This is an automatically translated article.
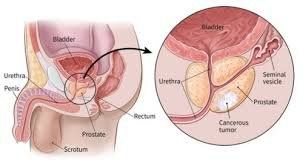
Prostate cancer is one of the most common cancers and the second leading cause of cancer death in men in the US. Scientists have discovered germline HOXB13 gene mutations in a group of prostate cancer patients that have further elucidated the etiology of prostate tumors and developed new treatments to combat them. tumor.
1. What is the function of the HOXB13 gene?
Highly evolutionary conserved HOX proteins, homeodomain-containing transcription factors are best known for their roles in body axis shaping and tissue differentiation of the developing embryo. Moreover, HOX proteins not only play a role in organogenesis and development, but they also contribute to the control of a number of other processes in cell maturation and proliferation, cell cycle, apoptosis, and differentiation. cells and cell genetics.
In humans, there are 39 HOX proteins divided into 4 gene clusters: A, B, C, D located on chromosomes 7p15, 17q21.2, 12q13, 2q31, respectively. Each cluster of genes describing 1-13 organized and expressed as 3' and 5' follows a spatial and temporal congruent pattern with development, although not all patterns described are present in each gene cluster.
The 3' HOX genes are most expressed in the anterior stem regions, forming early in development. Whereas the 5' HOX genes encode many posterior stem regions that form later in development.
Tissue specificity is determined by partial nested expression of several HOX genes in a given body region. For example, in human prostate tissue where 36 out of 39 HOX genes were found to be expressed at levels detectable by qRT-PCR, genes such as HOXA13 and HOXB13 were most expressed and yielded the highest concentrations. The most meanful.
The HOXB13 gene provides instructions for producing a protein that attaches to specific regions of DNA and regulates the activity of other genes. On the basis of this role, the protein generated from the HOXB13 gene is called a transcription factor. The HOXB13 protein is part of a large group of transcription factors known as the homeobox protein family. The HOXB13 protein is thought to play a role in the development and maintenance of the skin. It also acts as a tumor suppressor, which means it keeps cells from growing and dividing too quickly or in an uncontrolled way.
The HOXB13 protein has a characteristic homeobox region called the homeodomain, which binds to DNA, and two other regions known as the MEIS interaction region. The MEIS interaction domains are thought to help regulate HOXB13 protein activity by controlling the binding of the homeodomain to DNA.
Gen HOXB13 cung cấp hướng dẫn cho sản xuất một loại protein mà tùy viên để khu vực cụ thể của DNA và quy định về hoạt động của các gen khác
2. Role and relevance of HOXB13 gene to prostate cancer
Researchers have discovered at least two mutations in the HOXB13 gene that are associated with an increased risk of prostate cancer. The disease may also be more severe in men affected by mutations in the HOXB13 gene.
These mutations are present in every cell of the body and can be passed on from generation to generation. As a result, they are linked to cancers in families. However, not everyone who inherits a mutation in the HOXB13 gene will develop prostate cancer.
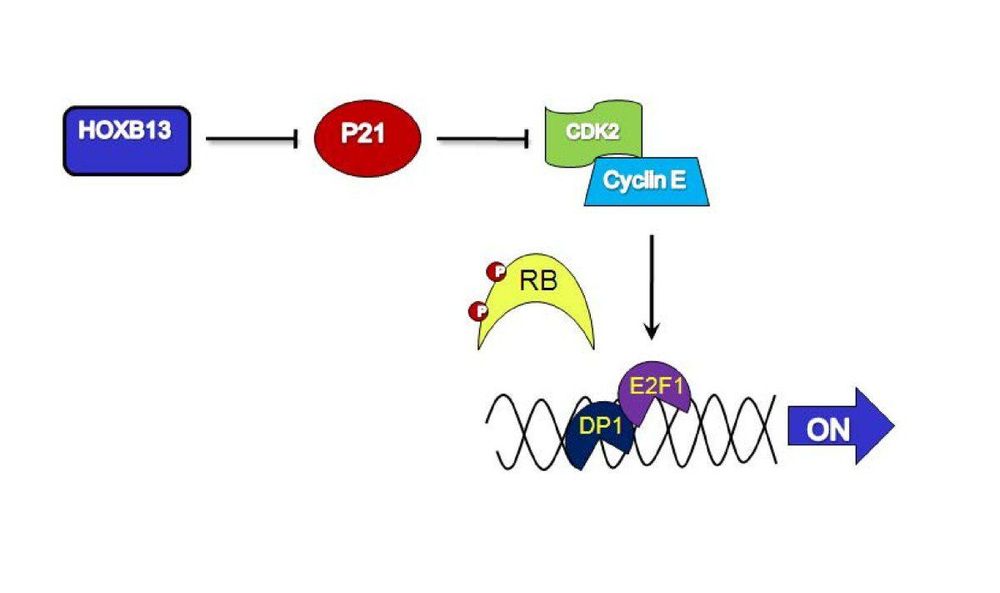
In prostate cancer, HOXB13 negatively regulates β-catenin/TCF4-mediated metabolism and subsequently inhibits cell growth.
