This is an automatically translated article.
Hair loss is a common side effect that occurs as a result of cancer treatment with methods such as chemotherapy or radiation. Chemotherapy-induced hair loss makes many cancer patients feel self-conscious about their appearance and puts a lot of pressure on their mental health. Currently, the FDA has approved the use of scalp cooling therapy, which helps reduce hair loss for cancer patients.
1. Causes of chemotherapy-induced hair loss in cancer patients
Excessive hair loss is one of the common side effects in cancer patients after treatment with therapies such as radiation and chemotherapy. These cancer treatments can significantly damage the cells in the hair follicles, leading to hair loss. Specifically:
Chemotherapy-induced hair loss: Chemotherapy often targets rapidly dividing cells in the body, including cancer cells and healthy cells. In fact, in the human body, hair follicles are considered to be the cells with the fastest division, so when applying chemotherapy, it can cause damage to these cells, causing them to die. inhibits growth and destruction, causing hair loss in cancer patients. Chemotherapy-induced hair loss usually occurs about 2 weeks after cancer treatment and can last from 1 to 2 months. In most cases of chemotherapy-induced hair loss, some or all of the hair is lost. Not only that, eyebrows, eyelashes and other areas of body hair are also at risk of loss, depending on the chemotherapy drugs used by the patient. Hair loss caused by radiation therapy: Radiation therapy is one of the effective cancer treatments, capable of attacking and killing growing cancer cells in the body. Unlike chemotherapy, radiation only affects the treated area. Hair loss caused by radiation therapy can often grow back once the treatment is over. The extent of hair loss in cancer patients will depend on the dose as well as the different types of radiation therapy. With high radiation therapy can lead to permanent hair loss for the patient. Other causes of cancer-related hair loss: For people with breast cancer who are treated with Tamoxifen, side effects such as thinning or hair loss may be experienced. Besides cancer treatments, patients can also experience hair loss due to iron and vitamin deficiency, thyroid problems, etc. Therefore, nutrition for cancer patients also plays a role. It is very important to help reduce hair loss.

Hiện tượng rụng tóc do hoá trị thường xảy ra sau khoảng 2 tuần điều trị ung thư.
2. Scalp cooling therapy for cancer patients
In fact, there isn't any treatment that can guarantee you won't lose your hair during and after cancer healing. However, some studies have found a way to help some patients reduce hair loss caused by cancer. Among them, we must mention the scalp cooling therapy, which helps reduce the psychological burden for patients during chemotherapy for cancer treatment.
The use of scalp cooling therapy to reduce hair loss caused by chemotherapy can help compensate for the patient's feelings of loss and low self-esteem. For many people with cancer, hair loss can cause the following mental problems:
Mental illness and illness. Not feeling comfortable in a social environment, leading to low self-esteem and isolation. Loss of self-esteem, feeling that you are no longer yourself. Hair loss is considered a major cause of emotional stress for cancer patients. Many studies have shown that about 47% of people with breast cancer feel hair loss is the biggest cause of damage to them, of which about 8% of patients refuse to undergo chemotherapy to avoid hair loss.
In order to improve and reduce hair loss due to cancer or hair loss caused by chemotherapy, patients can be applied scalp cooling therapy, which helps chemotherapy drugs not affect too much hair follicles. .
For scalp cooling, during chemotherapy, the patient will be wearing a special cap that is connected to a coolant circulation machine. The cap cools the scalp to 63 - 67 ̊ F. The patient will wear this special cap for at least 30 minutes before, during, and about 60 – 90 minutes after the treatment.
Scalp cooling caps can cause blood vessels in the head to constrict from the cold, which helps prevent chemotherapy drugs from reaching and affecting the hair follicles. Scalp cooling has been recognized for its effectiveness in reducing chemotherapy-induced hair loss in cancer patients. In addition, it is also approved by the FDA for use in chemotherapy for breast cancer and many other cancers. Thanks to scalp cooling therapy, about 50-60% of cancer patients can significantly reduce their risk of hair loss.
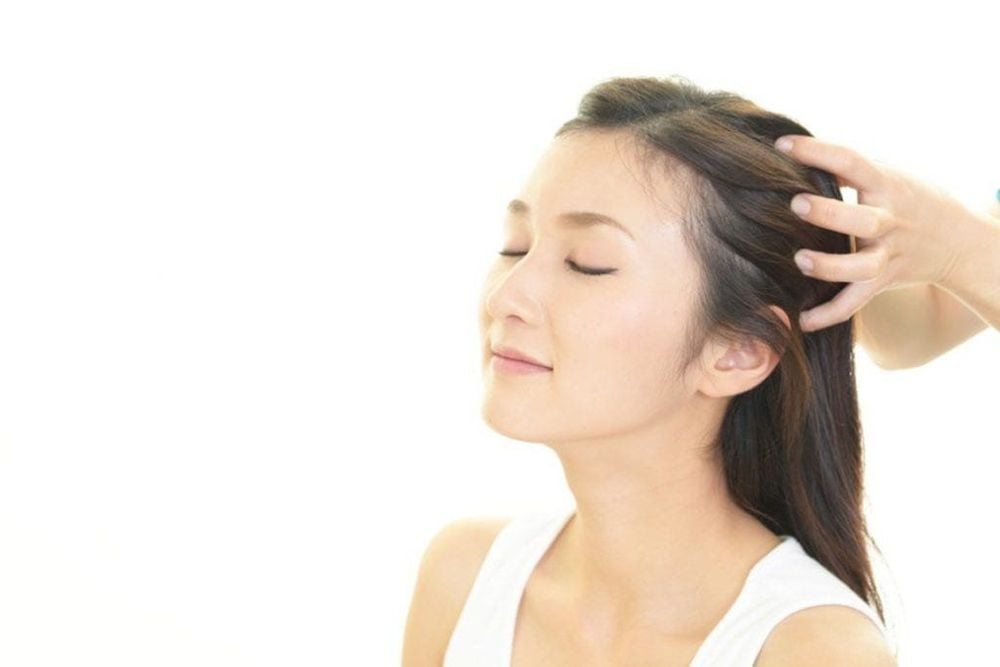

Liệu pháp làm mát da đầu giúp khắc phục tình trạng rụng tóc do hóa trị.
3. Can hair grow back after chemotherapy?
Hair loss caused by chemotherapy can be reduced and hair will grow back when the drug is no longer attacking the hair follicles. In general, the rate at which hair grows back depends on many factors, including the patient's health, age, and response to cancer treatment.
The case of permanent hair not growing back after chemotherapy is very rare, this only happens when the hair follicles are severely damaged by the chemical. Some breast cancer drugs, such as docetaxel, can cause permanent hair loss when taken in high doses.
Most of the time, cancer patients' hair after chemotherapy will grow back at the following time points:
From 2 to 3 weeks: Thin and light hairs will start to grow back. 1-2 months: Stronger hairs begin to grow. From 2 to 3 months: The hairs can grow up to 2.5 cm long. 6 months or more: The hairs can grow about 5-7 cm long and cover bald patches on the scalp. From 12 months or more: The hair can grow from 10-15 cm, allowing the patient to comb and style as usual. In general, hair loss-prone areas tend to grow back the fastest. This area includes the hair on the top of the head, has a faster growth rate than hair in other areas, in which eyelashes and eyebrows will take longer to recover.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.
References: Mayoclinic.org