This is an automatically translated article.
Purine is a substance found in food and produced naturally by the body. Purines are found in a number of foods. Purines aren't bad, but you want to avoid high amounts. When your body digests purine, it produces a waste product called uric acid. The accumulation of uric acid crystals in the joints can cause a number of health problems such as kidney stones and a type of arthritis known as gout...1. What are Purines? The Importance of Purines
Purines are natural substances found in all cells of the body and in virtually all foods. In humans, purines are converted to uric acid, which acts as an antioxidant and helps prevent damage caused by reactive oxygen species. Continuous supply of uric acid is important to protect human blood vessels.Purines are found in many foods and in varying degrees. They are metabolized (broken down) into uric acid, a waste product normally excreted in the urine. If there is too much uric acid in the blood, people can develop a condition called hyperuricemia.
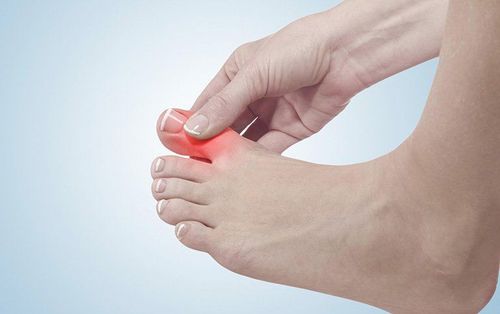
Hyperuricemia is a precursor to gout, which is a rheumatoid arthritis disease in which excess uric acid develops into tiny needle-like crystals in soft tissues and joints. Hyperuricemia can occur if the kidneys do not excrete uric acid properly, but can also arise from consuming too many purine-rich foods.
Tăng axit uric máu là tiền thân của bệnh gút, là một bệnh viêm khớp dạng thấp, trong đó axit uric dư thừa phát triển thành các tinh thể nhỏ như kim trong các mô mềm và khớp
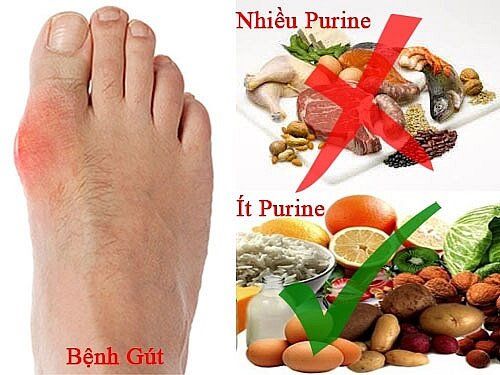
2. Classification of food groups according to purine content
Based on the purine content in foods, people are divided into 3 main food groups.Group A (low purines content about 0 - 50 mg / 100g of food) includes:
Fruits and vegetables: All fruits and vegetables except those in group B Dairy products: milk , cream. yogurt, cheese, eggs are high-fat dairy products Grains: All but those in group B (most breads and cakes, most breakfast cereals, cookies, rice) , barley, wine stew, pasta and pasta) Candy, jam Products such as butter, most cooking oils, lard Beverages: including coffee, tea, caffeinated soft drinks Group B (average purine content is about 50 - 150mg / 100g of food) including
Poultry: duck, chicken, geese, etc. Red meat: Veal, beef, lamb, pork, bacon smoke... Fish: except those in group C, oysters, mussels, and shellfish like shrimp and crab... Whole grains: including oatmeal and brown rice... Legumes like soybeans, soybean meal, tofu, chickpeas, peanuts, peanut butter, cashews, peas... Vegetables: broccoli, kale, spinach, asparagus, avocado , mushrooms... Group C (high purine content about 150 - 1000 mg/100g food)
Domestic or wild animals: pheasant, quail, rabbit, wild game meat, animal offal (kidney, heart, liver, spleen...) and food from animal organs such as (pate, sausage...) Fermented meat products: spring rolls sour... Caviar: cod roe, salmon roe... Scallop, herring, mackerel, salmon, crayfish, lobster, anchovies, sardines, fish sauce...

