This is an automatically translated article.
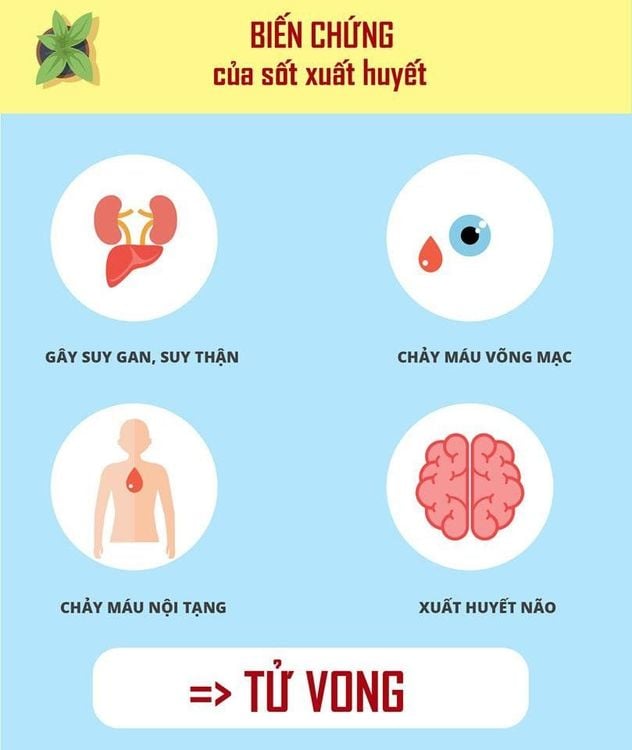
The article was written by Specialist Doctor II Pham Thi Khuong - Infectious Doctor, Pediatrics Center - Vinmec Times City International General HospitalIn our country, circulating dengue fever is very common, occurs all year round, but often breaks out into a large epidemic in the rainy season, especially from July to October every year. The risk of dengue fever (DHF) complications in children: Causes liver failure, kidney failure, retinal hemorrhage, brain hemorrhage and leads to death as shown below.
1. Which children are at risk of complications from dengue fever?
These are infants, infants and children who are undernourished as well as over-nourished, or have comorbidities such as diabetes and hypertension ... or have secondary infections. These are risk factors for severe dengue in children.
Children with dengue fever may progress more severely than adults, and are at greater risk of complications. Dengue fever in children often has a high fever that is difficult to lower, especially in the early days, so it is easy to lose water, dry skin, dry lips, fatigue and poor appetite.
Trẻ suy dinh dưỡng thuộc nhóm đối tượng nguy cơ cao bị biến chứng khi mắc sốt xuất huyết
2. How to treat complicated fever in children?
Children with complicated dengue fever must be treated in the hospital as soon as possible, requiring quick and accurate management because the diagnosis is difficult, the acute and complicated course in children is very easy to die.Disease manifests as a viral infection such as: At first, children often have high fever continuously for 3-4 days, cough, skin congestion, body aches, eye socket pain, vomiting and possibly diarrhea. Dengue fever is difficult to reduce with antipyretic (paracetamol) in the first 3 days and after 3-5 days when the fever starts to decrease, it will appear, manifested as weakness, punctate skin hemorrhage, nosebleed. (nosebleed), bleeding gums, vomiting blood, passing black stools... Severe illness from day 3 to day 5, 6 of the illness.
Therefore, when detecting a child with suspected signs of dengue fever, it is necessary to immediately go to a medical facility for appropriate examination, diagnosis and treatment; Do not allow new complications to occur because any delay can lead to the risk of death when serious complications occur.
3. Guidelines for follow-up and prevention?
It is worth noting that so far there is no specific treatment to destroy the pathogen (Dengue virus) and no specific vaccine. Therefore, dengue fever is now considered a dangerous disease because it is both acute and highly contagious. Therefore, when a child has a fever and is suspected of having dengue fever, it is necessary to see a specialist immediately and treat as directed. If you can go home for treatment, follow-up visits every day according to your doctor's appointment. Even morning and afternoon during peak days of illness. If there is one of the following signs, it is necessary to take the child to the hospital immediately:
Crying, irritability, irritability or lethargy Abdominal pain

Cha mẹ cần chú ý khi trẻ xuất hiện triệu chứng đau bụng
Nosebleeds, bloody teeth or vomiting blood, black stools Cold hands and feet, lying in one place, not playing, refusing to breastfeed, stop eating Especially young children living in (local) areas with dengue fever need be very alert to unpredictable complications of dengue fever. To prevent dengue complications in children, it is advisable to treat dengue fever at kindergartens only after being examined and approved by a doctor.
Pay attention to re-examination by appointment. Parents are also particularly concerned about which fever-reducing drugs are allowed in this disease. When the child has a fever ≥ 38.5oC, give the child an antipyretic drug Paracetamol at a dose of 10-15mg/kg body weight, repeat the dose every 4-6 hours if the child has a fever again. Combine with warm compresses on both sides of the groin, armpits, and sides of the neck where there are large vessels to avoid complications of high fever causing convulsions. Use soft, easy-to-digest foods Do not take aspirin: In dengue fever, bleeding occurs. Aspirin prevents platelet aggregation, anticoagulants, so the bleeding caused by dengue fever cannot be stopped, increasing the acidity of the stomach (especially gastrointestinal bleeding). Particularly for children, special attention should be paid to this ban because: aspirin is a predisposing factor for Reye's syndrome (brain edema and fatty liver failure with a mortality rate of about 30-50%. permanent brain damage). Do not use antibiotics unless indicated. Do not self-administer at home. To prevent dengue fever, it is necessary to clean the house, do not let the water stand still so that there is no place for mosquitoes to lay eggs. To avoid mosquito bites, you should sleep under a mosquito net even during the day. Spray mosquito killer where you live.

Khi phát hiện trẻ nhỏ mắc sốt xuất huyết, cha mẹ cần đưa trẻ đến gặp bác sĩ ngay
Customers can directly go to Vinmec Health system nationwide to visit or contact the hotline here for support.
Articles refer to the source: Ministry of Health