This is an automatically translated article.
Small cell cancer, large cell cancer or some other terms are often used to describe the symptoms, characteristics as well as the type of cancer that the patient is having. So what do the terms used for cancer mean?
1. What does small cell, large cell mean?
The terms “small cell cancer” and “large cell cancer” are actually phrases that describe the appearance of cancer cells under a microscope.
Examining and paying attention to the characteristics of cancer cells will help the doctor determine the type of cancer a patient has, where the cancer started and how abnormal the cells are. any. In particular, when combined with testing methods to determine the size of the cancerous area, this information will help the doctor know:
The progression or possible outcome of the cancer (prognosis) ). The most effective treatment for a specific cancer. Several other common terms are used to describe the appearance of cancer cells, including:
Clear cell: The inside of the cell is clearly visible, such as some ovarian cancer, uterine cancer and kidney cancer. Spindle cell: Spindle cells are cells that are narrower at both ends than in the center. Some of the more common types of rhabdoid cell carcinoma include gastrointestinal cancer, breast cancer, skin cancer, and other soft tissue cancers. Large cell cancer: These are cells that are larger than normal cells in the body. Certain types of large cell cancers such as lymphoma or lung cancer. Small cell cancer: Small cell cancers are cells that are smaller than normal cells in the body. Some of the most common types of small cell cancer are prostate cancer, small cell lung cancer, or neuroendocrine cancer of the pancreas. Squamous cell: Squamous cells are flat cells. Some common types of squamous cell cancer, such as skin cancer or any other type of cancer, begin to form in the lining of certain organs in the body, such as the bronchi of the lungs. Adenocarcinoma: Cancer that originates in glandular cells in the body, including prostate, breast, stomach, and endometrial cancers. Anaplastic: This term describes very abnormal-looking cells in the body. It is so anomalous that it can make it difficult for doctors to pinpoint the source of these cells. Metaplastic: This term describes tumors that are made up of many different types of cells, with different shapes. Poorly differentiated cancer: This is a very unusual appearance. In normal tissues of the body, cells become differentiated depending on their location, for example breast cells look different from colon cells. If the cells look completely different from normal cells, they are called poorly differentiated cells.
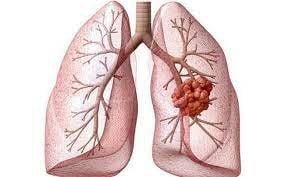
Ung thư tế bào lớn và ung thư tế bào nhỏ giúp bác sĩ xác định được loại ung thư.
2. Other factors that help classify cancer
Here are some other factors that help categorize cancer, including:
The area where the cancer starts to grow in the body, such as the breast or liver. Cancers in several organs may present similarly. For example, most of the most common types of kidney cancer are clear cell cancers. On the other hand, breast cancer rarely presents with clear cell carcinoma. So, bright cells in a breast biopsy may show that cancer did not originate in the breast but has spread to another area of the body, such as the kidney. The type of tissue the cancer grows from, including sarcoma and carcinoma. Carcinoma is cancer that starts in the skin or in the lining tissues that cover internal organs. Meanwhile, a sarcoma is a cancer of the bones, fat, cartilage, muscles, blood vessels, or other connective or supporting tissues in the body. To summarize, small cell cancer and large cell cancer are terms that describe the appearance of cancer cells under the microscope. Examining and paying attention to the characteristics of cancer cells will help doctors determine the type of cancer a patient has as well as the degree of abnormality in the cells.
Currently, at Vinmec International General Hospital, it has become a prestigious address in cancer screening with many outstanding advantages:
A team of highly qualified and experienced doctors. Comprehensive professional cooperation with domestic and international hospitals: Singapore, Japan, USA, .. Comprehensive treatment and care, multi-specialty coordination towards individualizing each patient. Having a full range of specialized facilities to diagnose the disease and stage it before treatment: Endoscopy, CT scan, PET-CT scan, MRI, histopathological diagnosis, gene-cell testing, .. There are a full range of mainstream cancer treatment methods: Surgery, radiation therapy, chemotherapy, stem cell transplant...
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.
References: Mayoclinic.org













