This is an automatically translated article.
The article was professionally consulted by Specialist Doctor I Nguyen Thi My Linh - Neonatologist - Department of Pediatrics - Neonatology - Vinmec Danang International General Hospital. Specialist Doctor I Nguyen Thi My Linh has 12 years of experience in diagnosing and treating pediatric diseases.Pulmonary fibrosis in premature babies is a disease that damages the lungs, which can lead to dangerous complications such as heart failure, respiratory failure. The disease affects the health and development of children.
1. What is pulmonary fibrosis in premature infants?
Pulmonary fibrosis is a lung disease that occurs when lung tissue is damaged and scarred. Thick and hard tissue makes it difficult for a child's lungs to function properly. As pulmonary fibrosis worsens, the patient becomes increasingly short of breath.Pulmonary fibrosis in premature infants, if not detected early and treated promptly, can easily lead to dangerous and fatal complications.
2. Causes of pulmonary fibrosis in infants
3. Symptoms of pulmonary fibrosis
Signs and symptoms of pulmonary fibrosis may include:Shortness of breath Dry cough Fatigue Unexplained weight loss Muscle and joint pain.
4. Complications of pulmonary fibrosis in infants
4.1 Pulmonary hypertension Pulmonary hypertension affects the arteries in the child's lungs. It begins when the smallest arteries and capillaries are compressed by scar tissue, increasing resistance to blood flow in your lungs. This in turn increases pressure in the pulmonary arteries and the lower right chamber of the heart (the right ventricle). Some forms of pulmonary hypertension are serious illnesses that gradually get worse and are sometimes fatal.
4.2 Right Heart Failure This serious condition occurs when the right ventricle pumps harder than usual to push blood through the partially blocked pulmonary arteries.
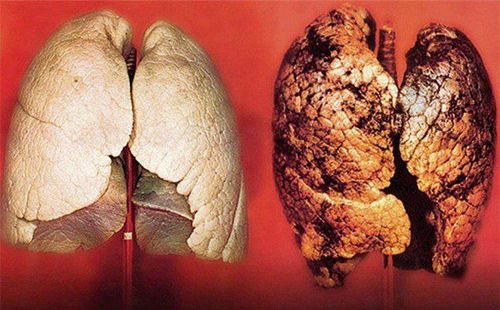
4.4 Lung cancer Persistent pulmonary fibrosis also increases the risk of developing lung cancer.
4.5 Lung Complications As pulmonary fibrosis progresses, it can lead to complications such as a blood clot in the lung, a collapsed lung, or a lung infection.
5. Diagnosis of pulmonary fibrosis in premature infants
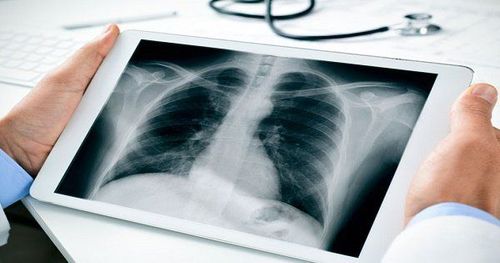
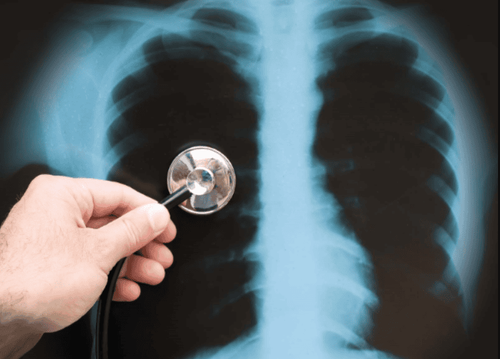
Chest X-ray: A chest X-ray may show the typical scar tissue of pulmonary fibrosis, and it may be helpful for monitoring. disease process and treatment Computerized tomography (CT): CT scanners use a computer to combine X-ray images taken from many different angles to create cross-sectional images of internal structures body. Echocardiogram : Helps assess the amount of pressure occurring in the right heart Pulmonary function test: Several types of lung function tests may be performed. Arterial blood gas test. Blood oxygen saturation Lung biopsy: If other tests fail to diagnose the condition, doctors may need to remove a small amount of lung tissue (biopsy). The biopsy is then examined in a laboratory to diagnose pulmonary fibrosis or rule out other conditions.
6. Treatment of pulmonary fibrosis in premature infants
Drug use: pirfenidone and nintedanib. These drugs can help slow the progression of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Oxygen therapy Pulmonary rehabilitation can help manage symptoms and improve everyday lung function A lung transplant may be an option for people with pulmonary fibrosis. However, lung transplantation can be associated with complications such as rejection and infection. The doctor can discuss with the child's family if a lung transplant may be appropriate for the child's condition. Vietnam is the first country in the world to announce a successful stem cell transplant to treat pulmonary fibrosis in premature babies. In 2017, Vinmec Time City International Hospital applied stem cell transplantation from bone marrow in the treatment of pulmonary fibrosis for 3 patients and all 3 were cured. After about 3 weeks to 1 month of stem cell transplantation, the patient was weaned from oxygen, was able to breathe on his own and the pulmonary fibrosis gradually disappeared (about 6 months).
Vinmec International General Hospital is one of the hospitals that not only ensures professional quality with a team of leading medical doctors, modern equipment and technology, but also stands out for its examination and consultation services. comprehensive and professional medical consultation and treatment; civilized, polite, safe and sterile medical examination and treatment space.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.