This is an automatically translated article.
The article was professionally consulted by Specialist Doctor I Tran Quoc Vinh - Emergency Doctor - Department of Resuscitation - Emergency - Vinmec Nha Trang International General Hospital. Doctor Tran Quoc Vinh has more than 6 years of working experience (starting in 2011) in the field of Emergency Medicine.Bee stings are a common occurrence when you are outdoors, most bee stings cause only some discomfort and only need home treatment to relieve the pain. However, there are cases of people who are allergic to bee stings or have been stung many times, and there will be a serious reaction that requires emergency treatment.
1. In case of no allergies
If there is only one sting and there are no symptoms of an allergic reaction, you may only need topical wound care such as cleaning and antibiotic ointment. Specifically as follows:The first thing to do is to pull out the stinger of the bee as quickly as possible because the longer it stays in the skin, the more venom it will secrete and cause pain and swelling to the person being stung. Calm. Although most bees only sting once, wasps can sting more. Therefore, if stung by a bee, calmly move or remove the child from the area of the sting to prevent the bee sting again. If the stinger is still in the skin, remove it by gently rubbing it with your fingernail or a piece of gauze. Do not use tweezers or squeeze to remove the stinger, as squeezing will cause more venom to be released into the skin. Wash the sting site with soap and water. Apply a cold pack to reduce swelling. However, if the swelling moves to other parts of your body, like your face or neck, go to the emergency room right away, as this could be a symptom of an allergy. Other signs of an allergic reaction include difficulty breathing, nausea, hives, or dizziness. You can take an H1 antihistamine (such as: chlorphenyramine, cetirizine, loratadine, diphenhydramine, ..) orally or a topical H1 antihistamine (phenergan) to treat itching, and ibuprofen (Motrin) or acetaminophen (Tylenol). Paracetamol (efferalgan) for pain relief, topical steroids (bethamethasone) can be used to reduce inflammation and allergies such as (Silkron, Gentrisone, Eumovate, ..). If the antibody potency produced by the tetanus vaccine is not sufficient, you may want to consider getting a booster shot of the vaccine after a bee sting.
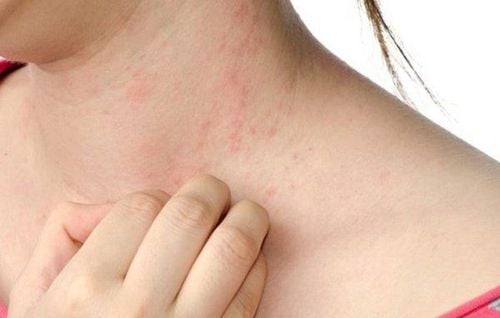
2. For mild and moderate allergies to bee stings
For mild allergy symptoms such as rash and itching all over the body but no respiratory symptoms or effects on other vital signs (heart rate, blood pressure, and temperature), you may be treated with Treat with antihistamines and steroids.If you have an allergic reaction such as a rash all over your body and have breathing problems such as shortness of breath, stridor or circulation problems that cause a drop in blood pressure that manifests as: dizziness, lightheadedness, you may An injection of antihistamines, steroids, and epinephrine (adrenaline) will be given. Some other treatments will be done at the scene or in an ambulance. You will then be transferred to a medical facility and monitored in the emergency department.
If you have been stung with itching all over your body (10 to 20 stings or more) or stung anywhere like your throat or inside your mouth but have no symptoms of an allergic reaction, you may still need to be admitted to the emergency department. be monitored, and your doctor will perform repeated blood tests to detect delayed allergic reactions or other complications. Or, if you are stung in your eyeball, you will be referred to an ophthalmologist for a vision exam and evaluation.
3. In case of severe allergy to bee stings
A severe allergic reaction or anaphylaxis to a bee sting is potentially life-threatening and requires emergency treatment. Take the patient to an emergency medical facility or call 911 if, after being stung by a bee, the patient has the following signs and symptoms:Skin reaction, including hives and itching and redness or pale Difficulty breathing Swelling of throat and tongue Rapid weak pulse Nausea, vomiting or diarrhea Dizziness or fainting Loss of consciousness People who have an allergic reaction to a bee sting have a 25% to 65% risk of anaphylaxis burned next. Therefore, if you are already allergic to a bee sting, it is important to talk to an allergist about precautions such as immunotherapy to avoid a similar reaction in the event of a repeat sting.
What to do in case of anaphylaxis
In anaphylaxis, a medical team will perform cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR) if the person stops breathing or the heart stops in combination with the following methods:
Injections Epinephrine (adrenaline) first-line drug to reduce allergic reactions Give oxygen Intravenous injection of antihistamines, steroids and possibly in combination with bronchodilators to reduce airway inflammation and improve respiratory symptoms Spontaneous injection of epinephrine epinephrine autoinjector
If you are allergic to bee stings, your doctor may prescribe an epinephrine autoinjector (EpiPen, Auvi-Q) and you will need to carry it with you at all times. . Therefore, the patient needs to make sure the medicine is expired, know how to use it, and re-instruct the family and people around how to use the auto-injector epinephrine in case the patient is in anaphylaxis so he cannot inject himself.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.