This is an automatically translated article.
Progestin-only birth control pills are one of the modern methods of contraception, widely used and especially suitable for women who are breastfeeding. The following article will help us learn more about this method of contraception.
1. What are progestin-only birth control pills?
Progestin-only birth control pills (abbreviated as POP - progestin only pill) are often called mini-pill. Each birth control pill contains a small amount of progestin, the synthetic form of the hormone progesterone. The drug comes in the form of a pack, consisting of 28 tablets. To receive a steady dose of the hormone, you need to take one pill a day.
Some people find that progestin-only birth control pills are more difficult to use than regular birth control pills because they have to be taken at the same time of day.
Progestin-only birth control pills are a good option for women who want to avoid pregnancy but are breastfeeding or cannot take estrogen for some other reason.
Thuốc tránh thai chỉ chứa progestin chỉ nên uống mỗi ngày một viên
2. Mechanism of action of birth control pills containing only progestin
Progestin-only birth control pills inhibit ovulation for about half of the menstrual cycles of women taking the pill. They prevent conception mainly by causing changes in the cervical mucus. The thick mucus makes it difficult for sperm to pass through the cervix. So even if you ovulate, sperm won't be able to reach your fallopian tubes to fertilize an egg. What's more, progestins can prevent pregnancy by thinning the lining of your uterus, making it less likely for an egg to implant there even if an egg has been fertilized.
The mini-progestin pill works better than the combination pill, and the effect of this hormone on your cervical mucus only lasts about 24 hours. That's why you have to be extra careful when you take estrogen-only birth control pills at the same time each day.
A newly researched progestin-only pill, which prevents ovulation by up to 99% of cycles and with less stringent usage, is available in Europe and elsewhere in the world , however the drug has not yet been approved by the FDA.
3. Can progestin-only birth control pills be used by nursing mothers?
Unlike combined oral contraceptives, progestin-only birth control pills are considered appropriate by many medical organizations for women who want to avoid pregnancy but are breastfeeding, including the Centers for Disease Control, World Health Organization, American Academy of Pediatrics, American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists, and Planned Parenthood of America.
Only small amounts of progestin pass into breast milk and research to date has shown no adverse effects from the drug on baby's weight gain, health or development. Most studies show no change in the amount of breast milk secreted by mothers using progestin-only oral contraceptives, and some studies even show a slight increase in milk supply when use this medicine.

Thuốc tránh thai chỉ chứa progestin có thể dành cho các mẹ đang cho con bú
4. Advantages of progestin-only birth control pills
If you're exclusively breastfeeding, haven't had a period yet, and are taking progestin-only birth control pills as directed, it's nearly 100% effective at preventing pregnancy for the first six months postpartum.
For women who are not breastfeeding, the minipill is 91 to 99% effective when taken regularly and correctly, meaning that about 1 to 9 women out of 100 who take the pill correctly will become pregnant within first year. This has led many people to choose the combined oral contraceptive pill over the progestin-only pill, which is estimated to be 99.7 to 99.9 percent effective when used as directed.
If you don't take your progestin-only birth control pills exactly as prescribed, for example, you take them at the wrong time or don't even take them at the same time every day, your risk of pregnancy is much higher, especially especially if you are not breastfeeding. And the more mistakes you make, the higher the risk. So, while the progestin-only pill is a reliable method of birth control for those who follow the directions exactly, it's not the best method for everyone.
If you think you will have trouble using progestin-only birth control pills properly, consider using another method, such as the IUD or the birth control shot (Depo-Provera), both Both are very effective and suitable for mothers who are breastfeeding.
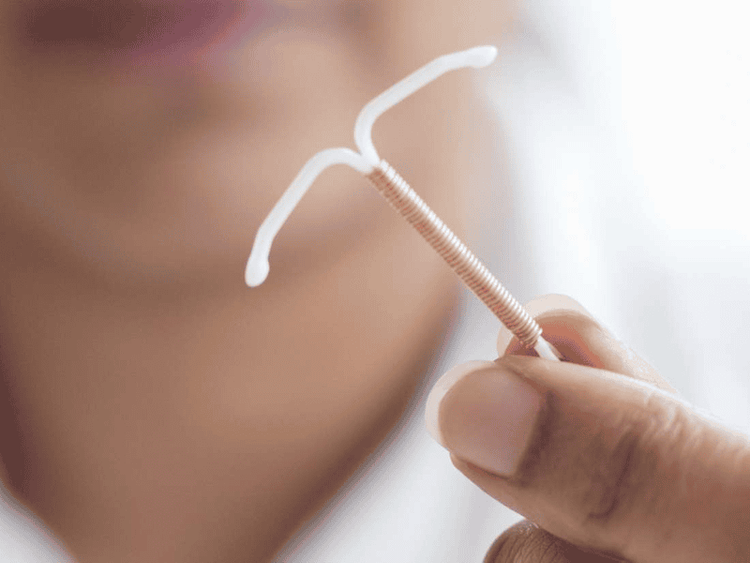

