This is an automatically translated article.
The article was consulted with Dr. To Kim Sang - Oncology Center - Central Park International General Hospital.Chemotherapy has long become an indispensable treatment modality in the management of most cancers, especially when the disease is advanced and metastatic. With chemotherapy, besides the desire to destroy cancer cells, it also partly affects the body's healthy cells, causing adverse effects or side effects.
1. What is chemotherapy?
Chemotherapy is a treatment method by giving chemotherapy drugs into the patient's body through intravenous or oral injection (infusion) to kill and eliminate cancer cells. This may be a suitable option for people with liver cancer that cannot be treated with surgery, cannot or does not respond to destructive treatments such as radiofrequency ablation, microwave ablation, embolization. or targeted therapy.Unlike surgery and radiation therapy, instead of only being able to treat cancer in the liver, chemotherapy goes into the bloodstream and can affect the whole body; which in turn helps to eliminate cancer cells if they have moved to other organs.
In addition, in the treatment of liver cancer, chemotherapy can also be used locally in the liver by infusing drugs into the hepatic artery. This method can be performed alone, called Hepatic Arterial Infusion Chemotherapy (HAIC) or in combination with embolization, called Transarterial Chemo-Embolization (TACE). With local chemotherapy, drug concentrations are more concentrated in the tumor and patients can reduce the risk of systemic side effects.
2. How effective is chemotherapy in the treatment of liver cancer?
Performing chemotherapy for liver cancer can bring the following main effects:Complete treatment of liver cancer: In some cases when the disease is detected early, small liver tumors can be eliminated. using the TACE method. This is also the most common method to treat primary liver cancer today. However, this treatment is not completely thorough and may need to be repeated several times.
Slow down the progression of liver cancer: If liver cancer has advanced or metastasized, it will be difficult to completely remove cancer cells from the patient's body. At this time, systemic chemotherapy will be performed to control and prevent the tumor from growing and invading other organs of the body, thereby prolonging the patient's life time.
Reduce pain symptoms caused by liver cancer: When the disease enters the final stage, the symptoms also gradually appear more and more clearly and have a more "visiting" frequency. The most common uncomfortable symptom is abdominal pain caused by a tumor. Chemotherapy drugs when given into the body can help control and relieve this symptom. As a result, the patient feels less pain and thereby improves the quality of life.
However, it should be noted that most chemotherapy drugs have very limited effectiveness in treating primary liver cancer and are not helpful in prolonging survival. A combination of chemotherapy drugs can help increase tumor control more effectively than using one drug alone, but this effect may not last long. Therefore, according to current treatment guidelines, in the treatment of advanced and metastatic primary liver cancer, systemic chemotherapy should not be preferred, instead the role of targeted drugs and immunosuppressive drugs.
Hóa trị giúp giảm các cơn đau của bệnh ung thư
3. What drugs are used for liver cancer
Here are some of the most common chemotherapy drugs commonly used in the treatment of liver cancer, including:Oxaliplatin 5-Fluorouracil (5-FU) Gemcitabine Cisplatin Capecitabine Doxorubicin (pegylated liposomal doxorubicin) Mitoxantrone In some cases In certain combinations, 2-3 drugs can be combined at the same time to improve the treatment effect. For patients who are in relatively good health and are able to tolerate a wider range of drugs, GEMOX (including gemcitabine and oxaliplatin) would be an appropriate choice. People with underlying liver disease may choose to use FOLFOX (including 5-FU, oxaliplatin and leucovorin).
4. How is chemotherapy for liver cancer done?
Chemotherapy can be given into the patient's body in many different ways, namely:4.1 Systemic chemotherapy Systemic chemotherapy is a form of drug administration through an intravenous (IV) route into the patient's body. or oral. After the drug is put into the body, it will enter the bloodstream and reach all organs. Therefore, this method is very useful for cases of liver cancer that has spread to other parts of the body.
For intravenous (IV) chemotherapy, the patient will have a catheter inserted into the central venous system to deliver chemotherapy drugs into the body. This catheter is called a central venous line (CVC). Their main use is to deliver drugs, fluids, or nutrients into the patient's bloodstream. In addition, the doctor can also use them to take blood samples for testing. Other routes of drug administration may be a peripheral intravenous line or through an instrument called a subcutaneous injection chamber.
Chemotherapy for liver cancer is usually given in cycles. A treatment cycle will last 2-3 weeks, depending on the medication the patient is taking. After each treatment phase, the patient will have a period of rest to help the body recover after taking the drug.
4.2 Hepatobiliary Intravenous Chemotherapy Intrahepatic Intravenous Chemotherapy (HAIC) is a technique that delivers drugs directly into the hepatic artery to deliver drugs directly to the tumor site. This method requires surgery to be able to place the injection chamber under the skin of the patient's abdomen. The doctor will connect the injection chamber to a catheter connected to the hepatic artery. During the procedure, the patient will be under general anesthesia. The chemotherapy drug is injected with a needle through the skin into the reservoir of the injection chamber, then it is released slowly and steadily into the hepatic artery.
Healthy liver cells metabolize most chemotherapy drugs before they can reach the rest of the body. Therefore, although this method is used for patients with higher doses of chemotherapy drugs than systemic chemotherapy, it does not increase the side effects. The most commonly used drugs for HAIC are floxuridine (FUDR), oxaliplatin, and cisplatin.
