This is an automatically translated article.
Stroke, also known as cerebrovascular accident, is the leading cause of disability and death worldwide. This is a form of brain damage that occurs when the blood supply to the brain is interrupted or significantly reduced, causing brain cells to starve of oxygen and nutrients and begin to die within minutes.
There are many risk factors that make a person more likely to have a stroke. These risks include controllable factors that you can change, and uncontrollable factors, which are things you cannot change. Fortunately, more than half of all strokes can be prevented with medical care and lifestyle changes.
1. Controllable stroke risk factors
High blood pressure (also called high blood pressure): A person's risk of stroke begins to increase when blood pressure remains above 115/75 mmHg. High blood pressure is the leading cause of stroke, it damages artery walls and can increase blood clotting activity, leading to the formation of blood clots that cause ischemic stroke. Controlling blood pressure significantly reduces the risk of stroke, as high blood pressure can increase the risk of stroke two to six times. Controlling blood pressure can only be with a healthy lifestyle, eating a scientific diet, and also requiring the use of antihypertensive drugs.
Smoking: Smoking doubles the risk of stroke. Besides damaging the lungs, smoking also damages the walls of blood vessels, increases the hardening of the arteries, makes the heart work harder, and raises blood pressure. Because cigarettes contain about 7,000 toxic chemicals such as carbon monoxide, arsenic, formaldehyde and cyanide. These toxins, after being absorbed into the lungs, will be transported into the blood to change and destroy cells in the body. Statistics show that up to 50% of young stroke patients smoke, the latest studies show a correlation between the number of cigarettes smoked per day and the risk of stroke. Changing the perception of young people's smoking behavior has never been easy. These studies are raising alarm bells for ex-smokers.

Hút thuốc lá là một trong các nguy cơ làm tăng gấp đôi nguy cơ đột quỵ
Not only direct smokers, but also passive smokers (inhaling secondhand smoke) are also adversely affected. Passive smoking also increases a person's risk of stroke. The good news is, for current smokers, if they stop smoking today, within two to five years, their risk of stroke will be the same as that of someone who has never smoked.
High cholesterol: a cholesterol level of 200 mg/dL or less is best for adults. Excess cholesterol can build up on artery walls and lead to blockage of these vessels. About 50-60% of young patients with cerebral infarction have dyslipidemia, there is a slight difference between men and women, in which men are more common than women. Young people with unhealthy eating habits such as eating too much fast food, using processed foods..., are increasingly facing diseases of large and small blood vessels earlier such as pathology. stroke, cardiovascular ...
Overweight and sedentary: studies in the United States show that about 10% of young stroke patients are overweight (body mass index >30). In addition, the waist circumference index, waist circumference / hip ratio, waist circumference / height ratio are also more closely related to stroke risk. The entire circulatory system is overloaded and being overweight opens the way for other risk factors for stroke, such as high blood pressure. A sedentary lifestyle increases the risk of stroke in young people.
Rapid economic growth has led to less healthy diets. Young people increasingly prefer to sit in front of a computer screen or use a mobile phone rather than participating in physical activities and sports. Since then, the risk of stroke in young people tends to increase gradually.
Drinking alcohol: According to studies, drinking alcohol, especially heavy alcohol, is closely related to an increase in cerebral hemorrhage in young patients. A study by the Lancet Medical Journal (UK) on alcohol use in 189 countries and territories in the period 1990 - 2017 shows that Vietnam is the country with the largest increase in alcohol consumption. world, nearly 90% since 2010.
2. Uncontrollable stroke risk factors
You cannot change the following stroke risk factors, but you can reduce their effect on your overall stroke risk by focusing on minimizing controllable factors in above. Risk factors for uncontrolled stroke include:Age: Although young people can also have a stroke now, the risk of stroke doubles every 10 years from age 55. Gender Gender: Men have a slightly higher risk of stroke than women. Race: Statistics show that African-Americans are nearly twice as likely to have a stroke as whites. Family history: If someone in your family has had a stroke, you have a higher risk of having a stroke.

