This is an automatically translated article.
The article was written by MSc Ta Quoc Ban, Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology - Vinmec Phu Quoc International General HospitalPostpartum infection is a dangerous disease that can cause bacteremia. This disease is caused by a number of bacteria such as: E.Coli, staphylococcus, streptococcus... caused. The forms of postpartum infection are very diverse, depending on the form, the treatment will be different.
1. Overview
Postpartum infection is an infection that occurs in a pregnant woman after giving birth that starts from the genital tract (Vagina, cervix, uterus).
Some common pathogenic bacteria
There are many types of bacteria causing postpartum infections: Staphylococci, streptococci, E. Coli, anaerobic bacteria such as Clostridium, Bacteroides.
Route of transmission: From the vagina through the cervix, through the fallopian tubes into the peritoneum.
Crossing the surface of vegetables causes blood infection.
Favorable factors: Poor nutrition, anemia, pregnancy toxicity, premature rupture of membranes, premature rupture of membranes, prolonged labor, vegetable peel procedure, uterine control, fluid closure...
2. Postpartum infection patterns
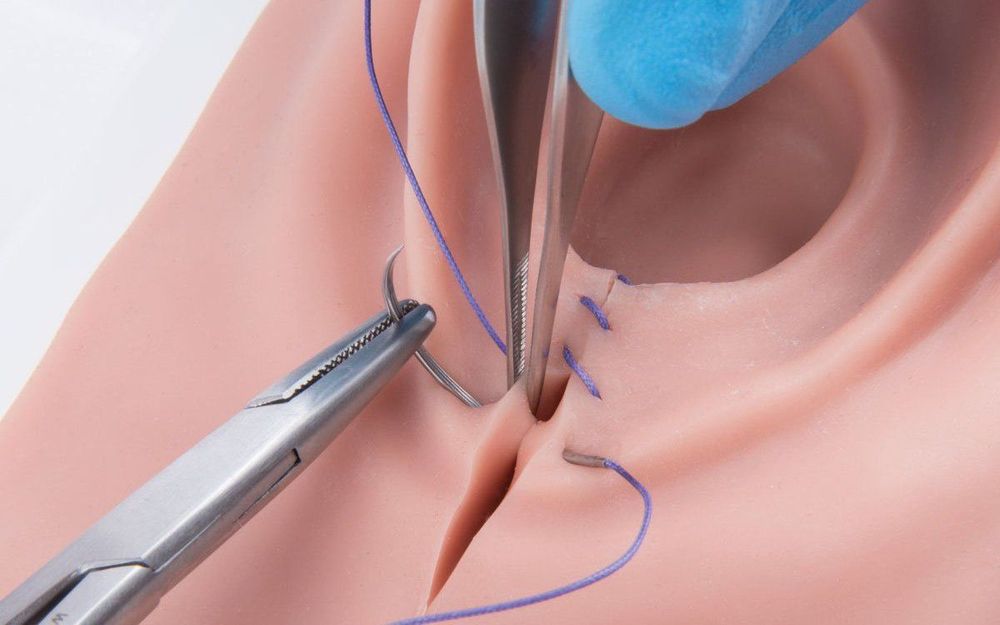
Nhiễm khuẩn tầng sinh môn có thể do khâu phục hồi tầng sinh môn không đúng kỹ thuật
2.1 Infection of perineum, vulva, vagina Cause
Perineal stitches are not sterile, perineal restoration stitches are not technically correct or not sutured, gauze is left in the vagina.
Symptoms
Fever is not high: 37.5-380C
Local wound: Swelling, redness, pain, festering.
Product does not smell.
Treatment
Topical care: Wash with antiseptic; cut thread when festering, close sanitary loincloth, sterile gauze.
2.2 Endometritis Cause
Remaining placenta, membranes left over, amniotic fluid infection, uterine control procedures, non-sterile artificial vegetable peel.
Symptoms
Fever 38 - 3805 (a few days after giving birth), fatigue, discomfort; The discharge is profuse, foul, mixed with blood and pus...; The cervix is dilated, the uterus is slow to contract, and the uterus is painful; Culture the fluid for bacteria and make an antibiotic chart; The more severe form of endometritis is generalized metritis. The inflammatory process spreads to the muscular layer of the uterus, there are small abscesses. Clinical symptoms are more severe than endometritis, easily causing peritonitis or bacteremia.
