This is an automatically translated article.
Prostate cancer or prostate cancer is one of the most common cancers in men. This is a dangerous disease that causes serious problems. However, the disease can be completely cured if detected early and treated promptly. Is prostate cancer hereditary?
1. What is prostate cancer?
The prostate gland is an organ in men and the reproductive system. The prostate gland is located around the urethra at the exit from the bladder in men. This organ plays a very important role because it helps to produce the seminal fluid that nourishes and transports sperm. Prostate cancer, also known as prostate cancer, is one of the most common types of cancer in men, occurring in the prostate gland. Prostate cancer usually progresses slowly and the disease is still confined to the prostate gland in its early stages. If detected and treated in time, the disease does not cause serious harm. Not all cancers can spread quickly, some melanomas can grow slowly, and some cancers require minimal treatment. To prevent and slow the spread of the disease, and at the same time reduce the mortality rate caused by the disease, cancer needs to be identified early and treated promptly. The chances of a cure for prostate cancer are higher if the disease is detected early while still confined to the prostate gland.
Currently, experts still cannot determine the exact cause of prostate cancer, but according to some studies, the patient's diet and genes have an impact on prostate cancer. The risk of disease is higher in people who eat a lot of fat.

Người ăn nhiều chất béo sẽ có nguy cơ mắc bệnh cao hơn so với người không ăn nhiều
2. Is prostate cancer hereditary?
Prostate cancer is a genetic disease, this factor accounts for about 5 - 10% of all prostate cancers. The development of prostate cancer is caused by a combination of common genes and environmental or lifestyle factors. Hereditary prostate cancer is rare, but prostate cancer can be passed on from close relatives and accounts for about 5% of all cases. Hereditary prostate cancer occurs when there is a change in a gene and is passed down in a family from generation to generation.
Family history is the biggest risk factor for prostate cancer.
You have a high risk of prostate cancer if there is a family history of the following:
Many first-degree relatives with prostate cancer Prostate cancer occurs in 3 generations in the same a family Many close relatives, such as father, brother, son, grandfather, uncle or nephew in the same family were diagnosed with prostate cancer before age 55. If your father, brother or son has prostate cancer, your risk is 2 to 3 times higher than the average risk. The risk is proportional to the number of relatives diagnosed with prostate cancer.
3. Other factors increase the risk of prostate cancer

Tuổi tác cũng là một yếu tố làm tăng nguy cơ ung thư tuyến tiền liệt
In addition to genetic factors, the following factors can also increase the risk of developing prostate cancer in men, including:
3.1. Age The risk of prostate cancer increases with age, especially after age 50. More than 80% of prostate cancer cases are diagnosed in people 65 years of age and older. Older men diagnosed with prostate cancer may face more challenges, especially in terms of cancer treatment.
3.2. Skin color Black men in the United States and other African-American men are diagnosed with prostate cancer more often than men of other races. Black men have a higher risk of dying from prostate cancer than white men.
3.3. Geographic location Prostate cancer occurs most frequently in North America and Northern Europe. Currently, prostate cancer is on the rise in Asian men living in urbanized environments, such as Hong Kong, Singapore, and North American and European cities, especially in those with a low-income lifestyle. living less physically active and eating less healthy.
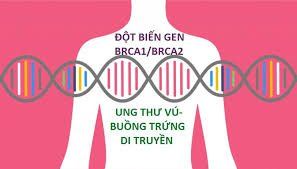
Các đột biến ở gen BRCA1 và BRCA2 có tỷ lệ nhỏ gây ra ung thư tuyến tiền liệt gia đình
3.4. Hereditary breast and ovarian cancer syndrome (HBOC) HBOC is associated with DNA repair mutations for the BRCA1 and/or BRCA2 genes. BRCA stands for "BReast CANcer". HBOC is often associated with an increased risk of breast cancer and ovarian cancer in women. However, men with HBOC also have an increased risk of developing breast cancer and a more severe form of prostate cancer. Mutations in the BRCA1 and BRCA2 genes are thought to cause only a small percentage of familial prostate cancers. Men with a BRCA1 or BRCA2 mutation should consider prostate cancer screening at an earlier age. Genetic testing may only be appropriate for families with a history of prostate cancer, who may also have HBOC. If you are concerned about this based on your own family history, you should consult a genetics specialist or doctor for more information.
3.5. Gene changes Other genes that may increase the risk of developing prostate cancer include HPC1, HPC2, HPCX, CAPB, ATM, FANCA, HOXB13, and mismatch repair genes. However, researchers have not yet determined what causes prostate cancer directly or specifically for the disease. Research to identify genes associated with an increased risk of prostate cancer is ongoing, and experts are constantly learning more about how specific genetic changes can affect the development of prostate cancer. prostate cancer. Currently, there is no genetic test to determine the likelihood of prostate cancer in men.