Vòng tránh thai cũng là một phương pháp tránh thai an toàn
If you want to get pregnant again, stop using this birth control pill. You don't have to take all your pills unless you want to. The effect of birth control only lasts for 24 hours after you take the last pill.
Some doctors recommend using a barrier method of birth control, such as a condom or a diaphragm, and waiting until you have had a few normal periods before trying to conceive because of this. This can help you determine your due date more accurately. If you get pregnant before your period returns to normal, don't worry, you can get an early ultrasound to determine when you're pregnant.
(Note: Taking folic acid or a prenatal vitamin at least a month before you start trying to conceive will help prevent some birth defects. That means you can take supplements. this while you are still taking a progestin-only birth control pill.).
5. When can nursing mothers take progestin-only birth control pills?
If you are not breastfeeding, you can start taking progestin-only birth control pills soon after giving birth. In fact, since you can ovulate as early as three weeks after giving birth, you'll need to start taking birth control pills no more than 21 days after giving birth to prevent pregnancy if you have sex during this time. .
If you are exclusively breastfeeding, it is best to wait six weeks after giving birth to start using this birth control pill. By that time, your milk supply should be well established. Besides, if you're exclusively breastfeeding, you won't ovulate for the first six weeks after giving birth, so there's no reason to start taking birth control before that.
If you only breastfeed occasionally and supplement your baby with formula, you will need contraception earlier than six weeks after giving birth if you plan to have sex during that time, so you can start using it. Use a progestin-only birth control pill for three weeks after giving birth.
If you decide to wait longer to start using this contraceptive, you can use it whenever you want, as long as you are sure that you are not pregnant, that is, if you have not had sex since giving birth or your last period, or if you have used another method of contraception regularly and as directed. If you start menstruating again, you can prevent pregnancy by starting a progestin-only pill on the next day of your period.

Nếu bạn không cho con bú, bạn có thể bắt đầu dùng thuốc tránh thai sau sinh
6. Do I need to use another backup method of birth control when I first start taking a progestin-only pill?
If you are menstruating and start using progestin-only birth control pills on the first day of your period, you do not need to use a backup method. If you start at any other time in your cycle, you'll need to use a backup method, such as condoms, from the start. Some experts recommend using a backup method of birth control for the first 48 hours after starting a progestin-only birth control pill, while others suggest using a backup method for seven days.
If you are using the LAM method of contraception), that is, you are exclusively breastfeeding for less than six months after giving birth and you have not started menstruating, your ability to prevent pregnancy has been reduced. up to 98%. Although you're not sure if you're pregnant, it's still a good idea to be cautious and use a backup method for the first 48 hours after starting a progestin-only birth control pill.
7. How to use progestin-only birth control pills
Before you start taking the medicine, read the instructions for use carefully. If anything is confusing, call your doctor and see the instructions for exactly how to take the medicine. Make sure you always have a backup pack of pills so you won't have a problem if the pharmacy closes or the medicine you take is no longer available.=
You will also need to carry a condom for backup birth control. when you first take your birth control pill, if you take it more than three hours late or forget to take it, or you run the risk of getting a sexually transmitted infection.
Finally, consider emergency contraception just in case.
It is very important that you take your pills at the same time every day and never miss a pill. Progestin-only birth control pills are a very low-dose contraceptive and you can't go wrong, especially if you're not exclusively breastfeeding. If you take your pill just three hours late, you'll need to abstain from sex or use a backup method for the next 48 hours.
Also, the contraceptive effect of progestin-only birth control pills on cervical mucus is highest 4 to 22 hours after you take it. So, if you usually have sex before bed, it's best to establish a regular pill time earlier in the day. Set your cell phone clock or alarm as a reminder.
Uống thuốc tránh thai nhưng bạn vẫn có nguy cơ bị mắc bệnh lây nhiễm qua đường tình dục
You may not have a period while on a progestin-only contraceptive or you may have irregular bleeding, but you will still take one pill a day, whether you are bleeding or not. And even if you don't have sex often, you still need to take the pill every day, or you won't be able to prevent pregnancy during sex.
Finally, if you or your partner is having sex with anyone else, you need to make sure your partner uses a latex condom (or a male or female polyurethane condom, if one in two is allergic to latex) every time you have sex. Birth control pills will not protect you against sexually transmitted diseases (STDs) like HIV, gonorrhea, chlamydia...
8. What happens if I forget to take a pill?
If you take your pill about 3 hours apart from your daily dose, take one pill as soon as you remember: This means taking two pills on the same day. Then continue to take one pill per day as usual. You will need to abstain from sex or use a backup method of birth control for the next 48 hours after you take the missed pill (unless you meet the criteria for LAM, as mentioned above).
If you feel confused about what to do, do not hesitate to call the medical staff or the clinic that prescribed the medicine for you. In the meantime, continue to take one pill a day and use backup birth control as well. If you suspect that you are pregnant, contact your doctor.
Note: If you have unprotected sex before you can have sex again within 48 hours after taking the pill, using emergency contraception will reduce your risk of pregnancy. It can work up to 120 hours (five days) after you have sex, but is most effective if used within the first 12 hours.
You can use emergency contraception, but you will need to check with your healthcare provider to see if your brand is right, if you have the right amount and how to take it.

