute blood loss, shock and sometimes life-threatening. Vaginal bleeding symptoms can be more or less depending on the extent of the damage. Vaginal tearing position is also not fixed, sometimes appearing in the right wall, left wall or posterior wall of the vagina. Therefore, doctors need to use specialized equipment to expose each part of the vagina, including the lower, right or left side, top and bottom. As a result, it is possible to accurately assess and classify injuries, thereby deciding the right course of treatment.
2. Classification of vaginal tear
Rách âm đạo dù ở mức độ nào cũng đều khiến bệnh nhân cảm thấy rất đau
Low-level tear: This is a tear in the lower third of the vagina, often accompanied by vulvar tear and perineal tear. (the area between the vagina and the rectum); Vaginal tear in the middle: This condition is less common, although the damage is severe and the bleeding is more, it is difficult to detect if it is not obvious; High vaginal tear: This is a tear in the upper third of the vagina, often accompanied by tearing of the same clothes, but in general, it is also rare. Vaginal tears, regardless of degree, make the patient feel very painful, sometimes it is difficult to sit upright. If the pregnant woman only has a slight vaginal tear, the uncomfortable symptoms will last for 1-2 weeks. During this time, actions that put pressure on the lower body such as going to the toilet, coughing or sneezing... also cause pain. By the second week, the tear will gradually heal and the sutures will dissolve on their own, but muscle and nerve strength still need a few more weeks to fully recover..
In case the patient has a vaginal tear in More severe cases also take longer to recover. The pain and discomfort can last from a few weeks to a few months. If the tear is too severe, there is also the risk of pelvic dysfunction, uterine prolapse, problems with excretion and sexual activity.
3. Prepare for vaginal restoration
3.1. Performer Immediately after being diagnosed with vaginal injury, the medical team needs to appoint an immediate vaginal restoration to prevent the mother from losing a lot of blood. The choice of person to directly perform the procedure will depend on the degree of shallow or deep tear, external, mid or internal tear. Specifically:If the tear is shallow and located in the outer third of the vagina: An experienced midwife or obstetrician performs the restoration; Remaining cases (upper/middle/deep 1/3 tear): Experienced midwife or obstetrician-gynecologist. 3.2. Equipment The necessary medical kit for the vaginal tear repair procedure includes:
Vaginal valve; CTC heart-shaped pen, antiseptic and needle clamp; A sharp, straight scissors; Tweezers; Polydine or povidine antiseptic solution; Only vicryl No. 1; One 10 ml syringe. 3.3. Before performing the vaginal restoration procedure, the doctor will evaluate the entire condition of the female patient by asking and checking the medical record so as not to miss information related to:
Amount of blood loss ; Pulse beat; Blood pressure readings; The degree of uterine contraction after normal delivery, need to use drugs to stimulate uterine contractions if not achieved; Some diseases are related to hemostasis - coagulation function, such as thrombocytopenia, prolonged APTT, decreased blood fibrinogen concentration, ...; Local allergies to anesthetics, pain relievers or antibiotics.

Trước khi tiến hành thủ thuật khâu phục hồi âm đạo, bác sĩ sẽ đánh giá toàn bộ thể trạng của nữ bệnh nhân
4. Steps to take
The procedure for suturing and recovering from a vaginal tear caused by an episiotomy during a vaginal birth or with an assistive device is as follows:The assistant holds the valve that exposes the vagina while the obstetrician or midwife has experience in vaginal, perineal and urinary catheterization; Local anesthetic with Lidocaine 2% 2 ml + 3 ml of distilled water for pain relief, but if the pregnant woman has received an epidural to relieve pain during and after childbirth, no additional dose is required; Sew up the vaginal tear from top to bottom; If the tear is shallow, sew a layer of squeezing stitches with vicryl or other self-dissolving threads; if the tear is deep and complicated, it must be sutured in many layers, the stitches are separated by self-dissolving thread; After stitching, it is necessary to disinfect the vagina; Check for sutures to the rectum by inserting a finger into the anus, if so, sutures need to be removed and sutured; The final step is to disinfect the anus. It should be noted that during the repair of vaginal tear, the upper layer must overlap the lower layer to avoid hematoma. Suture of the lower layer requires a close fit over the base of the lesion, which not only helps to prevent hematoma but also avoids suturing to the rectum.
5. Monitoring and handling of accidents

Trước khi tiến hành thủ thuật khâu phục hồi âm đạo, bác sĩ sẽ đánh giá toàn bộ thể trạng của nữ bệnh nhân
Pulse, blood pressure and vaginal bleeding. If bleeding continues, the suture needs to be re-examined; Manifestations of hematoma often cause pregnant women to feel pressure in the vaginal area, anus - rectum area, and a feeling of pressing and straining. Management of hematoma by examining the vagina and removing all the hematoma from the suture, then suturing the entire fundus with a separate multi-layer stitch to avoid leaving a gap; Amount of blood loss and tests of red blood cells, hemoglobin, blood transfusion in case of need; Give the mother antibiotics within 5 days after stitches. To limit the risk of vaginal tearing during vaginal delivery, women need to adhere to the pushing positions as directed by the doctor during labor. In addition, before giving birth 4-6 weeks, pregnant women should refer to performing squat exercises to support women who are about to give birth and regularly massage the perineum area every day for about 15 minutes with lubricant to help soften the tissues. , making the muscles of the reproductive tract become more flexible and stronger.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.