This is an automatically translated article.
Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) is a biomolecular technique that uses the specificity of antibodies, as well as the sensitivity of enzyme assays, to detect and quantify molecules. such as hormones, peptides, antibodies and proteins.1. Types and readings of ELISA results
ELISA is used as a diagnostic tool in medicine and plant pathology, for quality control testing in many different disciplines.There are many types of ELISA tests for many types of infections such as direct, indirect, sandwich, competitive, but all follow the general principle of antigen detection by immunological specific antibodies. The special feature here is that the antibodies are bound to an enzyme (enyme-linked), and after the antigen-antibody reaction occurs, a specific substrate (substrate) is added to the enzyme to be broken down. degrade the substrate to products, proportional to the amount of antigen to be measured. Measuring signals, most commonly the color change of a chemical, will calculate the amount of antigen present in the test specimen.
2. Applications of ELISA test in Medicine
2.1 From cancer screening to drug testing and pregnancy Identifying early cancer markers is one of the ongoing challenges developed and researched by scientists due to the fact that early detection of cancer has the potential to be curable. , prolonging survival time and improving the quality of life for cancer patients. ELISA-based techniques are available and widely used in clinical practice to test patients with early-stage cancers including ovarian and breast cancer.In addition, ELISA is used to detect concentrations of illicit substances such as cannabinoids, amphetamines, opiates, cocaine, benzodiazepines and methadone, which can be determined by ELISA in urine samples. The method can also be used to monitor drug levels in patients receiving treatment for, for example, anti-infective antibodies in rheumatoid arthritis and inflammatory bowel disease patients.
ELISA is also commonly used to test for human chorionic gonadotrophin (hCG) hormone in urine to detect women who are pregnant or some other disease.
The ELISA test can be used to diagnose specific conditions such as:
HIV Lyme disease Pernicious anemia Rocky Mountain spotted fever Rotavirus diarrhea Carcinoma squamous cell carcinoma Syphilis Varicella-zoster virus toxoplasmosis, which causes chickenpox and shingles Zika virus ELISA is often used as a screening tool before more specialized tests are ordered. Your doctor may order this test if you have signs or symptoms of any of the above conditions or use it to rule out a condition your doctor suspects.
Xét nghiệm ELISA để chẩn đoán bệnh cụ thể như HIV
2.3 Food allergy ELISA is widely used in the food industry to detect the presence of allergens to warn users about possible allergens as required by law. France. This application greatly benefits from the sensitivity of ELISA and can detect levels of potential food allergy contaminants at concentrations as low as parts per million (ppm). In addition, this technique also has the advantage of being able to test for oils and other substances such as egg whites or milk that cannot be detected by methods such as PCR.
2.4 Virus detection by viruses Advantages of using ELISA to detect viruses are widely used in developing countries, where infection rates are often very high and can reach vulnerable populations It is best to check the spot and give the results immediately, thereby allowing the doctor to take timely and accurate treatment measures.
3. How is the ELISA test performed?
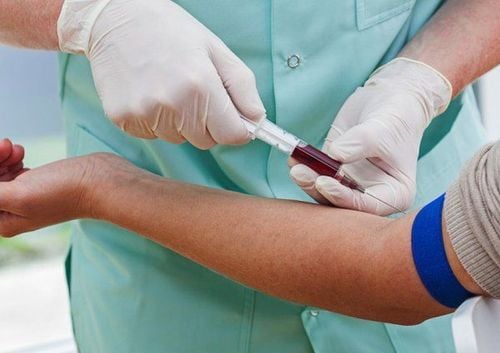
Xét nghiệm ELISA rất đơn giản bằng cách lấy mẫu máu của người bệnh tại nhà hoặc tại bệnh viện
The blood sample will be sent to the laboratory for analysis. In the lab, a lab technician will add a sample to a petri dish containing the suspected antigen associated with the disease the doctor is suspecting to have. The technician inserts an enzyme into a petri dish and observes how the patient's blood and the enzyme's antigen react with each other. If the patient's blood contains antibodies against the antigen, the two will bind to each other. Therefore, if the patient is positive for the suspected disease, the test paper will change color.
4. What do patients need to prepare before the test?
The patient does not need to prepare for this test. The blood draw was quick and only slightly uncomfortable. The patient should notify the medical staff if the patient is afraid of needles or becomes dizzy or fainted when seeing blood or needles.5. What is the risk to the patient?
Người bệnh cần nói cho bác sĩ trước khi xét nghiệm nếu bản thân có vấn đề trong việc lấy máu trong quá khứ
Patients should tell their doctor before the test if they have had problems drawing blood in the past, bruise easily, or have a bleeding disorder such as hemophilia .
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.
References: News-medical.net and Healthline.com