This is an automatically translated article.
Stillbirth is the death of a fetus in the womb after the 20th week of pregnancy. Stillbirth leaves parents with difficult-to-relieve pain, even negatively affecting psychological well-being in later pregnancies. Understanding the causes and risks of stillbirth will help the mother proactively prevent this dangerous pregnancy complication.1. What is the cause of stillbirth?
A large proportion of stillbirths occur in otherwise unexplained healthy fetuses. However, there are still some causes that have been found, which are of great help in preventing stillbirth.
1.1 Due to complications of the placenta The placenta is a very important organ, playing a role in providing blood and nutrients for the life and development of the fetus. About half of stillbirths are related to abnormalities of the placenta, specifically a condition in which the placenta separates from the uterus, also known as placental abruption.
Currently, scientists are continuing to conduct more studies to find out more specific effects of placental complications on stillbirth.
1.2 Other causes of stillbirth Here are some direct or indirect causes of stillbirth in pregnant women:
Bleeding (hemorrhage) before or during labor; Placental abruption : A condition in which the placenta detaches from the uterus before the baby is born, which may manifest as bleeding or abdominal pain in the mother; Preeclampsia: A pregnancy complication that causes high blood pressure in pregnant women; Umbilical cord problems: The umbilical cord can protrude into the uterus before birth (umbilical cord prolapse), blocking the baby's oxygen supply before she can breathe on her own; may tightly wrap or knot around the fetal neck and limbs; Cholestasis of pregnancy or obstetric cholestasis (ICP): A liver disorder that causes severe itching in pregnant women; Birth defects, with or without chromosomal abnormalities; Pre-existing medical conditions in the mother, eg diabetes, hypertension; Exposure to environmental toxins during pregnancy, such as pesticides or carbon monoxide (CO); History of the mother or family history of thrombosis , thrombophlebitis or pulmonary embolism ; Infection during pregnancy.

Tiền sản giật thai kỳ có thể gây thai lưu
1.3 What are the infectious diseases that cause stillbirth? One in ten stillbirths is caused by an infection during pregnancy. Infections are usually caused by bacteria moving from the vagina into the uterus. This group of bacteria includes: group B streptococcus, escherichia coli (E.Coli), klebsiella, enterococcus, haemophilusenza, chlamydia, mycoplasma or ureaplasma.
Some bacterial infections, such as chlamydia , mycoplasma or ureaplasma are sexually transmitted diseases and can be prevented by using condoms.
Other infectious diseases that can cause stillbirth include:
Rubella : Especially dangerous for pregnant women in the first 3 months. Viruses transmitted from mother to child during this period can cause birth defects; Influenza: Experts recommend that pregnant women get a seasonal flu vaccine, at any stage of pregnancy; Parvovirus B19: The virus causes "red cheeks" syndrome - a common infection in children, very dangerous for pregnant women; Coxsackie virus: Causes hand, foot and mouth disease; Cytomegalovirus: A common virus spread through body fluids, such as saliva or urine, that causes some symptoms in the mother; Herpes simplex: The virus that causes genital herpes and mouth sores; Listeriosis: An infection that occurs after a pregnant woman eats food contaminated with the bacteria listeria monocytogenes, found in milk and dairy products that have not been properly refrigerated, but also in pate, raw meat or frozen,... Leptospirosis: An infectious disease spread by rats; Lyme : A rare disease transmitted from ticks to humans and animals; Q fever: Infection caused by bacteria from animals such as sheep, goats, cows; Toxoplasmosis: An infection caused by parasites in the soil or cat feces; Malaria: A serious tropical disease caused by the Plasmodium parasite that is transmitted from person to person through mosquito bites.
