This is an automatically translated article.
The article is written by Ths.Bs. Pham Manh Chung, head of the imaging department at Vinmec Ha Long International Hospital.Contrasts are iodine-containing substances used to enhance the contrast level of body fluids or structures during imaging studies. In addition to the diagnostic benefits, the use of contrast agents can be accompanied by some undesirable side effects.
1. Side effects, unwanted effects of contrast agents
Hypersensitivity reactions Hypersensitivity reactions most commonly occur within 30 minutes of administration of the contrast agent, however reactions may also occur as late as several hours to several days.
The risk of hypersensitivity reactions is higher in the following cases: previous reaction to contrast material. History of bronchial asthma or other allergic disorders.
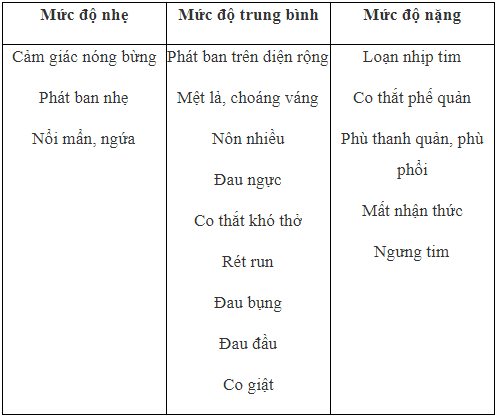
Phản ứng quá mẫn phân thành 3 mức độ:
Serious reactions as well as death are very rare.
Anaphylactic reactions may occur independent of dose or route of administration or rate of injection. Mild symptoms of hypersensitivity may be the first sign of a serious reaction.
In severe hypersensitivity reactions, patients with cardiovascular disease are often at increased risk of serious events.
Because of the potential for hypersensitivity reactions after administration, patients should be monitored for at least 30 minutes after administration. Emergency facilities should be available to all patients.
Thyroid dysfunction The risk/benefit should be carefully evaluated in patients with known or suspected hyperthyroidism or goiter, because contrast media can cause hyperthyroidism and thyrotoxic attacks. in these patients. Thyroid function testing should be performed in patients with suspected hyperthyroidism.
Central Nervous System Disorders The risk of contrast-related neurologic complications is increased in patients with CNS disorders. Neurological complications are more common in patients with cerebral angiography and related procedures.
Caution should be exercised in conditions in which the seizure threshold may be reduced such as in patients with a history of epilepsy.
Factors that increase the permeability of the drug across the blood-brain barrier will increase the delivery of the contrast agent into the brain tissue, possibly leading to reactions on the central nervous system.
Anxiety states Severe excitement, anxiety, and pain may increase the risk of side effects or worsen contrast-related reactions. Care should be taken in these patients to minimize anxiety.
Impaired renal function Contrast-induced nephrotoxicity, manifesting as transient impairment of renal function after contrast administration, may occur.
Acute renal failure can occur in some cases: the patient already has impaired renal function. Loss of water. Diabetes. Multiple myeloma/Paraproteinemia. Repeated and/or high dose of contrast agent.
All patients receiving contrast media must ensure adequate hydration.
Cardiovascular diseases The risk of developing clinical signs associated with hemodynamic changes and arrhythmias is increased in patients with cardiovascular disease or severe coronary artery disease. Administration of intravenous contrast media may precipitate acute pulmonary edema in patients with heart failure.
Severe myasthenia gravis : Contrast may increase symptoms of severe myasthenia gravis. Pheochromocytoma: Patients with pheochromocytoma may be at increased risk of developing a hypertensive crisis. Embolic events: In addition to contrast, many factors include procedure time, number of infusions, catheter and syringe material, underlying medical condition, and concomitant use of other drugs. may contribute to thromboembolic events.
Pregnant women: the use of non-ionic contrast agents has not been fully proven to be safe for pregnant women. Contrast should not be used during pregnancy unless the benefits outweigh the risks and need to be determined by the physician.
Lactating mothers: Contrast secretion into breast milk is very low. Harm to the nursing infant is unlikely. Breastfeeding should be discontinued for at least 24 hours after the contrast scan before re-feeding the infant.

Bà mẹ cho con bú cần lưu ý khi tiêm thuốc cản quang
2. How to use contrast agent safely for patients
2.1 Before shooting
Customers will be checked by doctors for safety issues (check list) before injecting contrast such as: history of drug allergy, history of bronchial asthma, diarrhea, dehydration, urinary incontinence sugar and are taking Metformin, have kidney failure. Indications to check renal function: Need to be evaluated before using contrast agent. Certain circumstances, such as ongoing hemodialysis, acute kidney injury, or the need for urgent imaging for life-threatening situations (eg, suspected serious injury, threatened aortic dissection) may cause A contrast-enhanced CT scan may be considered without waiting for the creatinine results. Discontinue current use of potentially nephrotoxic drugs, especially: non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, diuretics should be discontinued before 24 hours, metformin should be discontinued before 48 hours. ACE inhibitors and receptor blockers do not require strict discontinuation. Patients need to fast for at least 4 hours before contrast injection. If the customer has a history of drug allergy, bronchial asthma, they will be prevented from reacting before being taken to the imaging department for contrast injection.
2.2 During shooting
Customers calm down, breathe gently, avoid anxiety, nervousness and are guided to practice breathing.

Khách hàng không nên lo âu, hồi hộp khi chụp
2.3 After shooting
The client is monitored in the imaging room or recovery room for at least 30 minutes to see if there are any unusual reactions. If there are no abnormalities, the client is directed to return to the clinic. If the patient is being treated as an inpatient, the doctor will have a monitoring regimen appropriate to the patient's current condition. If the patient is an outpatient, without risk factors, he can go home. Drink plenty of water, monitor urine output for 24 hours. If you find that the amount of urine is less than normal, go back to the hospital to check your kidney function. Return to the hospital when there are any unusual signs. The diet is the same as any other normal day. Vinmec International General Hospital is one of the hospitals that not only ensures professional quality with a team of leading doctors, modern equipment and technology, but also stands out for its examination and consulting services. and comprehensive, professional medical treatment; civilized, polite, safe and sterile medical examination and treatment space.
Customers can directly go to Vinmec Health system nationwide to visit or contact the hotline here for support