This is an automatically translated article.
The article was written by Master, Doctor Tran Thi Diem Trang - Department of Examination & Internal Medicine - Vinmec Central Park International General HospitalPulmonary embolism is a blockage in the normal flow of blood. This blockage makes gas exchange difficult. Pulmonary embolism causes patients to have respiratory impairment, and at the same time reduces quality of life.
1. What is pulmonary embolism?
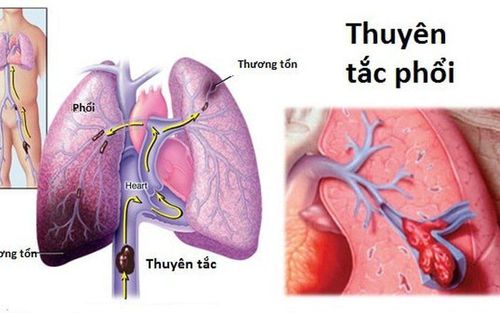
Pulmonary embolism (pulmonary embolism) is a blockage of a pulmonary artery. Blood flows through the lungs from the right heart to take in oxygen and remove carbon dioxide and then circulates from the lungs back to the left heart to be pumped out to the rest of the body.
Pulmonary embolism is when a blood clot enters a blood vessel and blocks the normal flow of blood. An obstruction occurs when a blood clot travels from another part of the body to the lungs. The blockage in the lungs causes pressure to return to the right heart, causing the right heart to expand and contract harder. This also affects the left heart, which is compressed by the right heart. Blood pressure will drop if the left heart is not pumping enough blood.
Pulmonary embolism refers to a thrombus that breaks and floats in a blood vessel, which can contain many thrombus. Deep vein thrombosis are blood clots that do not move and are located deep in a vein. Often, blood clots that form in a vein in the leg become a pulmonary embolism. The thrombus can migrate into different areas of one or both lungs. The severity of a pulmonary embolism depends on how much blood is not reaching the lungs.
Besides, lower extremity venous thrombosis, pulmonary embolism may arise from the renal, upper extremity or right heart veins.
2. The relationship between deep vein thrombosis and pulmonary embolism
Blood clots that form and develop in veins in the legs and arms are called deep vein thrombosis. When a patient has a deep vein thrombosis in an arm or leg, there will be some signs of damage such as pain, swelling, heat, and redness.
To detect blood clots, venous blood flow studies such as Doppler ultrasound will be performed. Early treatment of DVT helps relieve symptoms and prevent pulmonary embolism.
3. Symptoms of pulmonary embolism

Typical clinical symptoms of pulmonary embolism such as:
Shortness of breath, dizziness: this is the most common symptom, the disease progresses quite quickly and the patient has a high risk of death. One study showed that about 17% of patients with syncope had blood clots in their lungs. Chest pain: you will feel pain when you take a deep breath, this is a sign of pulmonary embolism. Coughing up blood: accompanied by mucus. This sign is uncommon and it also warns the patient that he may have lung cancer. This is a very dangerous symptom. Patients with pulmonary embolism have chest pain, coughing up blood often accompanied by other circulatory symptoms such as tachycardia, distended neck veins, decreased blood pressure, shock...
The patient may have chest pain lasts from a few minutes to a few hours.
Besides, patients with pulmonary embolism may feel dizzy and lose consciousness, skin becomes pale, and vomit.
4. Factors that increase the risk of pulmonary embolism
The following are some factors that increase the risk of pulmonary embolism (pulmonary embolism):Obese women Women after giving birth Patients after heart surgery or having a stroke or heart attack Patients with severe trauma , hip or femur fracture Sitting for a long time on a train, plane or after a long period of inactivity Surgery that can cause blood clots such as surgery on the legs, abdomen, hips, brain Cancer: the tumor has synthesis and secretion of procoagulants. At the same time, chemotherapy also increases the risk of venous thrombosis Having a stroke or heart failure Patients with serious infections Women taking oral contraceptives In the absence of any of these factors Above does not mean there is no risk of disease. Therefore, when you see any signs of the disease, you should go to specialized medical facilities for examination, diagnosis and treatment.
5. How to prevent pulmonary embolism
To prevent pulmonary embolism, you should pay attention to some of the following issues:Do not lie down or sit for too long, so exercise regularly. Maintain a healthy weight. Your doctor will give you prophylactic anticoagulation if you must lie still. Should wear comfortable clothes, not too tight to avoid blood circulation. No smoking. Take medicine according to the doctor's prescription, do not arbitrarily buy medicine for treatment. Patients with medical diseases, pregnant women, and those with limited mobility should pay special attention. Pulmonary embolism, if not treated early, will cause many serious complications, the patient has a high risk of death. When you see symptoms of the disease, you need to immediately go to a reputable medical facility for an accurate diagnosis of your health condition.

Currently, at Vinmec International General Hospital, fibrinolysis is being applied for emergency treatment of patients with pulmonary embolism. With modern imaging equipment, CT perfusion results are available within 7 minutes and performed routinely.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.