This is an automatically translated article.
Some medications that are taken by mouth and some that are given by injection have the goal of helping your body produce as many eggs as possible for an IVF cycle. However, there are also some fertility drugs that have associated side effects.
1. Fertility drugs for women
Some fertility drugs try to promote ovulation in a woman who does not ovulate regularly. Others are hormones that women must take before IVF.
1.1. Ovulation Pills
About a quarter of women of childbearing age have problems ovulating. Medications that can treat
Metformin (Glucophage): This substance can reduce insulin resistance. Women with polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS), especially those with a body mass index > 35, may be insulin resistant, which can also cause ovulation problems. Dopamine agonists: These drugs reduce levels of a hormone called prolactin. In some women, having too much prolactin causes ovulation problems. Clomiphene (Clomid): This drug can trigger ovulation, and many doctors recommend it as the first choice of treatment for a woman with ovulation problems. Letrozole (Femara): Like clomiphene, letrozole can trigger ovulation. Among women with polycystic ovary syndrome, especially those who are overweight or obese, letrozole may work better. A 2014 study found that 27.5% of women with polycystic ovary syndrome who took letrozole eventually gave birth, compared with 19.1% in those taking clomiphene. Gonadotropins: This group of hormones stimulates activity in the ovaries, including ovulation. When other treatments don't work, your doctor may recommend using follicle-stimulating hormone and luteinizing hormone in the group. People receive this treatment as an injection or a nasal spray. In about 10% of infertility cases, doctors cannot find a cause.

Một số loại thuốc được dùng bằng đường uống và một số loại thuốc được sử dụng bằng đường tiêm
1.2. Hormones before IVF
Drugs cannot treat some causes of infertility. When doctors can not determine the cause of infertility, they will use the following intervention methods:
Intrauterine insemination: This is the introduction of sperm directly into the uterus around the time of ovulation. It can improve your chances of conceiving when there are problems with cervical mucus or sperm motility. Your doctor may recommend the following before an IUI:
Ovulation medications: For example, clomiphene or letrozole, which can cause the body to ovulate and possibly release an extra egg. Ovulation trigger: Since determining when ovulation is essential, many doctors recommend ovulation "trigger" injections of the hormone human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG). Progesterone: This hormone can help maintain an early pregnancy and women often take it through a vaginal tablet. In vitro fertilization (IVF): Involves removing one or more eggs so your doctor can fertilize them with sperm in a petri dish. If the egg develops into an embryo, the doctor will implant it in the uterus. IVF requires several medications, including:
Ovulation suppression: If a woman ovulates too early, IVF may not work. Many doctors prescribe gonadotropin antagonists to prevent premature ovulation. Ovulation pills: IVF is more likely to be successful, like IUI, if the ovaries release many eggs. Your doctor will prescribe clomiphene or letrozole to increase the chances of this. hCG. Progesterone: A woman undergoing IVF will take progesterone to help support an early pregnancy. When treating infertility, your doctor may recommend temporary hormonal birth control to help regulate your menstrual cycle. It can also help prepare the body for artificial insemination.
2. Side effects of fertility drugs
Adverse reactions are unwanted symptoms caused by drugs. You may or may not experience side effects depends on:
The type of medicine you take The dose of the drug Your body Here are the side effects and risks of some fertility drugs:
2.1. Clomid Side Effects and Risks
Clomid works by tricking the body into thinking there isn't enough circulating estrogen. To do that, it blocks receptors in the body from responding to the hormone estrogen. Most of the side effects of Clomid are due to low estrogen levels.
Manifestations include:
Hot flashes (suddenly feeling hot in the face, sweating, rapid heartbeat) Bloating, abdominal discomfort Weight gain, Headache, Lightheadedness, Nausea, Dizziness, Breast tenderness, Menstrual bleeding Vaginal dryness A rare but serious risk of Clomid is blurred vision. Occurring in less than 1.5% of women during clinical trials, this side effect may include blurred vision, glare, or flashing lights.