HAIC may be the treatment of choice in cases of large liver tumors invading the portal vein. Although HAIC helps reduce systemic side effects, because it is an invasive procedure, patients can still experience complications such as thromboembolism, peptic ulcer due to drug leakage and infection or blockage of the transmission line. Not all cases can use this technique because most liver cancer patients cannot tolerate surgery to place the infusion chamber into the hepatic artery.
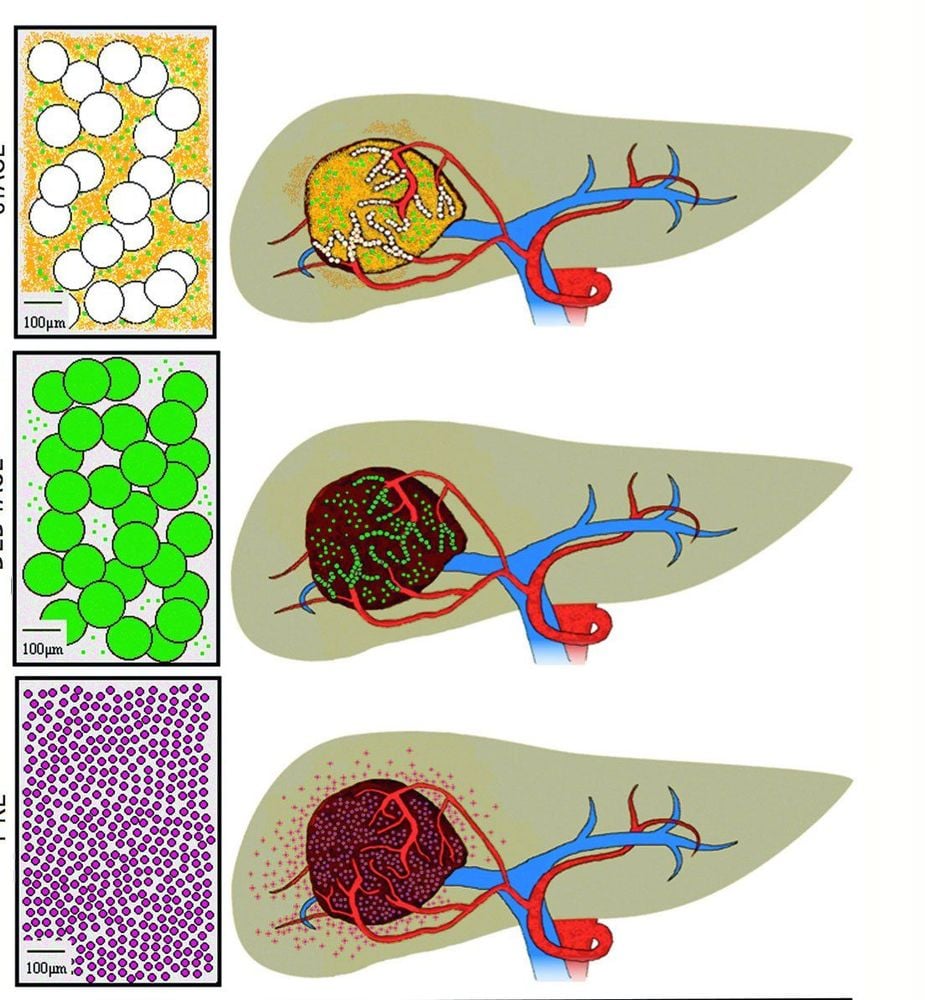
Kỹ thuật đưa trực tiếp thuốc vào động mạch gan
5. Side effects of chemotherapy
Systemic chemotherapy is a therapy that affects the entire body, so when using chemotherapy drugs to treat liver cancer, the occurrence of side effects is inevitable. Each patient will experience different symptoms, and these side effects often depend on the type, duration, and dose of the drug used.Here are some of the most common side effects, including:
Mouth ulcers Hair loss Diarrhea Eating no appetite Frequent fatigue, nausea or vomiting Ease of infection due to low white blood cell count Easy bruising and bleeding due to reduced blood platelet count However, the patient should not be too worried when these symptoms occur, as they usually do not last long and will disappear after the treatment is over. treat. You can prevent or reduce symptoms of nausea or vomiting by using supportive medications. Ideally, when you see any suspicious signs occurring due to the drug, you should immediately notify your doctor for timely remedial measures before things become more serious.
6. How to manage chemotherapy side effects
To manage the unwanted side effects that can be caused by chemotherapy, the patient should do the following:6.1 Take time to rest Cancer treatment is a long battle, it makes for the patient to always be in a state of fatigue. To overcome this, you should spend more time resting to refuel your body.
6.2 Healthy and balanced diet Other healthy cells in the body are also affected by chemotherapy drugs, so you need to get enough calories and protein to help your body regenerate cells. these healthy cells during treatment. A healthy and nutritious diet will include lots of green vegetables, fruits and low fat.
6.3 Exercise regularly Exercise helps reduce stress, fatigue, and at the same time stimulates the taste buds, helping you eat better.
6.4 Avoid alcohol abuse Alcohol not only affects overall health, but also reduces the effectiveness of anti-cancer drugs, making treatment more difficult.
6.5 Vitamin supplements Vitamin supplements are essential to help patients improve their health and well-being.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.