This is an automatically translated article.
This article is professionally consulted by Master, Doctor Vu Quoc Anh - Pediatrician - Pediatrics - Neonatology Department - Vinmec Danang International General Hospital. The doctor has nearly 10 years of experience as a resident and treating physician.Peptic ulcer disease is an inflammatory disease and loss of mucosal organization limited to the part of the digestive tract that secretes acid and pepsin. The disease is often overlooked because adults mistakenly believe that children have common digestive diseases such as digestive disorders, stomach worms,...
1. Diagnosing gastritis - duodenal ulcer
1.1. History The doctor will examine you by asking questions to determine the condition of the child:Location of pain, duration of pain, pain or constant pain, does pain spread to other places, pain intensity, pain Is it related to bowel movements or meals, does it increase with eating, ways to relieve pain, symptoms associated with pain, number of times per week, per month, anyone in the family? Did the child take any medicine that affects the stomach, did he change his diet before the pain? Have a fever? Do you have yellow urine? Do you have painful urination? 1.2. Examination Clinical signs and symptoms of peptic ulcer are very poor, so starting from the diagnosis of exclusion. Look for signs of anemia, examine all organs: liver, gallbladder, urinary tract, rectal examination. Look for signs of malnutrition. Occasionally, signs of complications such as gastrointestinal bleeding (melena, vomiting blood, anemia) or pyloric stenosis are seen.
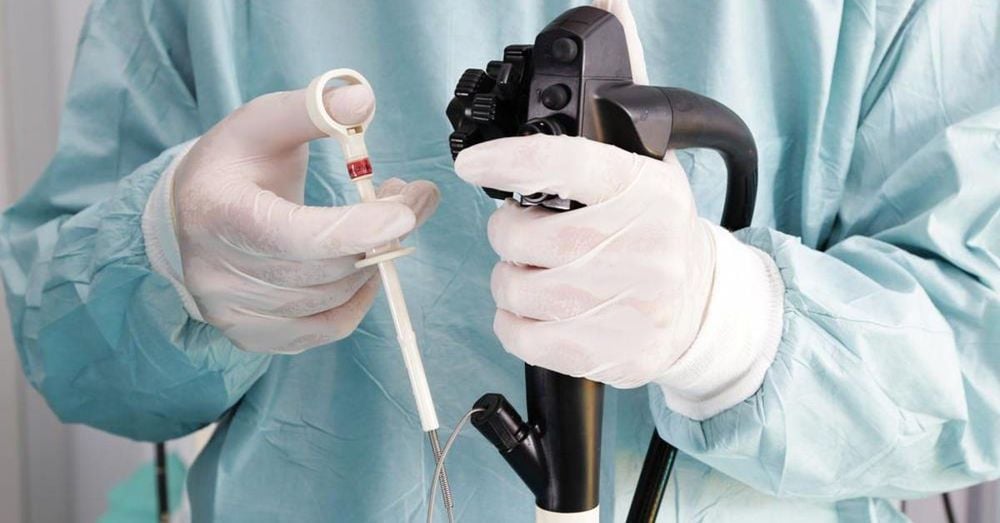
1.3. Recommend X-ray examination of the stomach and duodenum. Gastroduodenal endoscopy: More accurate than X-ray, through endoscopy, biopsy is needed to examine histopathology.
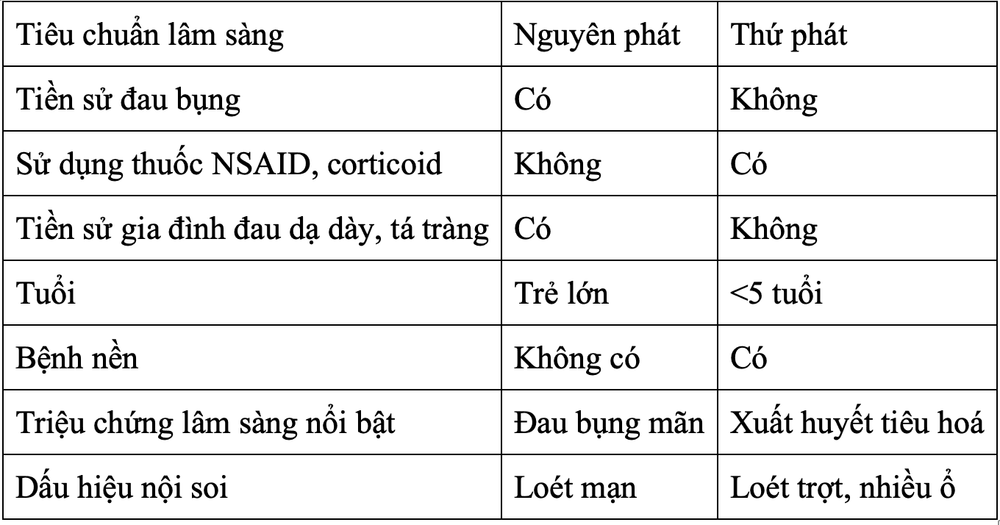
1.5. Primary or secondary diagnosis?
2. Treatment of gastritis - duodenal ulcer
2.1. General principles of treatment Based on pathology to rule out pathogenic factors such as spirochetes, Helicobacter pylori, stress, increased secretion of HCl,... Normalize gastric function. Enhance mucosal regeneration, eliminate comorbidities. 2.2. Treatment goals a) Reduce ulcer-causing factorsUse drugs that inhibit the secretion of HCl and Pepsin. Use drugs to neutralize HCl secreted into the stomach - duodenum. b) Enhance protective factors
Use mucosal coatings and ulcer dressings. Take medications that stimulate mucus production. c) Eradicate Helicobacter pylori
Treat with antibiogram if HP is detected.

Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.