Risks:
Twins or multiples Ovarian hyperstimulation syndrome (OHSS) Irreversible vision disorders Ovarian cysts
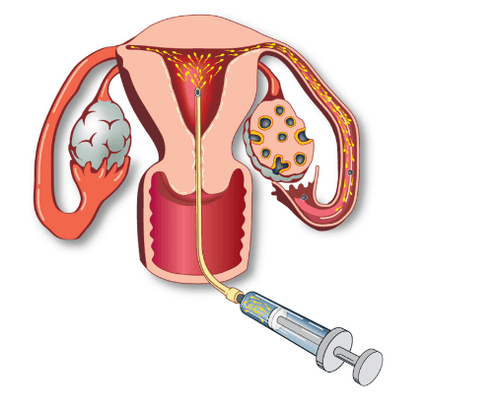
Thụ tinh trong tử cung là việc đưa tinh trùng trực tiếp vào tử cung đúng khoảng thời gian rụng trứng
2.2. Letrozole side effects and risks
Letrozole is used similar to Clomid. Studies have found that women with PCOS and women who are Clomid-resistant (who do not ovulate while taking Clomid) may have more success with letrozole. Common side effects:
Fatigue Dizziness Headache Bloating, abdominal discomfort Hot flashes Blurred vision (much less common than Clomid) Difficulty sleeping Unusual vaginal bleeding Breast pain Although rare, but Women taking Femara may develop a condition known as ovarian hyperstimulation syndrome (OHSS), which can manifest with symptoms ranging from bloating and diarrhea to shortness of breath and chest pain.
2.3. Gonadotropins Side Effects and Risks
This is an injectable hormone. These include drugs like Gonal-F (FSH), Follistim, and Ovitrelle (hCG). The injection can be used alone or in combination with other medications during an IVF cycle. Side effects:
Bloating, abdominal pain Headache, nausea Upper respiratory tract infection Sinus congestion Mood changes Acne Breast tenderness Weight gain Pelvic discomfort Bleeding, or unusual spotting Vomiting Pain, redness at injection site Dizziness Risks:
Twin or multiple pregnancy Ovarian hyperstimulation syndrome (OHSS) Ovarian cyst Injection site infection Adnexal torsion Ectopic pregnancy Blood clots
2.4. GnRH Agonist Side Effects and Risks
GnRH agonists like Lupron are most commonly used during IVF treatment. They shut down the body's natural reproductive system so your doctor can control ovarian stimulation and maturation. Low estrogen levels are responsible for many of the side effects of GnRH agonists.
Side effects of cetrorelix acetate (Cetrotide) include:
Injection site rash Abdominal pain Headache Headache Common side effects of ganirelix acetate (Antagon, Ganirelix, Orgalutran) include:
Ovarian upset Head Vaginal bleeding Pain or bruising at the injection site Nausea Stomach pain Risks:
Stillbirth Birth defects Ovarian hyperstimulation syndrome (OHSS)
Một số loại thuốc kích thích trứng có tác dụng phụ liên quan
3. Coping with the side effects and risks of taking medications
Inform your doctor of any unusual signs or symptoms while you are taking the medicine. It is not possible to completely avoid all side effects. However, there are some things you or your doctor can do to reduce your risk. For example:
Some side effects can be avoided or reduced by taking the medicine at night or with food. Talk to your doctor about the best time and way to take your medication. Your doctor should also use the lowest dose then gradually increase the dose for optimal effect. The most important thing is to always follow your doctor's orders. To reduce your risk of having a twin or multiple pregnancy, it's important to closely monitor your cycle. With gonadotropins or Clomid, ultrasound can be used to determine how many potential follicles are developing. Every follicle is a potential baby, if you conceive. A few suggestions to avoid drug side effects:
Acetaminophen is best for your headache. You should not take ibuprofen (Advil, Motrin) or naproxen (Aleve, Midol) because there is some concern that these medicines might interfere with ovulation and implantation of the embryo. Remove clothes when feeling hot, drink plenty of water during fertility treatment because using hormones can dehydrate the body and make you feel more thirsty. Keep your spirits up: Infertility treatment can make you tired and feel very bad. Find a way to change your mood, change the atmosphere with some new experiences or sit quietly and read a book. Share with your husband so that you both have sympathy for each other.
Currently, to fulfill the desire to become a father and mother, infertile and infertile customers can come to the Reproductive Support Center - Vinmec International General Hospital. This is the leading center in Vietnam, built and applied a comprehensive examination and treatment process, combining both gynecology and obstetrics and gynecology to provide the optimal method for each patient's case.
Advantages when customers choose Vinmec fertility center:
Equipped with modern equipment, clean air system according to international standards to ensure lab quality, single cabinet system to optimize quality embryo, improving the success rate for each cycle of artificial insemination. Implement most advanced assisted reproductive techniques in the world: ICSI (intracytoplasmic sperm injection); support embryo escape membrane; Reproductive reserve: embryo freezing, sperm freezing, oocyte freezing to help customers take the initiative in giving birth at will, transferring embryos on day 5, minimizing pregnancy; male infertility techniques (PESA, MESA, TEFNA, TESE) Besides advanced reproductive support methods, a team of good doctors in the country and the world, with prestige and long experience in the field of infertility .
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.
References: drugs.com, medicalnewstoday.com, ovohealth.com, verywellfamily.com