This is an automatically translated article.
The article was written by the Doctor in charge of the Dental - Jaw - Facial Unit - Interdisciplinary Department - Vinmec Times City International General Hospital.
Periodontal abscess, also known as periodontal abscess, can occur with any type of periodontitis, so it is not classified as a type of periodontitis but is a specific symptom. .
1. What is a periodontal abscess?
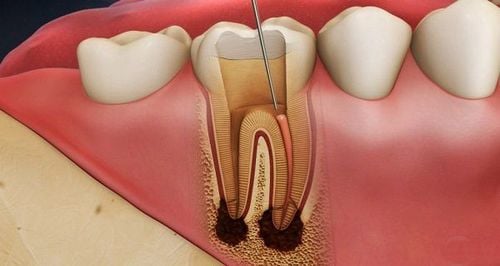
Periodontal abscess is a localized, pus-filled infection that accumulates in the connective tissues of the periodontal pocket. Infection causes rapid destruction of adjacent alveolar bone and periodontal ligament
According to some US studies, periodontal abscess is the third most common dental emergency, accounting for 7%-14 % in all dental emergencies.
2, Manifestations of periodontal abscess
Patients with periodontal abscess may experience mild to severe pain. When touching, touching the abscess area, the patient will feel pain; sensitive teeth, teeth that move, wobble, or protrude; Bad taste in mouth, local swelling of lymph nodes, fever and malaise. These symptoms are more common when the patient is in an acute inflammatory state, but when there is drainage, the abscess becomes chronic and the symptoms decrease.

Áp xe nha chu khiến miệng xuất hiện mùi hôi khó chịu
Clinical examination often shows gingival swelling along the lateral edge of the root, gingival surface swelling and redness, with bleeding on probing. Pus may be present on exploratory or gentle palpation or when incision is made for drainage. X-ray examination may or may not show signs of bone loss.
Lesions often occur in the setting of pre-existing periodontitis as can be an exacerbation of untreated chronic periodontitis or are still in the process of chronic periodontitis. For example, detached tartar can enter adjacent tissues, or remove incomplete tartar or food debris that remains and lodges in deeper parts of the pocket. Other contributing factors include changes in the subgingival flora (eg, secondary to systemic antibiotic therapy) and decreased host resistance (common in diabetics). In addition, some periodontal abscesses arise in the absence of periodontitis due to the existence of foreign bodies, local trauma, or anatomical anomalies of the teeth, etc.
If left untreated, acute periodontal abscesses can be chronic, long-lived with a history of repeated purulent discharge. Manifestations of chronic periodontal abscess are a protrusion from deep structures that open to the gingival mucosa along the root. The opening of the fistula may be covered by a mass of granulomatous tissue, making it difficult to detect. Chronic periodontal abscesses are usually asymptomatic. However, some patients still feel a dull pain, slightly protruding teeth and want to grit their teeth. Chronic periodontal abscess may turn acute when the orifice is obstructed.

Bệnh nhân bị áp xe sẽ thấy đau lợi âm ỷ và hơi trồi nhẹ
Diagnosis of periodontal abscess is based on a number of factors such as history, clinical symptoms and additional laboratory tests.
It is important to distinguish periodontal abscess from periradicular abscess or periapical abscess caused by infection emanating from the pulp, and to emphasize this distinction. , the term lateral periodontal abscess is commonly used. The differential diagnosis can be made based on history, clinical examination, pulpal examination, and appropriate radiographs.
The microbiota involved in periodontal abscesses are nonspecific and they are usually dominated by anaerobic gram-negative bacteria.
3. Treatment of periodontal abscess
Treatment includes incision and/or drainage with drainage to remove plaque, tartar, food debris or foreign body... that caused the abscess. Treatment may also include periapical pocket irrigation and slight correction of the bite. Systemic antibiotics are indicated if the patient presents with fever or other signs of systemic infection. Supportive care includes pain medication, warm salt water rinses, and a soft diet. After resolution of the acute infection, any underlying chronic periodontitis should be addressed.
Chích rạch để xử lý áp xe nha chu
Periodontal abscess occurs when pus collects in the connective tissue wall of the periodontal pocket and is commonly seen in patients with periodontitis. Therefore, the first thing is to drain the pus, so it depends on the decision that there is an exchange and cooperation between the doctor and the patient whether to try to save the tooth (retain the tooth) or remove the tooth.
If it is decided to try to save the tooth, an initial drainage can be made by removing tartar and cleaning the affected root. If this does not relieve the pressure, a small incision can be made at the most appropriate point or a small flap can be created to expose the lesion and clean.
Patients should be advised to use hot saline mouthwash during the healing period to facilitate drainage. Once the lesion has stabilized, root curettage or periodontal surgery may be necessary to stimulate rapid healing. This type of lesion will require careful, long-term monitoring to ensure that recurrence does not occur
Systemic antibiotics are indicated if the patient presents with fever or other signs of systemic infection. Supportive care includes pain medication, warm salt water rinses, and a soft diet. After resolution of the acute infection, any underlying chronic periodontitis should be addressed.
To register for examination and treatment of oral health problems at Vinmec International General Hospital, you can contact the nationwide Vinmec Health System Hotline, or register for an online examination HERE.