This is an automatically translated article.
The article is professionally consulted by Master, Doctor Cao Thanh Tam - Cardiologist - Cardiovascular Center - Vinmec Central Park International General Hospital.A person can have a stroke without any warning symptoms, a condition known as silent cerebral infarction (SCI) or silent stroke. If this happens more often, there is a greater risk of memory loss and more serious stroke complications.
1. Silent stroke
When it comes to stroke, people may immediately remember its typical symptoms such as paralysis or loss of movement of some body parts, difficulty speaking or eating, cognitive disturbances... However, There is a type of stroke that does not show any of these symptoms, which is called a silent stroke.
Similar to an ischemic stroke, a silent stroke occurs when the blood supply to the brain is interrupted, causing brain cells to lack oxygen and die. But the silent stroke is different in that, the brain regions that are ischemic do not take over the body's functions such as movement, thinking, etc. Therefore, it is difficult to recognize brain damage in these areas. if not perform computed tomography.
Some studies show that 1/3 of people over 70 years old have experienced at least 1 silent stroke and the occurrence of many silent strokes can cause typical symptoms such as:
Impairment Memory Mood disorders : Inability to control emotions, laughing or crying at inappropriate times. Change your gait. Can get lost in familiar places Loss of bowel and bladder control

2. Diagnosis of a silent stroke
The diagnosis of silent stroke should be based on the cause and symptoms of the disease and need to be distinguished from other types of stroke. So how to know which is silent stroke, which is ischemic stroke, hemorrhagic stroke or which is just a transient ischemic attack (TIA)? You can find the answer based on the following table:

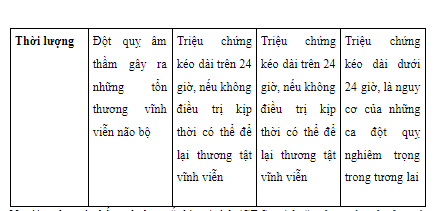
In addition, based on the results of computed tomography (CT Scan) or magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) can help identify areas of the brain that are damaged or stopped working thereby making a conclusion about a silent stroke. quiet.
3. Silent Stroke Treatment
There is no way to restore the activity of the brain area damaged by a silent stroke. In some cases, other areas of the brain can take over the function of the damaged area, but if silent strokes continue to occur, the consequences will be very serious. People with silent strokes Silence can regain some lost or limited abilities with rehabilitation therapies including:Physical therapy to help restore motor function of the body Consult a pathologist about language and speech to improve daily communication Using psychological and sociological measures for post-stroke psychological disorders. There are also many people using Alzheimer's drugs for people with dementia after many silent strokes, but the effectiveness has not been proven. Besides treatment methods, forming habits in daily life is also a way for stroke patients to train themselves to recover their memory, for example:
Practice completing tasks routine work at fixed times of the day. Get in the habit of putting personal items in their place like keys, medicine, toothbrush, razor, etc. Make a detailed to-do list for the day. Keep each medicine separately in a bag or box with their names and uses. Participating in some games can improve memory.

Silent strokes often have no symptoms or obvious symptoms that many people mistake for the aging state of the elderly. Because it is difficult to detect, silent strokes have the potential to cause irreversible damage to certain areas of the brain. However, they can be completely prevented by:
Regularly check blood pressure and blood sugar index Regular exercise Reduce salt intake in the body Maintain a reasonable weight Eat lots of vegetables, limit fat and fast foods Do not smoke and drink less beer and alcohol. A stroke is a medical emergency, especially a silent stroke, because without oxygen and nutrients from the blood supply to the brain cells and the affected part of the brain, the brain will gradually die. leave dangerous complications. Therefore, when there are signs of brain stroke, relatives need to take the patient to medical centers. Early treatment can prevent serious complications or death.
Currently, Magnetic Resonance Imaging - MRI/MRA is considered a "golden" tool for brain stroke screening. MRI is used to check the condition of most organs in the body, especially valuable in detailed imaging of the brain or spinal nerves. Due to the good resolution and contrast, MRI images allow to detect abnormalities hidden behind bone layers that are difficult to detect with other imaging methods. MRI can give more accurate results than X-ray techniques (except DSA angiography) in diagnosing brain diseases, cardiovascular diseases, strokes,... Moreover, the process MRI scans do not cause side effects like in X-rays or computed tomography (CT).\
Vinmec International General Hospital currently owns a 3.0 Tesla MRI System, which is equipped with state-of-the-art equipment by GE. Healthcare (USA) with high image quality, allows comprehensive assessment, does not miss the injury but reduces the time taken to take pictures. Silent technology helps to reduce noise, create comfort and reduce stress for the client during the shooting process, resulting in better image quality and shorter imaging time. With the state-of-the-art MRI system With the application of modern methods of cerebral vascular intervention, a team of experienced and well-trained neurologists and imaging specialists, Vinmec is a prestigious address for stroke risk screening and screening. reliable goods.
In the past time; Vinmec has successfully treated many cases of stroke in a timely manner, leaving no sequelae: saving the life of a patient suffering from 2 consecutive strokes; Responding to foreign female tourists to escape the "death door" of a stroke ;...
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.
Reference sources: healthline.com, webmd.com