This is an automatically translated article.
The article is professionally consulted by Dr. Le Duc Hiep - Internal Medicine and Cardiovascular Interventionist - Cardiovascular Center - Vinmec Times City International General Hospital.Coronary stents are a big step forward in the treatment of diseases related to the vascular system that feeds the heart. This is the most specific treatment for ischemic heart disease caused by coronary stenosis, especially acute myocardial infarction. However, patients should continue to be closely monitored for progress after the intervention because there are a number of possible complications after coronary stenting.
1. Complications after coronary stenting
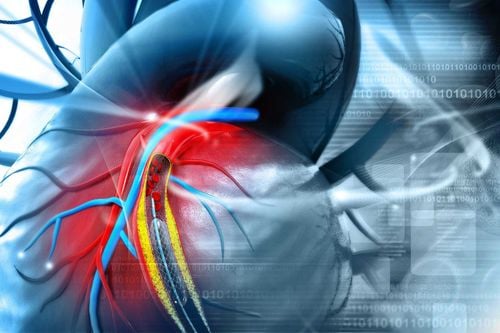
1.1. Stent is essentially a metal frame, which is placed inside the coronary lumen as a support with the task of widening the lumen of the narrowed coronary branches as well as fixing the vessel wall to prevent blockage. come back. Currently, coronary intervention usually uses two main types of stents: conventional stents and drug-eluting stents.In which, drug-eluting stent is a special type because it is coated with a layer of drug that is gradually released into the vessel lumen after stenting to limit the formation and growth of scar tissue; Thereby, helping to keep the artery lumen always smooth and coronary artery not narrowing.
The first and serious coronary stenting complication that needs to be mentioned is the formation of a blood clot (thrombus) in the stent lumen, causing blockage of the artery again. Besides, the patient still has manifestations of myocardial ischemia or even a re-infarction. Blood clots can form at any time, possibly immediately after a stenting procedure. Therefore, anticoagulation should be used during adequate intervention and maintenance of antiplatelet drugs before and after stenting as prescribed by the physician seriously. The drug should not be stopped or stopped to avoid the formation of blood clots causing acute coronary occlusion. Patients need to adhere to the treatment, take the medicine regularly and not stop taking it on their own. This will help prevent blood clots. Many large studies around the world have shown that stopping these drugs increases the mortality rate due to stent thrombosis.
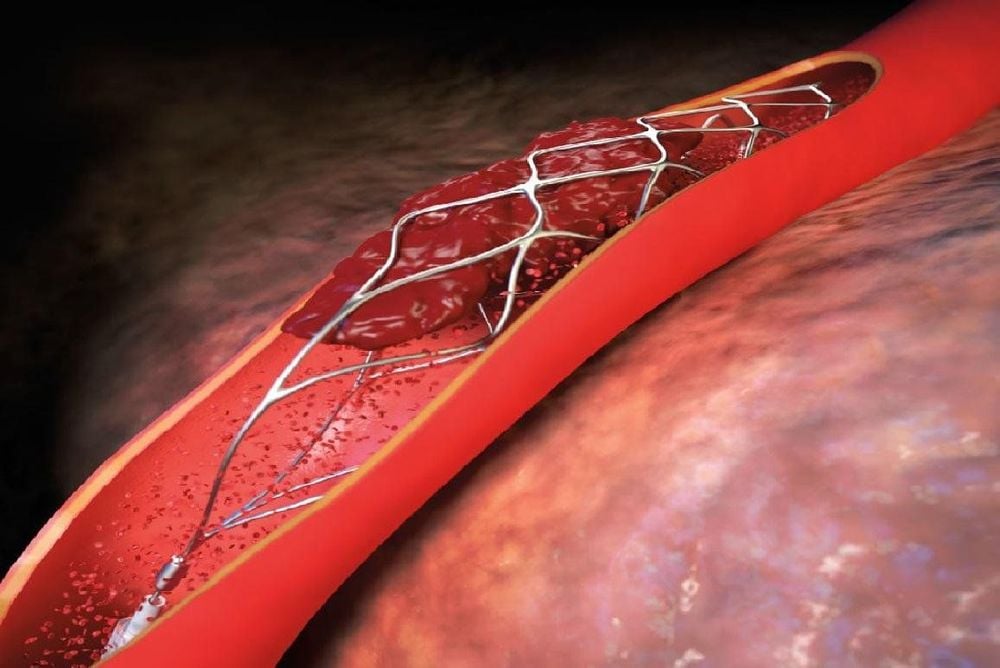
Tình trạng huyết khối trong lòng stent xuất hiện sau đăt stent mạch vành.
1.2. Bleeding from antiplatelet drugs As mentioned above, most patients need to use anticoagulants after stenting to prevent thrombosis. Therefore, a complication after coronary stenting associated with the use of antiplatelet agents (eg, aspirin, clopidogrel) is an increased risk of bleeding. In which, the most important and common is gastrointestinal bleeding due to gastric ulcer.
Patients with a history of hemostasis disorder or previous gastric bleeding should inform the treating physician because these are absolute contraindications to anticoagulants.
Some other bleeding conditions the patient may experience such as bleeding under the skin or places with medical intervention such as inserting a needle or catheter. Bleeding may be mild, discontinuation can be adjusted. But some cases of heavy bleeding can be life-threatening. Therefore, doctors and medical staff need to closely monitor bleeding after stenting.
1.3. Re-stenosis after stenting Stenting does not mean that the coronary artery is completely protected, without restenosis. Complications of coronary stenting can be encountered as coronary artery blockage again due to the formation of atherosclerotic plaque at other sites or at the stent site itself. This coronary stent complication rate is about 15% for classical stents and is reduced to 10% for drug-eluting stents.
Drug-eluting stents significantly reduce the risk of restenosis, but do not completely prevent this risk. Therefore, patients are always combined with drug therapy after stenting to minimize the risk of restenosis.
1.4. Stroke An ischemic stroke can occur during or after coronary stenting. During the procedure, the catheter inadvertently sloughs off plaque in the blood vessel, and it is these plaques that travel through the blood stream causing blockage of the cerebral blood vessels. However, patients should not be too worried about this complication because the rate of stroke complications is very low.