Nếu quên liều thuốc, bạn có thể uống ngay 1 viên khi nhớ ra
9. Are there any medications that can reduce the effectiveness of progestin-only birth control pills?
Some drugs and herbal preparations can affect how oral contraceptives work, and vice versa: Progestin-only birth control pills can make some other medicines less effective. So check with your doctor if you're taking a medication other than a progestin-only birth control pill.
Conversely, you also need to tell your doctor about the medicine you are taking before using the progestin birth control pill. Some medicines can make progestin-only birth control pills less effective, such as the antibiotic rifampin, an antifungal medicine called griseofulvin, barbiturates, some HIV medicines, and others.
If you need to take a medication that could potentially make a progestin-only pill for a long time, talk to your doctor about other methods of birth control. If you're only taking the pill for a short time, you can continue to use a progestin-only pill, but you'll need to use backup contraception at the same time and for 48 hours after the pill is cleared from your body. body.
Because some drugs take longer to clear from the body, you may need to use a backup method for a few days after you stop taking them.

Khi sử dụng thuốc tránh thai bạn nên tham khảo ý kiên bác sĩ
10. Unwanted effects of birth control pills containing only progestin
If you vomit about 2 hours after taking the pill, you do not need to take another pill. If you vomit earlier, take another pill.
If you have sex while sick or 48 hours later, use a backup method. While you're sick, your body may not be able to absorb enough of the hormone from the pill to work as a contraceptive.
The most common side effect of progestin-only birth control pills is light, unpredictable vaginal bleeding or spotting. This is even more common if you forget to take your medicine or take it late.
You can continue to have regular periods, but your period may be shorter and may last longer than usual. Your periods may also become irregular or stop altogether. A small percentage of women using progestin-only birth control pills experience prolonged or heavy menstrual bleeding.
If you are breastfeeding, you will not have a period for many months after giving birth. And taking progestin-only birth control pills can delay your period longer.
Although rare, the use of progestin-only birth control pills can cause headaches, breast tenderness, and nausea. Some less common effects include weight gain, mood swings, acne...
Contact your doctor right away if you have any of the following:
Abdominal or pelvic pain Bleeding unusually heavy or frequent vaginal discharge Severe headaches Jaundice (your skin or eyes become unusually yellow) Also call your doctor if you think you may be pregnant. As long as you've taken your pills regularly and correctly, a missed period doesn't mean you're pregnant. But if you miss your period after several months of regular periods, contact your doctor.
Switching birth control methods can be complicated. You don't have to finish your current pack or wait until your period starts to switch to a new method. In fact, you may need to start a new birth control method a week before you stop using your old method.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.
Reference source: babycenter.com