This is an automatically translated article.
Radiation therapy is one of the most common treatments for breast cancer. There are two main types of this method, including external radiation therapy and internal radiation therapy. Each treatment has its own advantages and disadvantages.
1. What is radiation therapy for breast cancer?
Radiation therapy is a treatment that uses high-energy rays or particles to kill cancer cells. In addition to other treatments, patients with breast cancer can receive radiation therapy in the following specific cases:
After breast-conserving surgery (BCS) helps prevent the risk of cancer recurrence in the same time breast or in nearby lymph nodes. After a mastectomy, especially if the cancer is larger than 5cm (about 2 inches), is found in many lymph nodes, or in certain areas of the surgical margin such as the skin and muscles. If the cancer has spread to other parts of the body, such as the bones or brain. The main types of radiation therapy that may be used to treat breast cancer are external radiation therapy (EBRT) and radiation therapy (brachytherapy).
Trắc nghiệm: Những lầm tưởng và sự thật về ung thư vú
Ung thư vú có tỷ lệ tử vong cao nhất ở nữ giới khiến họ rất lo sợ bản thân mắc phải căn bệnh này. Tuy nhiên, không ít chị em có những hiểu biết thái quá về ung thư vú. Thử sức cùng bài trắc nghiệm sau sẽ giúp bạn loại bỏ được những nghi ngờ không đúng về căn bệnh này.
Bài dịch từ: webmd.com
2. External radiation therapy (EBRT) for breast cancer
This is the most common type of radiation therapy given to women with breast cancer. A device outside the body focuses radiation on the area affected by the cancer. The areas that need radiation therapy will depend on the type of surgery the patient has: mastectomy or breast-conserving surgery (BCS). It also depends on how far the cancer has spread (has it reached nearby lymph nodes).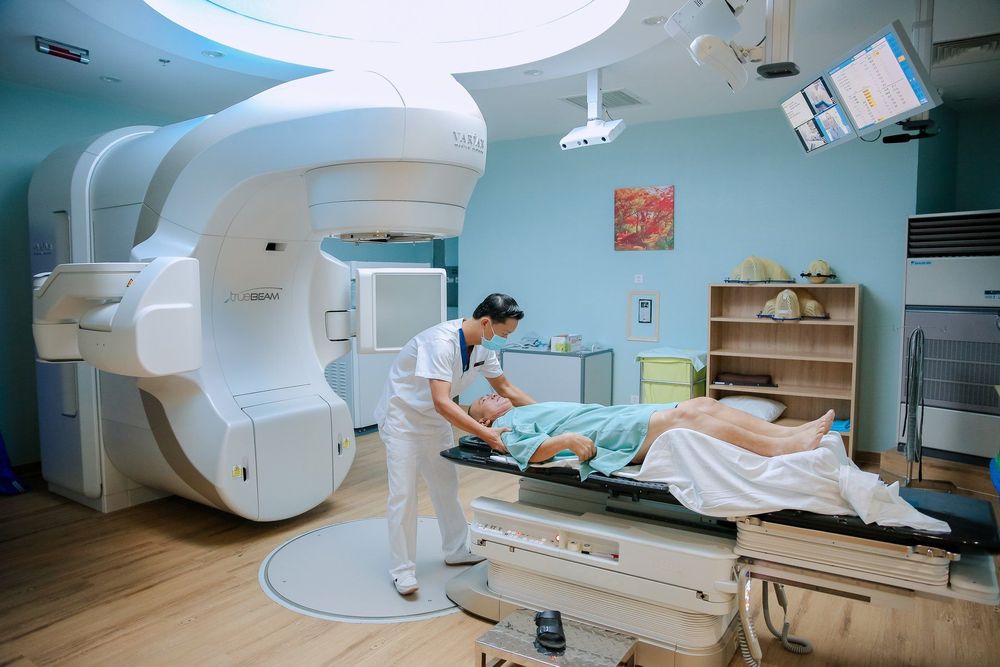
If you have had a mastectomy and there are no lymph nodes with cancer cells, the radiation will focus on the chest wall, the scar from the mastectomy, and any areas where the ducts are located. outside the body after surgery.
If you have had breast-conserving surgery (BCS), there is a high chance you will have radiation therapy to the entire breast and increased radiation therapy to the area in the breast where the cancer was previously removed (tumor base) to help prevent them from coming back.
In cases where cancer is found in the lymph nodes under the arm (axillary lymph nodes), the area may also be treated with radiation. Occasionally, patients may also receive radiation therapy in other areas such as the node above the collarbone (the supraclavicular nodes) and the nodes below the breastbone in the center of the chest (lymph nodes inside the mammary gland).
2.1.When is external radiation done? Breast cancer patients can receive external radiation therapy (EBRT) after surgery, and this is done only when the surgical site has healed (usually takes about a month or so). If you are being treated with chemotherapy, your radiotherapy sessions will be delayed until the chemotherapy is finished.
2.2.How is external radiation therapy performed? Before starting treatment, the doctor will figure out the exact angles to aim the radiation beams and determine the appropriate radiation dose for each patient. The area being treated with radiation will be marked with an ink stain or a small tattoo on the skin.
External radiation therapy is similar to an X-ray, but the radiation level is usually stronger. Furthermore, radiation therapy itself does not cause pain to the patient. Each treatment only lasts a few minutes, but preparation can take longer.
3. Classification and schedule of external radiation therapy (EBRT) for breast cancer
3.1.Radiation to the whole breast The standard schedule for radiation therapy to the whole breast is 5 days a week (Monday to Friday) and lasts for 6-7 weeks. Another option is hypofractionated radiation therapy, in which radiation is also delivered to the entire breast, but in larger daily doses, and lasts only about 3-4 weeks.
