This is an automatically translated article.
The article was professionally consulted by a Doctor of Obstetrics and Gynecology - Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology - Vinmec Hai Phong International General Hospital.Amniotic fluid plays an important role in the survival and development of the fetus. The amount of amniotic fluid of each woman can be different and increase or decrease depending on the time of pregnancy. In the case of too much amniotic fluid in the womb, which is called polyhydramnios, there is a high risk of causing kidney failure in the baby. Therefore, mothers need to understand well to have timely prevention and treatment methods.
1. What is polyhydramnios?
Polyhydramnios is a high-risk pregnancy for women about the cause of polyhydramnios and warns of the risk of preterm birth during pregnancy.Amnionic fluid index (AFI) > 24 - 25 cm, or when greater than the 95th or 97th centile for gestational age. To confirm the diagnosis of polyhydramnios, the doctor will do an ultrasound. Polyhydramnios occurs in about 1% of pregnancies...
Trắc nghiệm: Bạn có hiểu đúng về dấu hiệu mang thai sớm?
Các dấu hiệu mang thai sớm không phải chỉ mỗi trễ kinh mà còn có rất nhiều dấu hiệu khác như xuất huyết âm đạo, ngực căng tức,… Điểm xem bạn biết được bao nhiêu dấu hiệu mang thai sớm thông qua bài trắc nghiệm này nhé!
Acute polyhydramnios Acute polyhydramnios usually occurs at 16-20 weeks of pregnancy, usually induces labor before 28 weeks, or because symptoms are so severe that the pregnancy must be terminated.
The main symptoms are caused by the rapid growth of amniotic fluid causing the uterus to enlarge rapidly, pressing on the diaphragm, causing difficulty breathing. The visual appearance depends on the extent of polyhydramnios and how quickly the onset of the disease is:
Rapidly enlarged and distended abdomen. The uterus is tight and painful. The fetal parts cannot be palpated, and on close examination, there may be signs of floating stones. Fetal heart is hard to hear. Vaginal examination revealed distended lower segment, dilated cervix, and dilated amniotic fluid. Mother's edema and varicose veins, especially the lower extremities due to compression of the inferior vena cava. Difficulty breathing in the mother and subsequent respiratory failure may occur. Fetal structural malformations should be excluded by ultrasound in this setting because acute polyhydramnios may be associated with fetal malformations such as obstruction of the esophagus or upper gastrointestinal tract, anencephaly, and spina bifida. live (spina bifida)...
Polyhydramnios Polyhydramnios accounts for 95% of cases of polyhydramnios and usually occurs in the last months of pregnancy. The disease progresses slowly, making it easier for the patient to adapt to the symptoms. The patient does not have much pain and does not have as much dyspnea as in acute polyhydramnios.
In the last three months, you will feel heaviness in the abdomen, abdominal distension, shortness of breath, heart palpitations. Symptoms usually develop slowly. Amniotic fluid gradually increases to a large amount, causing the uterus to stretch, causing difficulty breathing and fatigue.
The doctor will examine:
The uterus is larger than the gestational age There are signs of waves crashing. Palpation is difficult to see the fetal poles and there are signs of floating stones. Vaginal examination reveals distended lower segment 3. Causes Maternal causes Diabetes before or during pregnancy is a common cause. If not controlled appropriately, polyhydramnios is easy. 10% of pregnant women with diabetes have polyhydramnios.
Anti-Rh antibodies and hemolytic diseases secondary to abnormal antibodies can cause severe fetal anemia or fetal edema associated with polyhydramnios. Hypertonic dystrophy (uncommon). Placental causes Choroidal hemangiomas can cause fetal heart failure and lead to polyhydramnios. Diseases that cause endometritis or placental lesions (syphilis). Fetal causes Fetal central nervous system abnormalities (cerebrovascular, neural tube defects) abnormalities. Structural defects of the digestive system (obstruction of the esophageal or alimentary canal). Fetal chromosomal abnormalities Non-immune edema: This phenomenon has a very poor prognosis and is often associated with polyhydramnios. A typical case of placental edema. Twin-to-twin transfusion syndrome is a disorder with a poor prognosis, occurring with an incidence of 15% in monochorionic, diamniotic twins, a complication of polyhydramnios in the recipient fetus. 4. Treatment of polyhydramnios Rest, diuretics, water and salt restriction are ineffective measures and should not be encouraged.
