This is an automatically translated article.
The article is written by MSc, Doctor Tran Thi Huyen Trang, Laboratory Department - Vinmec Times City International Hospital
Determination of PIVKA-II levels helps detect Vitamin K deficiency before routine coagulation test results change or bleeding occurs. PIVKA-II is not normally present, but in people with liver disease and malignant liver disease, PIVKA-II can be present even though the body is not deficient in vitamin K. PIVKA-II levels are determined to aid in the diagnosis. Diagnosis and prognosis in patients with HCC and monitoring of patients with HCC during treatment.
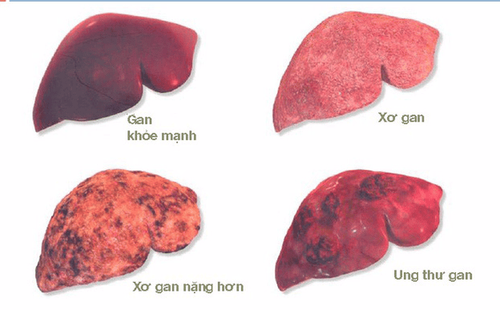
Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is the 6th most common cancer worldwide and accounts for more than 90% of primary liver cancers. According to statistics of the World Health Organization (WHO), Vietnam has the third highest rate of liver cancer by male sex in the world. In Vietnam, liver cancer ranks first among the most common cancers in men and fifth in women with the number of cases in 2018 being 25,335. The prevalence in our male population is 39/100,000 population, while the female prevalence rate is 9.5/100,000 population.
Hepatocellular carcinoma, if diagnosed at an early stage and properly treated, has a positive prognosis. The 5-year survival rate for treated patients is 50-70% depending on the study. Therefore, screening measures for early detection of hepatocellular carcinoma are currently very focused on research and development.
Ung thư gan đứng đầu trong các loại ung thư phổ biến nhất ở nam giới
1. Methods of early screening for liver cancer
Ultrasound: easy to perform, low cost, widely used, most HCCs develop from cirrhosis, so ultrasound monitoring in patients with advanced chronic liver disease should be done regularly. However, because the effectiveness of ultrasound is operator-dependent, efficacy is reduced in overweight and obese patients, and suboptimal in early detection of HCC, additional biomarkers are needed. . AFP: is a normal glycoprotein produced during pregnancy in the yolk sac and in the fetal liver. If the fetus develops normally, the concentration of AFP found in maternal serum will increase, and only negligible amounts of AFP will remain in the postpartum circulation. Serum AFP levels decline rapidly after birth and by adulthood to < 9 ng/mL. AFP is also considered a tumor marker for some types of cancer (especially primary liver cancer). AFP levels are often elevated in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma, but can also increase in chronic hepatitis or cirrhosis, stomach cancer, lung cancer... Many studies have shown that AFP's diagnostic sensitivity for HCC is only 39-45% and specificity is 76-94%. PIVKA-II: is an abnormal form of des-carboxylated prothrombin (DCP) produced by vitamin K deficiency or in patients treated with warfarin or phenprocoumon. Des-carboxylated prothrombins are functionally defective due to their inability to bind calcium and phospholipids. Determination of PIVKA-II levels helps detect Vitamin K deficiency before routine coagulation test results change or bleeding occurs. PIVKA-II is not normally present, but in people with liver disease and malignant liver disease, PIVKA-II can be present even though the body is not deficient in vitamin K. PIVKA-II levels are determined to aid in the diagnosis. Diagnosis and prognosis in patients with HCC and monitoring of patients with HCC during treatment.
Tiến hành các chẩn đoán hình ảnh và xét nghiệm để sàng lọc sớm ung thư gan
2. In what cases is PIVKA-II indicated?
Indications for patients at risk: Chronic hepatitis B virus (HBV) or hepatitis C virus (HCV) infection, cirrhosis, alcoholism, obesity, diabetes, alfatoxin toxicity, Alpha deficiency -1-antitrypsin... Often used in conjunction with other tumor markers such as alpha-fetoprotein (AFP) and/or AFP-L3 to monitor treatment efficacy and recurrence of HCC. The PIVKA-II test is indicated to aid diagnosis and prognosis in patients with HCC and to monitor HCC during treatment.
3. Meaning of PIVKA-II23 . test
Normal PIVKA-II levels are < 40 mAU/mL. With a cut-off value of 240 mAU/mL, PIVKA-II has a sensitivity of 14-54% and a specificity of 95-99% in the diagnosis of HCC. Many studies have shown that an increase in PIVKA-II often reflects disease status, tumor size, and portal vein invasion. In addition, after surgery to remove the tumor or after treatment for liver cancer by other methods, the concentration of PIVKA-II decreased rapidly. The return of PIVKA-II after treatment represents disease recurrence or treatment failure. PIVKA-II >400 mAU/mL is associated with HCC recurrence in liver transplant patients Combining PIVKA-II, AFP and AFP-L3 significantly improves detection of HCC with a sensitivity of 84% and a specificity 94%
Kết quả xét nghiệm PIVKA-II23 phản ánh tình trạng của bệnh và kích thước khối u
4. Notes when reading PIVKA-II test results
Test results should be combined with other data such as clinical symptoms and other tests. Hypomorphic antibodies in human serum, rheumatoid factor (RF) may react with immunoglobulins in the reagents, interfering with the assay. Patients with frequent exposure to animals or exposure to animal serum products may interfere and produce abnormal test results. Therapeutic drugs containing Vitamin K analogues may give false negative results. PIVKA-II values may be falsely positive when patients are treated with antibiotics, vitamin K antagonists, are nutritionally deficient in vitamin K, or patients have alcohol-related liver disease. Currently, Vinmec International General Hospital offers cancer screening and early detection packages suitable for many subjects at risk of different diseases, including the liver cancer screening package - early detection of cancer. since the time when there are no symptoms. When registering for the package of screening and early detection of liver cancer, customers will receive:
Examination and consultation with an oncologist through an oncology appointment. Peripheral blood cell analysis. Assess liver function through tests such as measuring ALT activity (GPT), measuring AST activity (GOT), measuring GGT activity (Gama Glutamyl Transferase), measuring total Bilirubin. Screening for hepatitis B and C virus infection through rapid HBsAg test and automatic immunological HCV Ab test. Screening for liver cancer through the quantitative test of AFP (Alpha Fetoproteine). Screening for liver tumors by abdominal ultrasound (general). Vinmec is also one of the medical facilities with a team of leading medical experts in the field of oncology, the most modern machinery in the region. Those will be good conditions to help the screening for early detection of liver cancer be quick, convenient and time-saving. Thanks to that, it is possible to screen for liver cancer, help detect liver cancer at an early stage so that appropriate and timely treatment measures can be taken.
If customers have a need to examine or use service packages at Vinmec, please book an appointment directly at the website or contact the hotline for service.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.