The HOXB13 gene mutations associated with prostate cancer alter the MEIS-interacting region of the HOXB13 protein. The researchers suggest that these changes may reduce the ability of these regions to regulate the interactions of the HOXB13 protein with DNA. As a result, the protein's tumor suppressor function is impaired leading to uncontrolled cell proliferation, which in turn can lead to prostate cancer.
2.1. Germline HOXB13-G84E Mutations and Prostate Cancer The identification of germline HOXB13 (G84E) mutations in a group of prostate cancer patients with a family history brought the HOXB13 gene into the spotlight of research. prostate cancer cure. This discovery highlights a novel transcriptional regulatory pathway that plays an important role in prostate development and tumorigenesis.
People with the HOXB13-G84E gene mutation have a significantly higher risk of developing prostate cancer than men without this mutation. The G84E mutation occurs in the MEIS interaction region, underscoring the importance of the MEIS-HOXB13 protein interaction in prostate cancer.
Another study found a significantly higher rate of G84S mutations in people with a family history of hereditary prostate cancer. The presence of the G84E mutation clearly influences the onset of prostate cancer, which contributes to cancer progression and metastasis.

Những người có đột biệt gen HOXB13-G84E có nguy cơ phát triển ung thư tuyến liệt cao hơn
2.2. Other germline HOXB13 mutations associated with prostate cancer risk Since the discovery of the G84E mutation, researchers have focused more on identifying other novel germline mutations of the HOXB13 gene. is associated with an increased risk of prostate cancer. New mutations of the HOXB13 gene that increase the risk of prostate cancer have begun to be identified.
The researchers identified a novel G135E mutation that was associated with an increased risk of prostate cancer in Chinese men and did not identify the presence of the G84E mutation in these men.
Researchers also identified A128D and F240L mutations in Portuguese men that are associated with prostate cancer risk.
Thus, mutations in the HOXB13 gene are associated with an increased risk of prostate cancer and the disease may also be more severe in men with the HOXB13 mutation. However, not everyone who inherits the HOXB13 gene mutation will develop prostate cancer. Genetic factors, other environmental and lifestyle factors also contribute to a person's risk of prostate cancer.
According to Globocan, about 350,000 people die each year in the world from prostate cancer and about 1.1 million new cases. Prostate cancer ranks fifth in mortality and second in incidence.
In Vietnam, in 2018 there were 1,873 deaths from prostate cancer, the number of newly discovered cases was 3,959. The mortality rate is still quite high due to the late detection and treatment of the disease.
To reduce the risk of dying from prostate cancer, it is important to have regular physical exams. In addition, it is necessary to deploy screening programs in high-risk subjects, people themselves also need to be more conscious in taking the initiative to go to health facilities for periodic screening.

Để giảm nguy cơ tử vong do ung thư tiền liệt tuyến, cần thường xuyên thực hiện khám sức khỏe định kỳ
Early cancer screening is considered a perfect measure in the timely detection and treatment of all types of cancer. Reduce the cost of treatment and especially reduce the mortality rate in patients. Vinmec International General Hospital always deploys and introduces to customers a HIGH-TECH CANCER CHECKLIST PACKAGE to help with gene testing, imaging, and biomarkers for early tumor detection. Vinmec International General Hospital has many early cancer screening packages. Only one gene test can assess the risk of 16 common cancers in both men and women (lung cancer, colon cancer). rectal cancer , breast cancer , pancreatic cancer , cervical cancer , stomach cancer , prostate cancer ,....)
Early detection of early signs of cancer through diagnosis imaging, endoscopy and ultrasound. The operation is simple, careful and accurate. A team of well-trained specialists, especially in oncology, are capable of handling cancer cases. With facilities, advanced and modern medical equipment and a team of doctors with deep expertise and experience. At Vinmec, the examination process becomes fast with accurate results, saving costs and time for patients.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.
References: ghr.nlm.nih.gov, genecards.org, sciencedirect.com
MORE:
Rapid biopsy for prostate cancer Robotic surgery to blow away prostate cancer for doctors Japan Is prostate cancer curable?