Dựa vào hàm lượng purin trong các loại thực phẩm mà người ta chia thành 3 nhóm thực phẩm chính
3. Purine content in specific foods
Highest purine content (400mg Uric Acid/100g and higher)| Thực phẩm (theo thứ tự bảng chữ cái) | Tổng số Purines tính bằng mg uric axit / 100 g (Trung bình) | Cao nhất | Thấp nhất | Tỷ trọng năng lượng mg / MJ |
| Cá, cá mòi | 480 | 399 | 560 | 519,5 |
| Gan bê | 460 | 837,5 | ||
| Cây nấm | 488 | 932,8 | ||
| Thịt bê | 1260 | 3012,9 | ||
| Gan bò | 554 | 1013,3 | ||
| Lá lách bò | 444 | 1052,6 | ||
| Tim lợn | 530 | 1382 | ||
| Gan lợn | 515 | 937,9 | ||
| Phổi lợn | 434 | 911,2 | ||
| Lá lách lợn | 516 | 1208,2 | ||
| Lá lách cừu | 773 | 1702,6 | ||
| Cá trích | 804 | 795,6 | ||
| Ca cao, sô cô la | 2300 | 1611,3 | ||
| Nấm men bánh mì | 680 | 2071,3 | ||
| Nấm men bia | 1810 | 1866,6 |
| Thực phẩm (theo thứ tự bảng chữ cái) | Tổng số Purines tính bằng mg uric axit / 100 g (Trung bình) | Cao nhất | Thấp nhất | Tỷ trọng năng lượng mg / MJ |
| Đậu trắng khô | 128 | 127,1 | ||
| Hạt đậu nành khô | 190 | 139,1 | ||
| Thịt hộp | 120 | 192 | ||
| Phi lê bò | 110 | 216,4 | ||
| Sườn bò | 120 | 185,4 | ||
| Thịt ba chỉ bò | 133 | 292,1 | ||
| Thịt bò nướng, thịt thăn bò | 110 | 120 | 110 | 201,4 |
| Thịt vai bò | 110 | 203,9 | ||
| Đậu đen, đậu xanh khô | 222 | 194,3 | ||
| Trứng cá muối | 144 | 141,6 | ||
| Thịt ức gà có da | 175 | 288,4 | ||
| Gà quay | 115 | 165,8 | ||
| Gà luộc | 159 | 149,2 | ||
| Chân gà | 110 | 152,2 | ||
| Thịt vịt | 138 | 146,2 | ||
| Cá cơm | 239 | 560 | ||
| Cá chép | 160 | 330,9 | ||
| Cá tuyết | 109 | 335,9 | ||
| Cá êfin (thuộc họ cá tuyết) | 139 | 425,2 | ||
| Trứng cá trích | 190 | 342,4 | ||
| Cá trích | 210 | 216,9 | ||
| Cá thu | 145 | 95 | 194 | 191,2 |
| Cá rô | 110 | 311,3 | ||
| Cá rô dại dương | 241 | 544,1 | ||
| Cá hồi | 170 | 110 | 250 | 202 |
| Cá mòi | 345 | 693,2 | ||
| Cá bơn | 131 | 125 | 137 | 376,2 |
| Cá hồi | 297 | 686,7 | ||
| Cá ngừ | 257 | 273,7 | ||
| Cá ngừ ngâm dầu | 290 | 246,2 | ||
| Thịt ngỗng | 165 | 116,7 | ||
| Nho khô | 107 | 86,4 | ||
| Thịt hun khói | 131 | 248,1 | ||
| Tim cừu | 241 | 367,6 | ||
| Thịt ngựa | 200 | 438,8 | ||
| Thận bê | 218 | 419,6 | ||
| Thịt bắp cừu | 182 | 371 | ||
| Đậu lăng | 127 | 114.45 | 164.65 | 93,8 |
| Hột gai | 105 | 67,4 | ||
| Gan gà | 243 | 426,3 | ||
| Tôm | 118 | 60 | 175 | 346,4 |
| Phổi bê | 147 | 389,1 | ||
| Con trai | 112 | 391,5 | ||
| Tim bò | 256 | 504,3 | ||
| Thận bò | 269 | 569,5 | ||
| Phổi bò | 399 | 961,4 | ||
| Lưỡi bò | 160 | 186 | ||
| Đậu Hà lan | 109 | 84,2 | ||
| Thận lợn | 334 | 784,5 | ||
| Lưỡi lợn | 136 | 208,2 | ||
| Cá chó | 140 | 406,7 | ||
| Hạt thuốc phiện | 170 | 86 | ||
| Thịt ba chỉ lợn | 100 | 80 | 110 | 92,3 |