Thay đổi gen cũng là một yếu tố làm tăng nguy cơ phát triển ung thư tuyến tiền liệt
3.6. Agent Orange Exposure The United States Department of Veterans Affairs (VA) lists prostate cancer as a disease linked to exposure to Agent Orange, a chemical used during the Vietnam War. . If you are a veteran who may have been exposed to Agent Orange, you should consult your doctor.
3.7. Eating habits There are no studies to prove that diet and nutrition can directly cause or prevent the growth of prostate cancer. However, many studies looking at the link between certain eating behaviors and cancer show a strong link. For example, obesity is linked to many cancers, including prostate cancer, and to avoid the risk of obesity, you need to eat a healthy, sensible diet.
4. Prostate Cancer Prevention
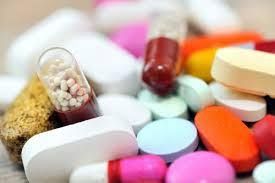
Sử dụng thuốc thuộc nhóm chất ức chế 5-alpha-reductase có thể giảm khả năng ung thư tuyến tiền liệt
Different factors cause different types of cancer. Experts are continuing to look at and determine what factors cause these cancers, including how to prevent the disease. While the disease cannot be completely prevented, you can reduce your risk of prostate cancer through a number of measures, such as:
4.1. Medication use A class of drugs called 5-alpha-reductase inhibitors (5-ARIs), including dutasteride (Avodart) and Finasteride (Proscar), are commonly used to treat BPH. They may also reduce the risk of developing prostate cancer in men. Some previous clinical trials have suggested that 5-ARIs are associated with prostate cancer, but newer studies suggest this is not true. According to the results of a long-term follow-up study published in 2013, 78% of men taking Finasteride or a placebo were still alive 15 years later. These results suggest that taking Finasteride does not reduce the risk of death in men with prostate cancer. The U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has not approved these drugs to be used to prevent prostate cancer. However, 5-ARI is FDA-approved for the treatment of lower urinary tract symptoms associated with BPH. The decision to use 5-ARI in each case is different. Anyone considering taking this medication should discuss with their doctor the possible benefits and side effects.

Ăn nhiều rau có thể làm giảm nguy cơ ung thư tuyến tiền liệt
4.2. Dietary changes There is not enough information available to make clear recommendations about the exact role of eating behavior in prostate cancer. Dietary changes may need to be made early to reduce the risk of developing prostate cancer later in life. Specifically:
Regularly eating foods high in fat, especially animal fat, can increase the risk of prostate cancer. However, it is not clear whether a diet high in animal fats increases the risk of prostate cancer. A diet rich in vegetables, fruits, and legumes, such as beans and peas, may reduce the risk of prostate cancer. Experts have yet to pinpoint which nutrient is directly responsible. Although lycopene, a nutrient found in tomatoes and other vegetables, has been shown to be associated with a reduced risk of prostate cancer, studies have not shown a relationship between lycopene and prevent cancer. There are currently no specific vitamins and minerals or supplements that have been shown in clinical trials to prevent prostate cancer. You should consult your doctor before taking any supplements to prevent prostate cancer. Specific changes to eating behavior can prevent or slow the growth of prostate cancer. Such changes need to be made early to have maximum effect later on. Currently, it seems that prostate cancer has not received proper attention in Vietnam. In 2018, as recorded by Globocan, Vietnam had 1,873 deaths from prostate cancer, while the number of newly discovered cases was 3,959. The cause is said to be that prostate cancer screening in Vietnam has not been paid enough attention, so new cases are often detected at a late stage, the higher the mortality rate.
Doctors recommend older men with risk factors for prostate cancer (family history of prostate cancer, prostate enlargement, history of radiation exposure) , urinary disorders...) need to go for screening (PSA test, prostate exam) for early detection if prostate cancer is present for the purpose of early detection and timely treatment.
For cases that have been diagnosed with prostate cancer, surgery is the best treatment if at an early stage, radiation therapy is applied in some cases. When the patient is no longer indicated for surgery and the cases fail after surgery or radiotherapy, endocrine therapy is applied.
Vinmec International Hospital Radiation Center has routinely performed radiotherapy for prostate cancer on the most advanced Clinac iX accelerator system (Varian Company, USA) today. Many patients achieve satisfactory results with few side effects, often making a full recovery after treatment. The clinics are fully equipped with high-tech and standard equipment, ensuring that patients are monitored, examined, and cared for comprehensively before, during and after radiation therapy.
Besides, in order to improve service quality as well as bring convenience to customers, Vinmec now also deploys Prostate Cancer Intensive Care Package. Customers wishing to consult on the diagnosis and treatment of prostate cancer can come to Vinmec International General Hospital
With equipped facilities, advanced and modern medical equipment and a team of Doctor with deep expertise and extensive experience. At Vinmec, the examination process becomes fast with accurate results, saving costs and time for patients.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.