This is an automatically translated article.
The article is professionally consulted by Specialist Doctor I Nguyen Hung - Department of Medical Examination & Internal Medicine - Vinmec Danang International General Hospital.
Peritoneal dialysis is a commonly used renal replacement therapy in patients with renal failure. What are the advantages of peritoneal dialysis and the possible complications of peritoneal dialysis, let's find out through the following article.
1. Peritoneal dialysis
What is peritoneal dialysis? Peritoneal dialysis, also known as peritoneal dialysis, is a method of using the patient's own peritoneum as a replacement membrane for the weakened kidney. Peritoneal dialysis helps to filter metabolites and electrolytes out of the patient's body, helping to maintain homeostasis.The peritoneum has an area roughly equal to that of the body, about 1-2 m2. Normally, the abdominal cavity holds about 100ml of physiological fluid and can hold more than 2 liters of peritoneal dialysis without causing discomfort or affecting respiratory function. The peritoneum is used as a semi-permeable membrane separating the two compartments, one side is the cavity containing the peritoneal filtrate, the other is the periperitoneal capillaries. During peritoneal dialysis fluid retention in the abdominal cavity, diffusion, ultrafiltration, and absorption processes occur simultaneously.
Diffusion is the phenomenon where solutes move from places with high concentrations in the blood such as urea, creatinine, potassium, ..
The difference between the osmotic pressure between the filtrate and the blood vessels helps water to penetrate from the blood cavity to the filtrate cavity, thereby helping to remove excess water in the body.
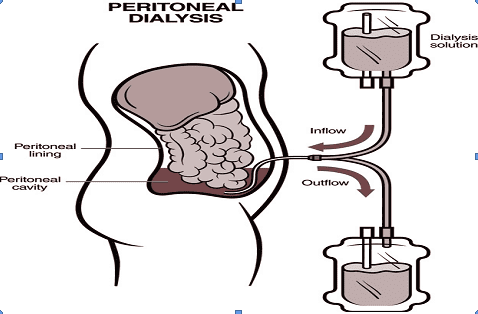
Acute peritoneal dialysis is used when an artificial kidney is not available or the patient has a contraindication to hemodialysis. Acute peritoneal dialysis is indicated in acute renal failure or severe progression of chronic renal failure, when blood pH ≥ 7.2, blood potassium ≥ 6.5 mmol/l, blood urea ≥ 30 mmol/l, along with Volume overload threatens acute pulmonary edema,...
Continuous outpatient peritoneal dialysis (CAPD) A fixed catheter is threaded through a line under the skin of the abdominal wall into the abdominal cavity to a proximal position with Douglas . The catheter commonly used is a Tenckhoff catheter with two stoppers. Catheterization was carried out in the operating room and fixed during the patient's peritoneal dialysis.
In continuous outpatient peritoneal dialysis, dialysis fluid is always present in the patient's abdominal cavity. Fluid is changed about 4 times a day, the process of changing and draining is done by hand, can be done at home. The translation exchange stages take place as follows:
Stage 1: put in translation. Sterile unfiltered fluid is inserted into the abdomen through a catheter. Stage 2: immersion. The filtrate is soaked in the abdomen for 4-8 hours depending on the concentration of the fluid. Stage 3: discharge the fluid. The soaked fluid is discharged under the action of gravity. After draining the soaked fluid, start adding fluid as in stage 1. Automatic Cycling Peritoneal Dialysis (ADP) Automatic Cycling Peritoneal Dialysis is divided into: Continuous Cycling Peritoneal Dialysis-CCPD) and night-time interval peritoneal dialysis (Nocturnal Intermittent Peritoneal Dialysis (NIPD), Tidal Peritoneal Dialysis (TPD).
Similar to continuous outpatient peritoneal dialysis, a catheter is established for fluid exchange. In continuous cycle peritoneal dialysis, 3-10 fluids per night are introduced into the body through an automatic cyclic fluid exchanger. During the day, a volume of peritoneal dialysis fluid is stored in the abdomen, which is drained before the night cycle.
Nocturnal intermittent peritoneal dialysis is similar to continuous cyclic peritoneal dialysis, except that no dialysis fluid is present in the patient during the day. At night, the number of filtration cycles performed is increased to compensate for the lack of daytime fluid retention.
Tidal peritoneal dialysis is a procedure that uses an initial volume of fluid intake followed by partial drainage at cyclic intervals.
Continuous outpatient peritoneal dialysis and automatic cycle peritoneal dialysis are used for patients with end-stage chronic renal failure when the glomerular filtration rate is < 15 ml/min, when the patient is far from dialysis centers. not perform hemodialysis or have contraindications to hemodialysis.
2. Advantages of peritoneal dialysis
3. Disadvantages of peritoneal dialysis
Complications of peritoneal dialysis may be encountered such as:The patient may have hyperglycaemia because the peritoneal dialysis fluid has a glucose concentration of 1.5 g%, 2 g% or 2.5 g%. Peritonitis , infection of the catheter outlet due to the patient's failure to follow the prescribed procedure when performed at home. Hypotension due to ultrafiltration with large withdrawal of fluid. The prevalence of hypertension is elevated in patients with early days of cirrhosis with ascites. Loss of protein through filtration Cardiac arrhythmias, hypothermia Patients may also experience risks such as: Leakage of fluid from the abdomen, catheter blockage, catheter drop in or out of the abdomen, bleeding at the catheter site or into the peritoneal cavity.
Not all patients are suitable for peritoneal dialysis, contraindications include:
Patients with peritoneal infection, peritoneal adhesions due to trauma or old incision The patient's peritoneum has fibrosis chemistry, the patient has recently had an abdominal aortic transplant. The patient has an intra-abdominal tumor

Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.