| Thịt ba chỉ lợn hun khói, sấy khô | 127 | 82,6 | ||
| Sườn lợn | 145 | 140 | 150 | 260 |
| Thịt heo phi lê | 150 | 145 | 150 | 334,8 |
| Xương hông lợn | 120 | 115 | 130 | 155 |
| Thịt chân giò lợn | 160 | 150 | 160 | 357,4 |
| Thịt chân giò lợn | 166 | 374,9 | ||
| Thịt vai lợn | 150 | 145 | 150 | 165,2 |
| Thịt thỏ | 132 | 95 | 150 | 207,7 |
| Xúc xích “Jagdwurst” | 112 | 127,8 | ||
| Xúc xích salami, Đức | 104 | 65,9 | ||
| Xúc xích gan | 165 | 122,2 | ||
| Xúc xích chiên từ thịt lợn | 101 | 80,2 | ||
| Con ngao | 136 | 505,8 | ||
| Tôm | 147 | 60 | 234 | 397,9 |
| Lá lách bê | 343 | 815,9 | ||
| Hạt hướng dương khô | 143 | 59,5 | ||
| Thịt gà tây | 150 | 237,3 | ||
| Thịt bò cốt lết có xương | 140 | 309,6 | ||
| Thịt bê phi lê | 140 | 347,3 | ||
| Thịt chân bê | 150 | 140 | 150 | 310,2 |
| Thịt bắp bê | 172 | 438,7 | ||
| Thịt cổ bê có xương | 150 | 326,9 | ||
| Thịt vai bò | 140 | 309,3 | ||
| Thịt hươu, nai | 105 | 205 | ||
| Thịt chân hươu, nai | 138 | 105 | 154 | 336,5 |
| Thực phẩm (theo thứ tự bảng chữ cái) | Tổng số Purines tính bằng mg uric axit / 100 g (Trung bình) | Cao nhất | Thấp nhất | Tỷ trọng năng lượng mg / MJ |
| Hạnh nhân ngọt | 37 | 15,7 | ||
| Quả táo | 14 | 60,1 | ||
| Quả mơ | 73 | 71,6 | ||
| Bắp cải | 78 | 834,6 | ||
| Măng tây | 23 | 19,71 | 29,57 | 310,9 |
| Quả bơ | 19 | 20,9 | ||
| Măng | 29 | 402,1 | ||
| Quả chuối | 57 | 152,4 | ||
| Lúa mạch nguyên vỏ | 96 | 71,1 | ||
| Giá đỗ | 80 | 378,3 | ||
| Đậu que Pháp | 37 | 20 | 43 | 266,9 |
| Đậu pháp khô | 45 | 40 | 50 | 39,4 |
| Thịt bắp bò Đức | 57 | 96,5 | ||
| Bia, rượu | 8.1 | 75,4 | ||
| Bia Đức | 13 | 75,2 | ||
| Bia tươi | 14 | 86 | ||
| Củ cải đỏ | 19 | 15 | 21 | 108,5 |
| Quả việt quất | 22 | 143,7 | ||
| Não bê | 92 | 203,1 | ||
| Bánh mỳ trắng, bột mì | 14 | 13,9 | ||
| Bông cải xanh | 81 | 691,6 | ||
| Cải bắp tím | 32 | 19,79 | 36,62 | 350,2 |
| Cải bắp trắng | 22 | 210,3 | ||
| Cà rốt | 17 | 14 | 25 | 155,9 |
| Bông cải trắng | 51 | 537,9 | ||
| Pho mát | 7.1 | 5 | ||
| Quả cherry | 17 | 75,5 | ||
| Rau diếp xoăn | 12 | 171,8 | ||
| Bột ca cao | 71 | 49,7 | ||
| Ngô | 52 | 140,9 | ||
| Cá, tôm càng xanh | 60 | 220,3 | ||
| Cải xoong | 28 | 200,8 | ||
| Bánh mì giòn | 60 | 44,9 | ||
| Dưa chuột | 7.3 | 141,7 | ||
| Nho Hy Lạp | 17 | 122,6 | ||
| Quả chà là sấy khô | 35 | 29,9 | ||
| Quả cây cơm cháy | 33 | 144,4 | ||
| Rau đắng | 17 | 297,7 | ||
| Cây thì là | 14 | 10 | 16 | 139 |
| Qủa sung | 64 | 60,4 | ||
| Cá chình | 78 | 45 | 110 | 57.2 |
| Xúc xích Đức | 89 | 68,74 | 129,52 | 80,2 |
| Qủa lý gai | 16 | 101,3 | ||
| Quả nho | 27 | 94,6 | ||
| Cải xoăn | 48 | 309,4 | ||
| Quả kiwi | 19 | 88,5 | ||
| Cải củ | 25 | 10,86 | 29,61 | 243,9 |
| Tỏi tây | 74 | 714,1 | ||
