This is an automatically translated article.
The article is professionally consulted by Specialist Doctor Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology - Vinmec Hai Phong International General Hospital.
Hysteroscopy is one of the modern techniques in the diagnosis and treatment of gynecological diseases in particular and women's health care in general. This is an invasive procedure, giving a clear image of the inside of the uterine lining, helping doctors have an accurate basis for identifying the disease as well as combining other procedures to treat the disease.
1. What is hysteroscopy?
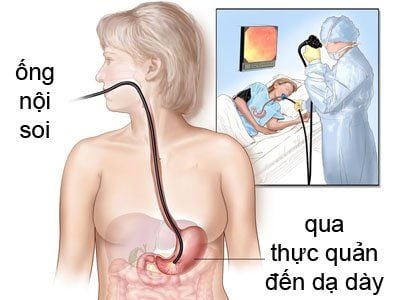
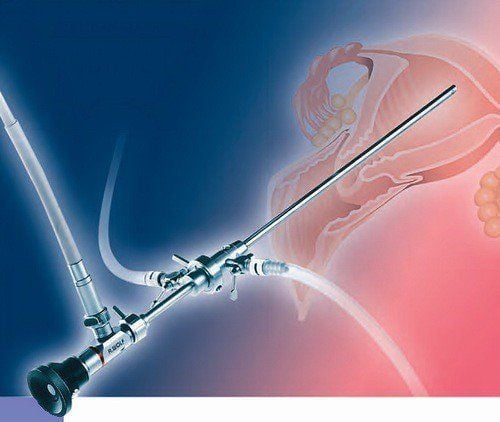
Exploratory hysteroscopy is a method that uses assisted instruments (a small tube with a camera attached to it called a hysteroscope) to view the internal structure of the uterus (also called the stomach). child). The endoscope will be inserted through the vagina and transmitted images to a monitor. Other instruments will be used in conjunction with the endoscope to treat the lesions.
Usually, during a hysteroscopy, the doctor will also perform a uterine biopsy - a procedure to remove small pieces of tissue from the endometrium for testing or viewing under a microscope. .
2. What is hysteroscopy for?
Endoscopic exploration of the uterus is often used to find the cause of abnormal uterine bleeding. Abnormal uterine bleeding when a woman has heavier or longer menstrual periods, less or more frequent than usual, bleeding after menopause. Sudden bleeding that occurs between periods is also called irregular bleeding.
In addition, hysteroscopy is also used in the diagnosis and treatment of the following gynecological diseases or obstetric problems:
Removal of adhesions in the uterine cavity caused by infection or from previous surgeries. For example, using burning instruments to remove endometrial diseases. Detect uterine fibroids, tumors, boils, endometrial cancer or malformed uterus. Diagnosis of small fibroids and polyps: sensitivity 90% and specificity 93%.

Consider the shape and size of the uterus to assess the cause of infertility. Laparoscopy to look from the cervix to the fallopian tubes, if these tubes are blocked, the doctor can clear these tubes with special tools through the laparoscope. Hysteroscopy diagnoses the cause of recurrent miscarriages (two or more in a row). Other tests may also be used in combination to find the cause. Laparoscopy to place an IUD in the uterus or find and remove a misplaced IUD. Having a sterilization procedure: using a hysteroscope to place a device into a woman's fallopian tubes (putting an IUD into the opening of the fallopian tubes, this is permanent birth control) .
3. Notes when performing hysteroscopy
Before performing the endoscopy, the patient should tell the doctor if he or she is in the following cases:
Are or suspect that you are pregnant Are taking any medications History of allergy to any drugs Blood clotting problems – stopping bleeding or taking anticoagulants such as aspirin or warfarin Treated vaginal, uterine, and vaginal infections within the last 6 weeks Have certain heart or lung conditions Best Hysteroscopy should be performed when not in the menstrual cycle. Do not douche, use tampons or vaginal suppositories for 24 hours prior to the hysteroscopy.
The patient can move around 6 - 12 hours after surgery. This is a diagnostic hysteroscopy, so the patient can eat, drink, and be discharged from the hospital after the procedure.
The patient may feel slight tightness or light bleeding for a few days after the procedure, the doctor will prescribe medicine to ease the pain for the patient. If the patient develops a fever, chills or severe bleeding, the doctor should be contacted immediately.