For women who are treated with breast-conserving surgery (BCS) and do not have cancer that has spread to the lymph nodes under the arm, the upper radiotherapy schedule will be the best strategy to prevent cancer breast recurrence.

3.2.Accelerated partial breast irradiation (APBI) In certain cases, patients may be offered accelerated partial breast irradiation (APBI) to deliver a larger radiation dose over a range of Shorter time for only one breast. There are different types of APBI, including:
Intraoperative radiation therapy (IORT): in this method, a single large dose of radiation is delivered to the removed tumor area (tumor base) immediately after during breast-conserving surgery (before closure of the breast incision). Three-dimensional radiation therapy (3D-CRT): in this technique, radiation therapy will be performed by special machines that can better project radiation on the tumor background. The course of treatment will be done twice a day and lasts for 5 days. Dose-modulated radiation therapy (IMRT): This is similar to 3D-CRT, but it can change the intensity of some radiation beams in certain areas. This helps deliver stronger doses to certain parts of the tumor base, while reducing damage to nearby normal body tissues. 3.3. Radiation therapy to the entire chest wall If the patient has had a mastectomy and no lymph nodes have cancer, radiation therapy to the entire chest wall, or radiation therapy to the scar of the mastectomy, can be used. breasts and other areas of the body with drainage. This method is usually applied daily, 5 days a week and lasts for 6 weeks.
3.4.Radiation to lymph nodes Whether you have had breast-conserving surgery or a mastectomy, if cancer is found in the lymph nodes under your arm, this area requires radiation therapy. . In certain cases, the lymph nodes above the collarbone (supraclavicular) and behind the breastbone in the middle of the chest (internal mammary nodes) will also receive radiation therapy along with the lymph nodes under the arm. This procedure will be done 5 days a week and lasts 6 weeks at the same time as radiation therapy to the breast or chest wall.
3.5. Possible side effects of external radiation therapy Some common short-term side effects of external radiation therapy for breast cancer include:
Swelling in the breast Skin changes in the treated area, almost like sunburn (redness, peeling, tanning) Fatigue
Therefore, after radiation therapy, you should avoid exposing that area to direct sunlight as it can make skin changes worse. The condition may get better within a few months, and changes in breast tissue usually disappear after 6-12 months, or even longer.
Besides, external radiation therapy can also cause some other side effects such as:
Breasts become smaller and firmer Radiation therapy can affect future breast reconstruction options. Women who have had radiation to the breast may have problems with breastfeeding. Sometimes damage to certain nerves in the arm. This is called brachial plexus disease, which can lead to numbness, pain, and weakness in the shoulders, arms, and hands. Radiation therapy to the lymph nodes under the arm can cause lymphedema, which leads to pain and swelling in the arm or chest. In rare cases, external radiation therapy can weaken the ribs, leading to fractures. Radiation therapy can cause long-term damage to the lungs and heart A very rare complication of external radiation therapy is the development of another cancer called an angioma.
4. Radiation therapy (Brachytherapy)
Brachytherapy is also known as radiation therapy or internal radiation therapy. This is another way to do radiation therapy. Instead of aiming beams of radiation from outside the body, radiation therapy uses a device containing radioactive seeds or pellets that are placed for a short time in the breast tissue at the area where the cancer has been removed. tumor background).
For some women who have had breast-conserving surgery (BCS), brachytherapy may be used (instead of radiation to the whole breast) as a form of accelerated partial breast irradiation. However, depending on tumor size, location and other factors to assess the suitability of this method for patients.
4.1. Types of radiation therapy The following are the most common types of radiation therapy, including:
Radiation therapy inside the body cavity: this is the most common type of therapy for women with breast cancer. The radiotherapy device will be inserted into the space left after breast-conserving surgery and left there until the treatment is complete. This device is like a small catheter. The end of the device inside the breast will then expand like a balloon so it can stay in place during the treatment, while the other end of the catheter sticks out outside the breast. For each treatment, one or more sources of radiation are placed down through the catheter and into the device for a short time and then removed. The treatment cycle is usually done twice a day and lasts for 5 days. At the last treatment, the device will be deflated and removed from the body. Interstitial radiation therapy: for this radiation therapy, several small catheters are inserted into the breast near the area where the cancer was removed and left in place for a few days. Then, radioactive pellets will be inserted into the catheter every day for a short period of time. 4.2.Side effects of radiation therapy inside the body cavity Like external radiation therapy, radiation therapy inside the body cavity can cause a number of effects, including:
Redness or bruising at the site Treatment position Breast pain Infection Damage to fatty tissue in the breast Weakness and fracture of the ribs in rare cases Fluid accumulation in the breast (serum) At Vinmec International General Hospital, Cancer Screening Package is available breast cancer, helping customers screen and detect breast cancer early even when there are no symptoms. When registering for the Breast Cancer Screening Package, customers will receive:
Examination and consultation with an oncologist. Breast cancer screening by bilateral breast ultrasound and mammogram. Vinmec has become a prestigious address in breast cancer screening with:
A team of highly qualified and experienced doctors. Comprehensive professional cooperation with domestic and international hospitals: Singapore, Japan, USA, .. Comprehensive treatment and care, multi-specialty coordination towards individualizing each patient. Having a full range of specialized facilities to diagnose the disease and stage it before treatment: Endoscopy, CT scan, PET-CT scan, MRI, histopathological diagnosis, gene-cell testing, .. There are full range of main cancer treatment methods: surgery, radiation therapy, chemotherapy, stem cell transplant... To register for examination and treatment at Vinmec International General Hospital, you are welcome. Please make an appointment on the website to be served.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.
Reference source: cancer.org