| Rau diếp | 13 | 9,75 | 29,25 | 274,4 |
| Dưa hấu, dưa vàng | 33 | 143 | ||
| Hạt đậu | 62 | 41,9 | ||
| Nấm | 58 | 55,48 | 60,52 | 858,2 |
| Nấm tươi | 92 | 1011,6 | ||
| Nấm đóng hộp | 29 | 488,5 | ||
| Hạt đậu Brazil | 23 | 8,3 | ||
| Các loại hạt đậu, đậu phộng | 79 | 33,8 | ||
| Yến mạch không có vỏ trấu | 94 | 63,6 | ||
| Trái oliu | 29 | 51,1 | ||
| Củ hành | 13 | 112,4 | ||
| Quả cam | 19 | 105,9 | ||
| Não bò | 75 | 140,7 | ||
| Lườn gà | 90 | 322,6 | ||
| Lườn gà, nấm | 50 | 1054,6 | ||
| Rau mùi tây | 57 | 266,2 | ||
| Vỏ và hạt đậu tươi | 84 | 245,7 | ||
| Hạt đậu khô | 95 | 84,78 | 166,56 | 82,7 |
| Quả đào | 21 | 119,6 | ||
| Quả lê | 12 | 2 | 17 | 51,5 |
| Hạt tiêu xanh | 55 | 681 | ||
| Não lợn | 83 | 161,71 | ||
| Quả dứa | 19 | 81,4 | ||
| Cá chim | 93 | 257,6 | ||
| Nho khô | 24 | 116,8 | ||
| Quả mận sấy khô | 64 | 67,9 | ||
| Khoai tây tươi | 16 | 53,6 | ||
| Khoai tây nấu chín | 18 | 60,3 | ||
| Lòng heo | 55 | 37,23 | 90,55 | 42,8 |
| Quả bí ngô | 44 | 422 | ||
| Trái mộc qua | 30 | 185 | ||
| Củ cải | 15 | 243,3 | ||
| Quả mâm xôi | 18 | 126,3 | ||
| Lúa mạch đen, nguyên hạt | 12 | 212,6 | ||
| Dưa bắp cải | 16 | 224,7 | ||
| Xúc xích “Blers Chicken” | 85 | 117,3 | ||
| Xúc xích "Fleischwurst" | 78 | 66,8 | ||
| Xúc xích "Mortadella" | 96 | 67,4 | ||
| Xúc xích "Munich Weisswurst" | 73 | 65,7 | ||
| Xúc xích Vienna | 78 | 65,7 | ||
| Xúc xích chiên thịt bê | 91 | 81,5 | ||
| Xúc xích Đức | 74 | 45,9 | ||
| Hạt vừng khô | 62 | 26,5 | ||
| Rau chân vịt | 57 | 844,7 | ||
| Quả dâu | 21 | 156,8 | ||
| Cá mè | 80 | 243,8 | ||
| Đậu phụ | 68 | 196,4 | ||
| Cà chua | 11 | 145,4 | ||
| Quả óc chó | 25 | 9,1 | ||
| Lúa mì nguyên hạt | 51 | 39,4 | ||
| Sữa chua | 8,1 | 27,7 |
Regular health check-up helps to detect diseases early, so that you can have a plan. treatment plan for optimal results. Currently, Vinmec International General Hospital has general health checkup packages suitable for each age, gender and individual needs of customers with a reasonable price policy, including:
Health checkup package general Standard 2020 General health check-up package VIP 2020 General health check-up package Special 2020 General health check-up package Children 2020 General health examination package Work permit - Issuance of work permits Examination results of people sick will be returned home. After receiving the results of the general health examination, if you detect diseases that require intensive examination and treatment, you can use services from other specialties at the Hospital with quality treatment and services. outstanding customer service.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.
References: nal.usda.gov; elevatehealthaz.com