This is an automatically translated article.
The article was professionally consulted by Specialist Doctor I Nguyen Hung - Endocrinologist - Department of Medical Examination & Internal Medicine - Vinmec Danang International HospitalUrinary tract infection is a disease that is easy to catch and very easy to recur. The disease can occur at any age as well as sex. Recurrent urinary tract infections not only cause discomfort due to inflammatory symptoms, bladder irritation, but also have the risk of causing dangerous complications that greatly affect the patient's health.
1. What is a urinary tract infection?
The human urinary system consists of the urethra, bladder, prostate gland (in men), ureters, and two kidneys. Urinary tract infection is an infection of one or more parts of the urinary system, characterized by the presence of bacteria in the urine or symptoms indicative of bacterial colonization of the organs. From an anatomical perspective, urinary tract infections can be divided into two groups:
Upper urinary tract infection: is an infection from the kidney to the orifice of the ureter in the bladder wall, the most common site of infection is: renal parenchyma and the wall of the renal calyces, the characteristic pathology is acute pancreatitis - pyelonephritis. Patients have typical symptoms such as high fever, chills, low back pain on one side, painful urination, frequent urination, blood in urine, cloudy urine. General symptoms are nausea, vomiting, body fatigue, weight loss, insomnia. Lower urinary tract infection: is an infection of the bladder, urethra and the male genitals, testicles and prostate gland. The forms of lower urinary tract infection can be: urethritis, cystitis, prostatitis, acute orchitis, epididymitis... If acute cystitis is present, the patient usually does not have a fever. . However, if prostatitis, orchitis is often high fever 39-40 degrees. Occurrence of symptoms of bladder irritation such as painful urination, frequent urination, cloudy urine, pain in the lower abdomen. If you have epididymitis or orchitis, you may experience severe scrotal pain.
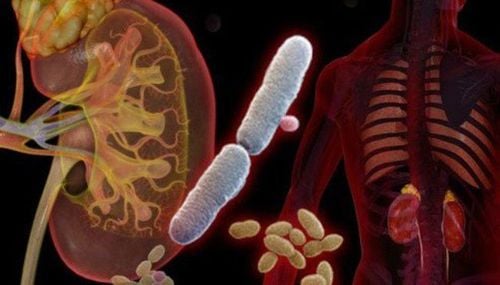
E. coli is the cause of more than 75% of urinary tract infections. Other common bacteria are: group D streptococcus, staphylococcus aureus, Leptospira, Salmonela, anaerobic bacteria Mycoplasma, Corynebacteria,... Bacteria invade urinary organs through 4 main ways:
The bacteria travel upstream, from the urethra, to the bladder, and then to the kidneys. This is the main entry route for bacteria. Blood-borne infections, the type of bacteria that often invade the bloodstream are cocci, often causing damage and abscesses in the renal cortex. Bacterial invasion through the lymphatic route: Infection in the colon through the lymphatic system can reach the urinary tract. However, this route of infection is rarely encountered in practice. Bacteria from nearby organs such as abscesses in the appendix, colitis, etc. can cause bladder infections.
2. Prevention of recurrent urinary tract infections
Urinary tract infection is a very common disease, it can occur in any gender, any age.In women, due to the short urethral structure, if not properly cleaned during menstruation, after intercourse or after defecation, bacteria can easily enter the bladder causing recurrent urinary tract infections. many times. Other causes of urinary tract infections in women are anatomical abnormalities, narrowing of the urinary opening, urethral diverticulum, etc., due to women in menopause, hormonal changes and urine pH changes. allow bacteria to enter. The causes of urinary tract infections in men are: unprotected sex, causes that obstruct or block urine drainage such as ureteral strictures, stones, sclerosis of the bladder neck, urethral strictures. ,... In elderly men, the most common cause of urinary tract infections is an enlarged prostate gland that compresses the urethra, leading to urine stagnation. Urinary tract infections in children are often caused by congenital malformations of the urinary tract.

To prevent complications and prevent recurrent urinary tract infections, it is necessary to note the following points:
When there are symptoms of UTI, it is necessary to actively treat, follow the instructions of the doctor, use drugs exactly as prescribed, absolutely do not buy drugs for treatment, do not arbitrarily stop taking medicine without consulting a doctor, do not use prescriptions of previous treatments when using for infections urinary recurrence. In women, special attention should be paid to hygiene before and after sexual intercourse. After defecation and urination, pay attention to cleaning from front to back, not in the opposite direction because bacteria from the anus can enter the ureter. Choose the right type of feminine hygiene solution, use it every day to prevent infection. For patients with recurrent UTIs more than 2 times in 6 months, doctors may prescribe low-dose prophylactic antibiotics for many months. Thorough treatment of prostatitis, which is the main cause of recurrent urinary tract infections in men. Drink plenty of water, more than 2 liters a day. Do not hold urine, holding urine will cause urine retention, creating favorable conditions for bacteria to invade. Patients with repeated urinary tract infections, if the above measures do not improve, should see a nephrologist - urologist to check the body for urinary malformations or urinary stones. are not. At Vinmec International General Hospital, we are implementing a urological screening package with many utilities, including: Early detection of possible urinary diseases. Especially prostate diseases (benign prostatic hypertrophy, prostate cancer). The pathology of urinary stones .... thereby helping customers take preventive measures.
When registering for the urological screening package, customers will be examined by urology specialist, ultrasound, urine culture... to detect disease accurately and timely.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.