Tiền sử gia đình là một trong các yếu tố không kiểm soát được tình trạng đột quỵ
Diabetes: Circulatory problems associated with diabetes can increase the risk of stroke, even when insulin and blood sugar levels are tightly controlled. Diabetes and hypertension: Diabetes occurs in 30% of young stroke patients. Especially in Southeast Asia, the proportion of young patients with cerebral infarction with diabetes is up to 54.8%. In Vietnam, there is a rapid increase in diabetes among young people, even children. Many cases of diabetes have been reported in children from 9 to 13 years old, young people from 20 to under 30 years old.
Cardiovascular disease: Having a heart attack can increase your risk of stroke. An additional risk factor for stroke is a heart abnormality called atrial fibrillation (AF), which is a specific type of heart rhythm abnormality that affects over one million Americans. Normally, all four chambers of your heart beat in the same rhythm, about 60 to 100 times a minute. In a person with atrial fibrillation, the left atrium may beat faster and uncontrollably up to 400 times a minute. If left untreated, atrial fibrillation can increase your risk of stroke by four to six times. This condition can be corrected with medication or surgery.
Recurrent stroke: A person with a history of stroke has a higher risk of having another stroke. This risk lasts for about five years and then declines over time. The risk is highest within the first few months after a previous stroke. People who have had a stroke may benefit from prescription medications to reduce their stroke risk. Transient ischemic attack (minor stroke): A person who has had a transient ischemic attack (TIA) has an increased risk of having a major stroke within a month, usually within two days. Medications, including aspirin, may be prescribed to help prevent future strokes. Cerebrovascular malformation: This is one of the leading causes of hemorrhagic stroke in young people. The abnormal growth of blood vessels in the brain can form aneurysms with thin blood vessel walls, which can cause a hemorrhagic stroke. Or blood vessels can be dissected, causing narrowing and blockage of blood vessels, leading to stroke and ischemic stroke. Currently, we still do not have any really effective measures to prevent cerebral vascular malformations. However, cerebrovascular abnormalities can be detected early through contrast angiography, or cerebral magnetic resonance angiography.
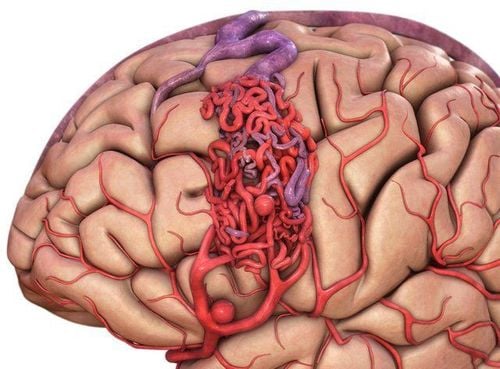
Bệnh lý dị dạng mạch máu não là một trong những nguyên nhân hàng đầu gây nên đột quỵ xuất huyết não
According to statistics of the World Health Organization (WHO), every year about 15 million people have a stroke, of which about 5 million are permanently disabled and 5 million die. Therefore, we need to take measures to prevent brain stroke in time. From the above causes, we see that stroke can be reversed, especially in young people, thanks to healthy living habits such as:
Being active in sports. No smoking. Limit alcohol consumption. Limit processed foods, use fast foods. Periodic health checks help to detect stroke early, so that a treatment plan can achieve optimal results. Currently, Vinmec International General Hospital has general health checkup packages suitable for each age, gender and individual needs of customers with a reasonable price policy, including:
Health checkup package general Standard 2020 General health check-up package VIP 2020 General health check-up package Special 2020 General health check-up package Children 2020 The patient's examination results will be returned to their home. After receiving the results of the general health examination, if any diseases are detected, they need to be examined and treated intensively. You can use services from other specialties right at the Hospital with superior quality of treatment and customer service.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.