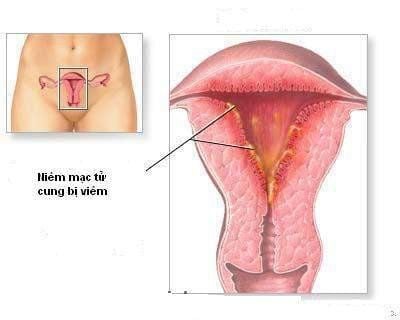
Viêm niêm mạc tử cung
Treatment
Use systemic antibiotics: Ampixilin, Gentamixin; Drugs to increase uterine contractions: Oxytocin, Ergotin; If the vegetable is left over, wait until the temperature drops or the fever disappears before curettage of the uterus; If the metritis is total, a partial hysterectomy and blood cultures are required to detect bacteremia early. 2.3 Pelvic peritonitis The inflammatory process is not localized to the uterine lining but develops into the pelvis and forms pseudomembranous tissues in the pelvic organs and causes adhesions. The reaction of the peritoneum will produce pockets of fluid mixed with blood and pus.
Symptoms
More widespread endometritis. Average 7 - 15 days; The temperature gradually increases from 39 - 400C, chills, fatigue, dirty tongue, bowel disorders...; There is abdominal wall reaction in the pelvis, the abdomen is mildly distended, the upper part of the pelvis is soft, the abdomen is soft; Vaginal examination: Small cervix, enlarged uterus, painful mobility; Vaginal sacs: swelling, pain; Vaginal examination combined with abdominal manipulation: the pelvic area has a solid, non-moving, painful mass; The white blood cell count is increased, and the fluid culture is done to look for bacteria that cause the disease. Progression: May be resolved with aggressive treatment, may develop into generalized peritonitis.
Treatment
Rest, ice, high-dose antibiotics, combination. If Apxe Douglas is extracted and drained through the sacroiliac pouch.

Kháng sinh liều cao giúp điều trị viêm phúc mạc tiểu khung
2.4 Total peritonitis Cause
After cesarean section is not sterile; After endometritis, total metritis is not well treated; After vegetable peel procedures, control the uterus; It is possible that bacteria spread from the pyelonephritis causing peritonitis. Symptoms
7 - 10 days after giving birth, or 3 - 4 days after cesarean delivery; Systemic symptoms: Dry lips, dirty tongue, sunken eyes, signs of toxicity, infection; Defecation is sometimes loose, defecation; Abdomen with abdominal wall reaction or peritoneal palpation (often unknown); Abdominal X-ray unprepared: Abdomen with dilated bowel loops, with water and gas levels; Electrolyte: Ca++, Cl- components decreased; Differential diagnoses with pelvic peritonitis, functional enterocolitis. Treatment
Systemic antibiotics; Replenish water, electrolytes; Partial hysterectomy ; Wash and drain the abdomen. 2.5 Sepsis is the most severe form of postpartum infection.
Symptoms
Whole body: Continuous high fever, fluctuating temperature, accompanied by high fever with chills, whole body fatigue, signs of infection, intoxication: dry lips, dirty tongue, difficulty breathing, yellow skin, dark urine; Obstetrics: Dilated cervix, enlarged uterus, slow contraction; painful uterine pressure; foul, dirty and bloody discharge; Auscultation: There may be rales;

Nhiễm khuẩn huyết dẫn đến sốt cao liên tục
Blood culture, fluid culture: If positive is certain, negative is not excluded, mainly based on clinical; Other tests: Decreased red blood cells, increased white blood cells, mainly neutrophils, decreased Hematocrit; Complications: Possible functional renal failure, interstitial nephritis, lung abscess, endocarditis. brain abscess, meningitis ...; Prognosis: Depends on the source of secondary infection and whether the treatment is correct and timely. Treatment
Use antibiotics according to the antibiogram. When no antibiogram is available, broad-spectrum antibiotics should be used: Cephalosporin; flagyl, quinolone group...; Combination of blood transfusion, heart support...; When temperature returns to normal or falls: partial hysterectomy to rule out primary infection. Prevention of postpartum infections
Treatment of inflammatory foci during pregnancy: Urinary tract infections, genital... Prevention of amniotic infections and prolonged labor. Birth: Do not leave vegetables, specify uterine control correctly, follow good hygiene and sterilization regime, specify correct episiotomy After childbirth: Avoid holding fluid, clean, and take care of the floor. correct biology. To get the best care and health protection during pregnancy and postpartum, to prevent postpartum infections and other dangerous diseases, pregnant women should use maternity services at medical facilities. reputation.
At Vinmec International General Hospital, there is a package maternity service as a solution to help pregnant women feel secure because of the companionship of the medical team throughout the pregnancy. When choosing Maternity Package, pregnant women can:
The pregnancy process is monitored by a team of highly qualified doctors Regular check-ups, early detection of abnormalities The package pregnancy helps to facilitate Convenience for the birthing process Newborns receive comprehensive care To register for examination and treatment at Vinmec International General Hospital, you can contact the nationwide Vinmec Health System Hotline, or register Check online HERE.