This is an automatically translated article.
The article was professionally consulted by Doctor General Internal Medicine Doctor - Department of Medical Examination & Internal Medicine - Vinmec Hai Phong International General Hospital.
Myocardial infarction is the leading cause of death in the world today. The diagnosis of myocardial infarction plays an important role in guiding treatment and reducing mortality from the disease. In particular, the diagnosis based on the electrocardiographic changes in the electrocardiogram is one of the main criteria in determining myocardial infarction.
1. What is an electrocardiogram?
An electrocardiogram (ECG) is a graph that records the changes in electrical currents inside the heart. The heart contracts to a rhythm and is controlled by a conduction system in the heart muscle.
The electrical currents of the heart are very small, only about a thousandth of a volt, but can be detected from electrodes placed on the patient's arms, legs and chest transmitted to the recorder.
An electrocardiogram will amplify the signal and record it on an electrocardiogram. Electrocardiogram is often used in medicine to detect cardiovascular diseases such as arrhythmia, heart failure, myocardial infarction...
2. How to diagnose myocardial infarction by electrocardiogram?
When the heart muscle is ischemic and lacks oxygen, leading to myocardial damage or necrosis, the ability of the heart muscle to conduct electricity will change. This change can be recorded on the electrocardiogram, which is one of the factors that make up the value of this laboratory method.
To diagnose myocardial infarction, it is necessary to observe a rhythm sequence and 12 leads on the electrocardiogram. Diagnosis of myocardial infarction when the electrocardiogram shows: ST segment elevation ≥ 1mm in ≥ 2 contiguous leads. Usually accompanied by mirror ST segment depression in the contralateral leads. At V2, V3 for accurate diagnosis, 2mm ST elevation in men and 1.5mm in women is required. Thus, the characteristic changes in myocardial infarction shown by electrocardiogram include:
ST segment elevation in the damaged myocardium ST segment depression in the opposite leads (mirror) Occurrence of waves Pathological Q R wave is reduced in amplitude T wave is reversed. Diagnostic criteria for acute myocardial infarction on electrocardiogram:
Pathological Q wave: Q wave duration > 0.04 seconds Q wave amplitude > 25% R wave in co-lead ST segment elevation in leads look at infarct and “mirror” depression in opposite leads T waves are deep and symmetrical in leads relative to infarcted myocardium
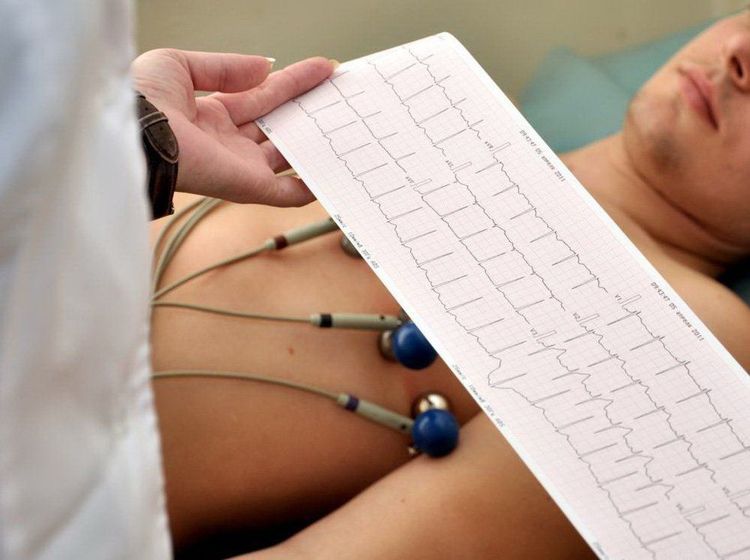
3. Determine the stage of myocardial infarction through electrocardiogram
When coronary insufficiency occurs suddenly, possibly due to a stress (emotional, physical exertion, cold, etc.) acting on the body, a heart attack can occur. Normally, the myocardial infarction area will have a necrotic area in the middle, then a damaged area around it and an ischemic area surrounding the damaged area. On the electrocardiogram image of myocardial infarction, all three types of signs will be obtained, but not at the same time, but often changing through three main stages, the stages of myocardial infarction:
Stage 1 (acute) ):
Occurs in the first 1, 2 days.
Curved wave: may have appeared pathological Q wave, QT segment lengthened.
Stage 2 (subacute):
From a few days to a few weeks is the most common: lower ST segment elevation, deep, sharp, symmetrical T waves (called Pardee coronal waves). Simultaneously, the pathological Q wave is clearly visible and the QT interval is elongated.
Stage 3 (chronic)
From months to years: ST segment is electrosynthetic, T waves can be positive or negative, and pathological Q waves are usually permanent.
4. Specific assessment of myocardial infarction status through electrocardiogram
The above-mentioned ECG signs are not present in all leads equally, but only in the lead where the electrode is placed (direct lead) over the infarcted myocardium. That is why they call these signs direct images.
In contrast, leads with electrodes placed in the contraradial region of the infarcted area will obtain signs of the opposite of the above findings, also known as "mirror images" or "indirect images". ".
Infarction can occur in many different areas of narrowing of the left ventricle (right ventricle rarely occurs). Depending on the affected area, the ECG can be classified into several types of infarction with the following stage 2 (subacute) signs:
Preseptal infarction – infarction in the left ventricular anterior wall and anterior septal part Interventricular:
Live image: QS wave, ST elevation, negative T wave in V2, V3, V4. Sometimes T waves are low or negative in V5, V6, aVL, and D1 (T1>T3) because the ischemic area spreads to the lateral (left) wall of the left ventricle. Anterior-lateral infarction: infarction in the lateral and anterior part of the left ventricle:

Live images: deep and wide Q waves, ST segment elevation, deep negative T waves in V5, V6, D1, aVL. Indirect imaging: ST segment depression, very high positive T waves in D3, sometimes in aVF. Posterior - inferior infarction: infarction in the posterior and inferior walls of the left ventricle:
Direct image: deep, wide Q wave, ST segment elevation, deep negative T wave in D3, aVF, sometimes even in D2. Indirect image: high positive T wave, can be pointed, symmetrical, ST segment can be depressed in V1, V2, V3, V4. Subendocardial infarction (left ventricle):
Mainly anterior - lateral wall: ST segment depression, sometimes T wave distortion in V5, V6, D1, aVL. Sometimes inferior posterior wall: ST depression at D3, D2, aVF. Myocardial infarction with bundle branch block:
In many cases, coronary insufficiency causing myocardial infarction also makes a branch of the bundle of His poorly nourished, producing bundle branch block, signs of bundle branch block associated with the basic signs of myocardial infarction.
Left bundle branch block + anterior - lateral infarction: Left bundle branch block. Right bundle branch block + posterior - inferior infarction: deep Q wave in D3, D2 + rSR' pattern in V1, V2. Right bundle branch block + anterior septal infarction: In V1, V2, V3 (V4), there is a QR pattern with late internal branch. Electrocardiogram is an effective technique to help diagnose myocardial infarction. This technique is being successfully applied by Vinmec International General Hospital in the examination and diagnosis of many types of cardiovascular diseases in general and myocardial infarction in particular.
SEE MORE
The risk of heart attack in young people is increasing What should heart attack patients eat? Warning risk of stroke, heart attack in cold weather
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.