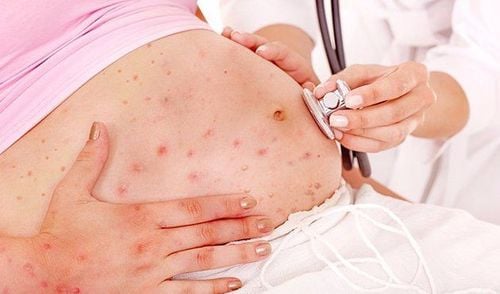
Mẹ bầu nhiễm Rubella trong 3 tháng đầu thai kỳ có thể gây thai lưu
2. Risk factors for stillbirth
Pregnant women at high risk of stillbirth include:
Pregnancy with twins or multiples; Fetal malnutrition; Women over 35 years old; Women who smoke, drink alcohol or abuse drugs during pregnancy; Obesity, with a body mass index (BMI) over 30; Have a pre-existing medical condition, eg epilepsy.
3. How to prevent stillbirth?
Based on the known causes of stillbirth, pregnant women or those planning to become pregnant can take steps to reduce their risk of stillbirth.
These measures include:
No smoking, avoiding places with smoke; Avoid alcohol and drug use during pregnancy. These agents can increase the risk of miscarriage and stillbirth, as well as seriously affect fetal development; Go for regular antenatal check-ups to closely monitor the baby's health progress; Ensure a healthy weight before deciding to get pregnant; Protect yourself from infections and avoid eating foods that are not good for pregnancy; If you experience abdominal pain or bleeding, notify your doctor as soon as possible (preferably the same day); Monitor fetal movements and talk to your doctor if you notice any unusual signs; As for the issue of weight during pregnancy, medical experts say that obesity increases the risk of stillbirth. The best way to ensure the health of mother and baby is to maintain a healthy pre-pregnancy weight (reaching a normal BMI). This way, you can reduce your risk of all the problems associated with obesity during pregnancy.
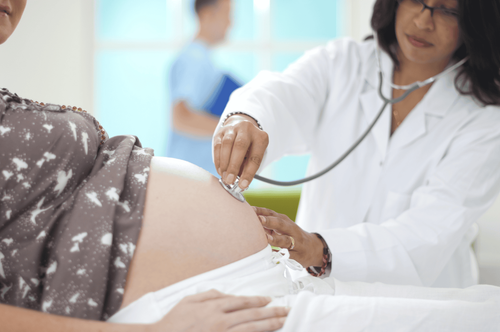
Mẹ bầu nên đi khám thai định kỳ đầy đủ để theo dõi sát diễn biến sức khỏe của em bé
If a woman has been obese during pregnancy, she should consult a doctor to improve her health. A healthy diet and reasonable exercise regime (such as walking or swimming...) are very good for pregnant women's health. However, before choosing a sport, pregnant women should consult a doctor to see if that sport is suitable for her body condition and how intense it should be.
In addition, many studies suggest that the sleeping position of pregnant women is also related to stillbirth. Specifically, pregnant women over 28 weeks of age sleeping in the supine position, with the back facing the bed can double the risk of stillbirth. This is explained by the lying position affects the flow of blood and oxygen to the fetus. According to experts, the safest sleeping position for pregnant women over 28 weeks is lying on the left or right side.
Stillbirth usually occurs in the 20th week corresponding to the second 3 months of pregnancy. To protect the health of both mother and baby, and to prevent stillbirth at this stage, pregnant women need to be cautious and pay attention to the following issues:
Comprehensive fetal malformation screening by ultrasound technology outstanding 4D sound. Screening for gestational diabetes, avoiding many dangerous complications for both mother and baby. Control the mother's weight reasonably to assess the health status of the pregnant woman and the development of the fetus. Understand the signs of threatened early delivery (especially in those carrying multiple pregnancies or having a history of miscarriage or premature birth) so that they can receive timely treatment to maintain pregnancy. To protect mother and baby during pregnancy, Vinmec provides a comprehensive Maternity service to monitor the health status of mother and baby, periodical antenatal check-ups with leading Obstetricians and Gynecologists. enough tests, important screening for pregnant women, counseling and timely intervention when detecting abnormalities in the health of mother and baby.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.
Reference source: webmd.com; nhs.uk