This is an automatically translated article.
The article was professionally consulted by a Doctor of Obstetrics and Gynecology, Vinmec Times City International General Hospital.After your baby is born, one of the tests that experts recommend for your baby is a hearing loss screening. However, many parents ignore it and it is not until the child is 2.5-3 years old that he or she has a hearing loss. Late detection will affect the baby's pronunciation and communication ability compared to peers. So when to screen, what is the cause, what is the screening method?
1. Importance of Hearing Loss Screening in All Newborns
1.1 What is hearing loss? Hearing loss (decreased hearing or deafness) can range from 3-4 per 1000 births to as high as 1-2 per 100 birthsHearing loss can be in one or both ears
One of the most common disorders compared to other disorders being screened widely is sickle cell anemia, G6PD deficiency, phenylketonuria or congenital hypothyroidism.
1.2 Why should it be identified and treated before the baby is 6 months old? Humans develop language by listening. Hearing is the basis for building social-emotional skills, cognitive skills, and subsequently reading comprehension and study skills.
Children who are discovered late (for example, when they are 2-3 years old) can suffer from permanent, irreversible disabilities in speech, language and cognitive development
Most Permanent hearing loss is caused by damage or loss of function of the auditory nerve that carries sound signals from the inner ear to the brain. However, only about half of all cases of hearing loss have an identifiable cause.
Of the identifiable causes, about half are due to reasons acquired during pregnancy and childbirth and about half are due to genetic causes
Therefore, it is recommended : hearing loss needs to be identified and treated if possible before the baby is 6 months old
>>> Newborn screening tests should be done soon after birth

Thính giác là cơ sở để xây dựng kĩ năng cảm xúc – xã hội, kĩ năng nhận thức, bé nên sàng lọc mất thính lực từ sớm

Đẻ non hoặc nhẹ cân, có các dấu hiệu của suy hô hấp sau đẻ, và phải thông khí hỗ trợ kéo dài là một trong các nguy cơ mất thính lực ở trẻ
4. Hearing loss screening methods
4.1 Measurement of otoacoustic emission (OAE) When the cochlea receives sound, a signal is transmitted to the brain. In addition, there is another distinct sound coming from the cochlea and returning to the ear canal. This very sound is called an “escape” echo sound from the cochlea. This “escape” sound is recorded through the microphone and becomes an image on the screen. If a “escape” response occurs, a “escape” response occurs. out” for the most important sounds for later hearing and speech development, the child was judged to have passed the test. The test usually lasts about 5-8 minutes.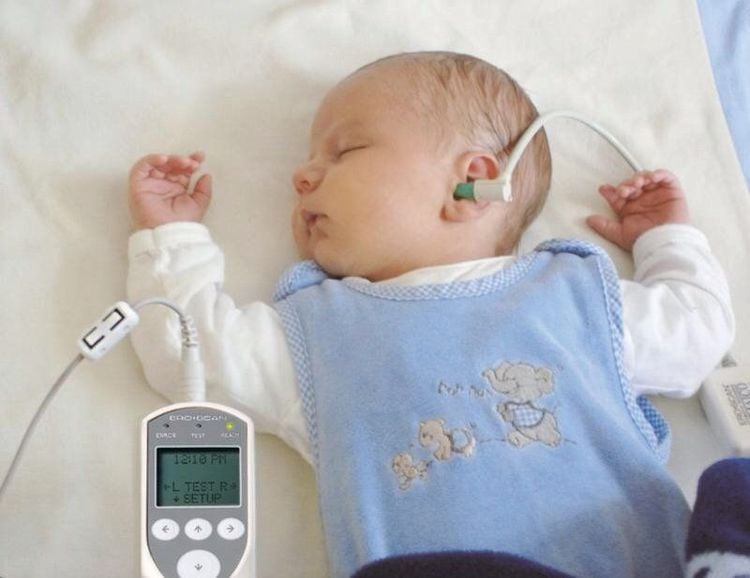
Đo lường âm thanh thoát ra từ ốc tai (otoacoustic emission – OAE) (Ảnh minh họa)
Acoustic stimuli are transmitted to the brain and the electrodes record as waves on the screen.
At what sound frequency hearing loss can be determined.
If it is for screening purposes only, the operator can use only a sound similar to a small click.
The test usually lasts about 5-10 minutes.
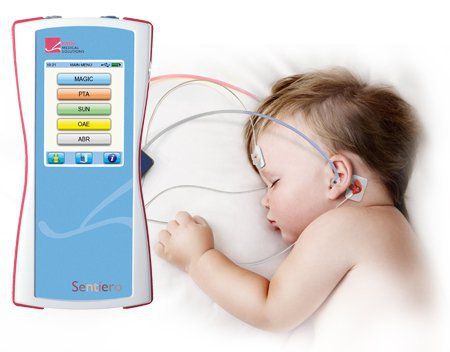
Đánh giá đáp ứng âm của cuống não (auditory brainstem response – ABR) (Ảnh minh họa)
Which method to use depends on the selection of the screening and training program.
Measurement by OAE is usually simpler, less expensive, but the false positive rate is higher than the false positive rate of ABR when performed within the first 3 days postpartum.
This difference is because the OAE method is more sensitive to the amniotic fluid or the substance that collects in the ear which is very common in babies.
5. Child Failure to Pass a Hearing Test About 2-10% of babies in the United States do not pass a hearing test the first time.
There can be a lot of amniotic fluid in the ear canal, and this amniotic fluid prevents acoustic stimuli from reaching the inner ear, or amniotic fluid collects in the middle ear cavity, behind the eardrum. It could be because the outside noise is too strong, the baby cries, or the baby moves during the test. If a child does not pass the test, it is necessary to wait at least 1 week before being tested again.
If there is clear evidence of hearing loss through these tests, the child should be referred to an audiologist for a complete diagnosis of the type and extent of hearing loss.