Đột quỵ nhồi máu não có thể xảy ra trong hoặc sau quá trình đặt stent mạch vành.
1.5. Coronary artery injury Coronary stenting is an invasive procedure. Therefore, during the intervention, the coronary artery itself can be seriously damaged. In particular, on the background of coronary atherosclerotic lesions, procedures such as balloon angioplasty can lead to rupture of the coronary artery. There are many methods to manage complications that cause coronary artery damage during the intervention; Depending on the specific situation, the interventional doctor will conduct treatment such as autologous fat injection to seal the coronary leak, place a stent cover, in some cases, emergency surgery can be performed to manage complications.
1.6. Cardiac Arrhythmias Because stenting is a direct intervention to the heart, some patients may experience arrhythmia complications such as too fast or too slow heart rate. Especially dangerous ventricular arrhythmias. However, the majority of arrhythmias are the result of myocardial infarction. Therefore, the implementation of the intervention will improve the arrhythmia and the patient's prognosis. After coronary stent intervention, there were many cases of arrhythmias; some of which are derived from myocardial infarction scars or the consequences of myocardial ischemia.
1.7. Some other complications Besides the complications after stenting the upper coronary artery, the patient may have some of the following conditions:
Bleeding at the catheter puncture site. Contrast allergy or anaphylaxis. Acute renal failure due to contrast media used in the intervention.

Người bệnh có thể gặp biến chứng suy thận câp do thuốc cản quang dùng trong can thiệp.
2. How to deal with complications after coronary stenting
Complications after coronary stenting are very low and most of them can be managed by doctors depending on the severity and severity. It is important that patients fear complications that delay this procedure. To maximize the effectiveness and limit the complications of coronary stenting, the doctor must conduct a careful clinical examination, take a complete medical history, and perform the necessary tests to evaluate the overall health of the patient. patient body.
In fact, the danger of coronary stenting complications while the patient is still in hospital is not worrisome. The most frightening thing is the period when the patient is treated on an outpatient basis with different drugs.
Stent placement does not mean that the patient is completely healthy, but the patient needs to maintain long-term medications, possibly for life. Among them, antiplatelet drugs are the most associated with complications after coronary stenting. Patients need to adhere to the treatment, not arbitrarily stop or use the wrong drug.
In addition, to limit the complications of coronary stenting, patients need to fulfill the following requirements:
Do not do heavy or overexertion during the first week after stent placement. Limit physical exertion for 4 days after surgery. Limit heavy sports in the first week such as jogging, swimming, tennis or football, etc. Use the medicine exactly as indicated after performing stent angioplasty. Periodic check-ups according to the instructions of the doctor, depending on the condition of each patient. Maintain a scientific and reasonable diet: Do not use alcohol, beer, coffee, tobacco, greasy foods, limit sweet or excessive eating. Diet rich in green vegetables and fruits. Maintain ideal weight, lose weight if obese. Practice gentle exercises such as yoga, meditation, ... to maintain health and promote the body's recovery process.

Người bệnh có thể tập các bài tập nhẹ nhàng giúp thúc đẩy quá trình hồi phục cơ thể.
3. When should a follow-up visit?
After coronary stent placement and hospital discharge, the doctor will continue to treat the patient with different drugs. Therefore, patients need to strictly follow the doctor's treatment, especially antiplatelet drugs to limit coronary stenting complications.
Most patients are scheduled to be re-examined at the cardiology clinic every month or every 3 - 6 months when the patient's condition is stable. However, when there are abnormal signs such as severe chest pain, shortness of breath, especially when exerted with dizziness, lightheadedness, nausea, signs of bleeding, etc., the patient needs to go to the hospital immediately. for the doctor to examine and treat appropriately. In addition, patients need to be coordinated between different specialties such as endocrinologists to control blood sugar levels, blood fats,... and minimize the risk of complications after coronary stenting. In order to limit the complications that occur after coronary stenting, patients should choose reputable medical facilities and specialized hospitals to perform and monitor and re-examine after the procedure.
Currently, at the Cardiovascular Center - Vinmec Times City International General Hospital is applying very effectively and safely techniques of coronary angiography, balloon angioplasty, angioplasty and coronary stenting; meet the needs of timely and effective examination and treatment of acute diseases such as acute myocardial infarction, cardiogenic shock, bradyarrhythmias requiring emergency medical equipment. The process of treatment and coronary stenting at Vinmec is always coordinated between specialties under the supervision of a team of experienced medical professionals, thus limiting the risk of possible complications. After the treatment process, the patient will also be monitored, re-examined, early recognition of complications (if any) for urgent treatment, ensuring long-term health for the patient.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.