Acute polyhydramnios Amniocentesis : Relieves respiratory symptoms for the mother. This is only temporary therapy. Termination of pregnancy by induction of labor: If the fetus has a structural malformation or chromosomal abnormality, the doctor will advise the parents on the prognosis and several options to choose from, including termination of pregnancy. termination of pregnancy. Chronic polyhydramnios In case of mild disease, there is no need to intervene but just wait for the fetus to reach full term if there are no other obstetric indications.
If the mother has difficulty breathing, has abdominal pain or has difficulty walking, she needs to be hospitalized.
Medical treatment of polyhydramnios: Recently, people used Indomethacin to treat polyhydramnios. This drug works to reduce the amount of amniotic fluid secreted or increase the reabsorption of amniotic fluid, reduce fetal urine output and increase the exchange of fluid across the fetal membrane. However, Indomethacin causes premature closure of the ductus arteriosus if used for more than 48-72 hours or after 32 weeks of gestation. There are several other known fetal and neonatal complications associated with the use of Indomethacin. These include: increased rates of necrotizing enterocolitis in neonates, pulmonary hypertension, and neonatal renal insufficiency. Because of the above reasons, Indomethacin is rarely used in polyhydramnios and must be used with great care. Dosage: 1.5-3mg/kg/day. Induction of labor: when the pregnancy is 38-39 weeks or the pregnant woman has difficulty breathing or walking. Amniocentesis at birth: In cases of polyhydramnios, the doctor will actively press the amniotic fluid to reduce uterine tension and help labor progress smoothly, while limiting placental abruption and umbilical cord prolapse. Due to the large amount of fluid, when this fluid is withdrawn suddenly, there is a rapid decrease in pressure and contact area between the placenta and the uterine cavity, which can cause placental abruption and prolapse of the umbilical cord. Therefore, when performing the procedure, the doctor needs to perform the amniocentesis procedure cautiously, using a needle to slowly drain the amniotic fluid. It is necessary to be prepared for the caesarean section to prevent complications during amniotomy.
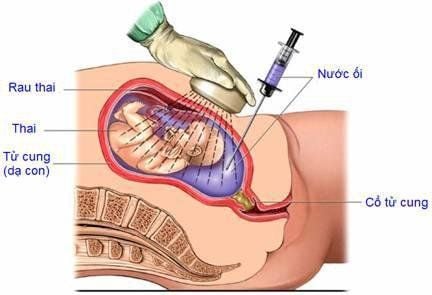
During labor, uterine contractions are usually weak due to the uterus being overstretched. Therefore, it is possible to press the amniotic fluid early to reduce the pressure of the amniotic cavity to help labor faster.
When there is amniotic fluid, pay attention to fix the fetal position to prevent prolapse of the umbilical cord.
If needed, uterine contractions can be supported with oxytocin infusion.
Because the uterus is too tight, there is a risk of postpartum bleeding due to uterine atony, so drugs must be given to contract the uterus immediately after birth
5. Prevention of polyhydramnios Eat adequate nutrition, drink enough water and reduce the amount of salt in the diet. Regular prenatal check-ups, prenatal screening tests as prescribed by the doctor. When there are signs of polyhydramnios, the doctor will closely monitor, do the necessary tests to find the cause and treat. So you need to follow the doctor's instructions. Polyhydramnios during pregnancy can pose dangers to both mother and baby not only during pregnancy but also during labor and child care later in life. Therefore, regular antenatal check-ups or prenatal screening tests are aimed at detecting abnormalities that may cause polyhydramnios. So don't forget your regular antenatal check-ups. Come to Vinmec International General Hospital for the best health advice.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.