This is an automatically translated article.
The article is professionally consulted by Master, Doctor Nguyen Thanh Nam - Radiologist - Department of Diagnostic Imaging - Vinmec Danang International General Hospital. The doctor has over 10 years of experience in the field of Diagnostic Imaging.According to the statistics of Globocan 2018, Vietnam is a country with the number of people with liver cancer ranked first (both in terms of mortality rate and number of new cases). It can be seen that liver cancer is one of the most dangerous cancers in human life, if not detected and treated promptly can cause death.
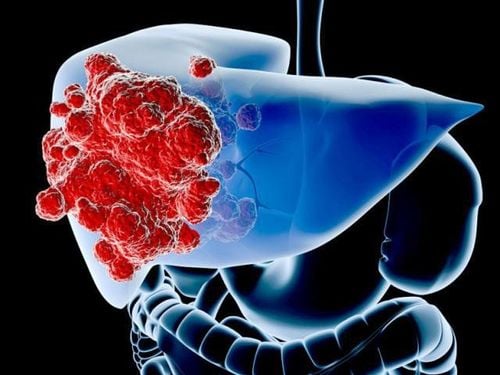
1. Primary liver cancer
Cancer that starts in the liver is called primary liver cancer. There are many types of primary liver cancer. Here are 4 common types of primary liver cancer:Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC): This is the most common type of liver cancer in adults. Hepatocellular carcinoma can have different growth patterns:
Localized mass: begins with a growing tumor. In the late stages of the disease, it will spread to other parts of the liver. Infiltrates will begin with many small cancerous nodules on the liver, not just a single tumor. This type of cancer is most common in people with cirrhosis. Cholangiocarcinoma: About 10-20% of cancers that start in the liver are intrahepatic cholangiocarcinomas. Cancer usually begins in the cells that line the small bile ducts in the liver. However, most cholangiocarcinomas actually start in the extrahepatic bile ducts.
Malignant hemangiomas (Angiosarcoma or hemangiosarcoma): These are rare cancers that start in the cells lining the blood vessels of the liver. People who have been exposed to vinyl chloride or thorium dioxide are more likely to develop these cancers. Others are caused by exposure to arsenic or radium, or with an inherited condition called hereditary hemochromatosis.
These tumors grow quickly and are often too extensive to be surgically removed by the time they are found. Chemotherapy and radiation therapy can help slow the disease, but these cancers are often difficult to treat. Hepatoblastoma: This is a very rare type of cancer in children, usually in those younger than 4 years old. The cells of hepatoblastoma are similar to those of fetal liver cells. About 2 out of 3 children with these tumors are successfully treated with surgery and chemotherapy, but the tumors are more difficult to treat if they spread outside the liver.
2. Secondary liver cancer (metastatic liver cancer)
Secondary liver cancer is a condition in which cancer cells in the extrahepatic organs metastasize to the liver and form a tumor there. Secondary liver cancer is different from primary liver cancer and its incidence is much higher than that of primary liver cancer.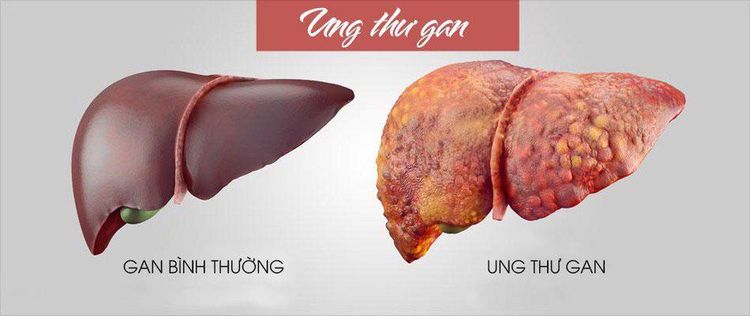
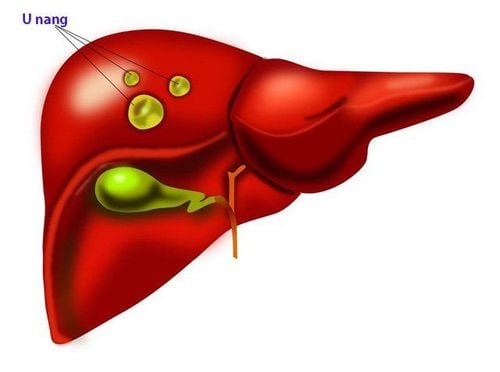
3. Benign liver tumor
Benign tumors are those that grow, but have not spread to other parts of the body. Benign liver tumors can be cured with surgery.Some common types of benign liver tumors:
Hemangiomas:
This is the most common form of benign liver tumor in both men and women. Vascular tumor size is larger in women than in men. There are 2 types of hemangiomas, including: single and multifocal. The location of the tumor is often unstable, with black blood vessels, or with a thrombus. Another case of hemangioma is an invasive hemangioma that spreads throughout the liver (Hepatic haemangiomatosis). Most hemangiomas require no treatment, except for more complex tumors that require surgery.
Focal nodular hyperplasia (FNH):
Usually asymptomatic, completely benign lesions, very rarely, pain in the liver or hepatomegaly. Doctors can diagnose FNH through ultrasound, CT, and these FNHs do not turn into malignant liver tumors.
Benign hepatocellular adenoma (HA):
Usually occurs in women of reproductive age and who use oral contraceptives for a long time. HA is less common than FNH. Patients can monitor the disease through regular ultrasounds and scans.
Regenerative proliferation (NRH) nodule:
Regenerative proliferation nodule is a mixed structure of hepatocyte proliferation with areas of hepatocellular atrophy or hepatocellular hyperplasia without connective tissue hyperplasia. The disease usually does not go through clinical diagnosis and is common in people over 60 years of age or in some other cases in children. NRH often causes symptoms of esophageal bleeding due to an increase in portal pressure. These benign tumors do not cause serious health consequences, so they do not require treatment.
4. Tests that may be performed
If signs point to a liver tumor, more tests may be done. Here are some of the most common liver cancer tests:Ultrasound: is the first technique in diagnosing liver cancer, widely applied because of its low cost, simple implementation, and no side effects. and gives a high accurate diagnosis rate (can detect liver tumors over 1cm in size). Ultrasound shows the location and size of the tumor. In addition, this diagnostic method also helps detect comorbidities such as cirrhosis, portal hypertension. At the same time, ultrasound also helps guide measures for liver cancer treatment such as liver resection, percutaneous tumor killing, etc. However, ultrasound does not reveal the nature of the tumor. Computed tomography (CT scanner): especially liver kinetics computed tomography (multi-stage liver) has high diagnostic value, sensitivity up to 94% for tumors >1cm. Selective hepatic angiography: allows the doctor to see the arteries in the liver that are enlarged by the tumor and the specific image of liver cancer. Currently, using digital angiography to erase the background helps doctors accurately observe the tumor status in the liver. This method has an accuracy of up to 90% for tumors less than 3cm. Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) of the liver: has a high diagnostic accuracy (diagnostic accuracy rate up to 97.5% with tumors over 2cm in diameter) and helps to detect invasive venous lesions in the liver.

Service selection Package for screening and early detection of liver cancer, patients will be examined, consulted and performed tests, diagnostic imaging to evaluate liver function, liver diseases and liver cancer screening.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.
Article referenced source: Cancer.org