This is an automatically translated article.
Peripheral neuroma that forms and grows near or on peripheral nerves. When the tumor causes sensory disturbances, restricts movement, affects aesthetics, grows at a rapid rate or is suspected of malignancy, peripheral neuroma surgery is indicated for complete removal.
1. What is a peripheral neuroma?
The human nervous system includes the central nervous system (including the brain, spinal cord) and the peripheral nervous system, which governs sensory and motor functions,... Peripheral nerve tumors form, grows near the peripheral nerves - which carry signals from the brain and spinal cord to the organs of the body.
Tumors in the peripheral nerves form due to proliferation of fibroblasts of the nerve sheath. Peripheral nerve tumors can grow anywhere along the path of nerves, appearing in any organ of the body.
Most peripheral neuromas are benign, slow-growing tumors. Tumors can grow alone or appear in many places. As the tumor grows, it affects nearby nerves, blood vessels, or tissues directly, causing pain, nerve damage, and loss of function in the affected areas. Specifically, the tumor can cause damage to the patient's vital functions, aesthetics, and even disability. Common symptoms include: Swelling, appearance of lumps under the skin, dizziness, loss of balance, pain, tingling or numbness, weakness, loss of function in the affected area,...
Nerve tumors Peripheral nerves can compress nerves, causing unpredictable complications, even lasting forever. Complications of the disease include: numbness, pain in the affected area; loss of function in the affected area; pain; having trouble keeping balance,...
The treatment for peripheral neuroma is surgical removal of the tumor. In some cases, if the tumor cannot be removed and it has not damaged nearby tissues and nerves, other treatments such as laser may be used.

Chóng mặt là triếu chứng thường gặp của u thần kinh ngoại biên
2. Details of surgical methods for peripheral neuroma
2.1 Indications/contraindications
Indications
Peripheral nerve tumors cause sensory disturbances, restrict movement, affect aesthetics; Peripheral nerve tumor growing rapidly, suspected malignancy. Contraindications
People with severe systemic conditions, many combined malformations such as cardiovascular complications, severe kyphosis,...; Tumor is located in the area of the nerve plexus or the tumor is large, invades blood vessels, ... it is difficult to remove the entire tumor, which can leave severe sequelae for the patient.
2.2 Preparation
Personnel performing: Neurosurgery or orthopedic specialist, surgical assistant, anesthesiologist, nurse; Technical equipment: Common surgical tools including knife, scissors, dissection, pince, needle-carrying needle, suction machine, unipolar/bipolar electric knife; Patients: To be asked about disease, detailed examination; be informed about the procedure's purpose, procedure and possible complications; fasting, hygiene and preoperative anesthetic examination; check and compare names, medical records, tests, ... before surgery; Medical records: Prepare according to regulations.
2.3 Performing surgery
Patient position: Depending on tumor location; Anesthesia: Depending on the location and size of the tumor to choose the appropriate anesthetic method: Local anesthesia, spinal anesthesia, plexus anesthesia or endotracheal anesthesia; Disinfect the large and spread surgical area; Anesthesia at the skin incision area; Choosing the skin incision depends on the location, size, and nature of the tumor and ensures the requirements such as being able to access the tumor widely and safely, nourishing the skin well, and being aesthetically pleasing; Skin incision and dissection layer by layer revealed the tumor. Tumors are usually round, smooth, and well-demarcated. Next, examine the structure of blood vessels and neighboring nerves before deciding to remove the tumor in whole or in part; Hemostasis; Place drainage in case of large incision and high risk of bleeding; Close the incision.
2.4 Follow-up after surgery
Closely monitor the patient's whole body condition including vital indicators such as temperature, respiration, pulse, blood pressure; Monitor neurological status: Focal neurological signs (progressive paralysis); Monitor bleeding from the incision; Monitor drainage if present, usually remove the drain within the first 48 hours after surgery.
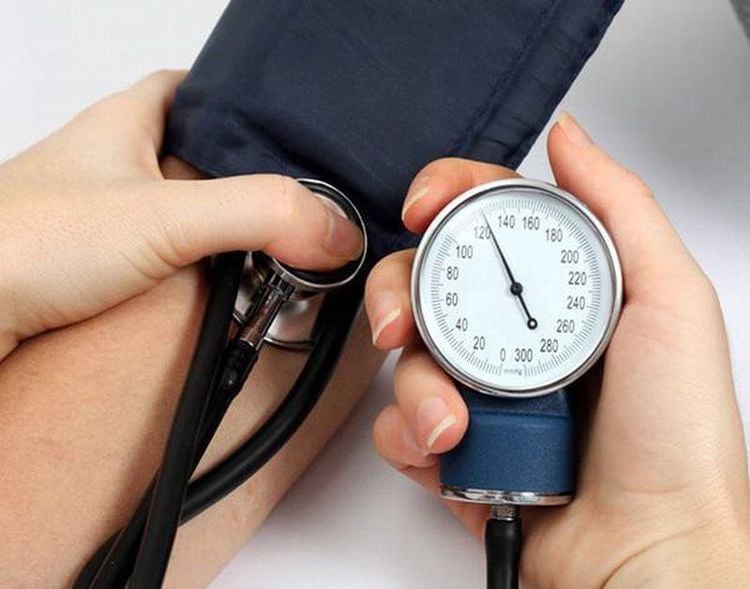
Sau mổ bệnh nhân cần được theo dõi huyết áp, nhiệt độ
2.5 Complications and how to deal with them
Bleeding: Treat by re-operating to stop bleeding; Infection: The treatment is medical treatment (using antibiotics); Progressive paralysis: Need to monitor and medical treatment (using anti-inflammatory drugs) combined with rehabilitation.
Peripheral neuroma surgery is a procedure that needs to be performed by a highly experienced and qualified doctor and requires patient cooperation. Therefore, when prescribed for this procedure, the patient must strictly follow the instructions of the doctor. This improves the chances of a cure and reduces the risk of complications.
Vinmec International General Hospital with a system of modern facilities, medical equipment and a team of experts and doctors with many years of experience in neurological examination and treatment, patients can completely peace of mind for examination and treatment at the Hospital.
To register for examination and treatment at Vinmec International General Hospital, you can contact Vinmec Health System nationwide, or register online HERE.