This is an automatically translated article.
Nerve blockade is an effective pain management and treatment technique that has gained wide popularity in recent times. This technique is performed alone or in combination with other pain control measures to bring the most effectiveness to the patient.1. Purpose of Nerve Blockade
A group of nerves, called the plexus or ganglion, that transmit pain sensations from a specific organ or body part can be blocked by injection of medication to a certain location. The injection contains this nerve blocker called a nerve block.
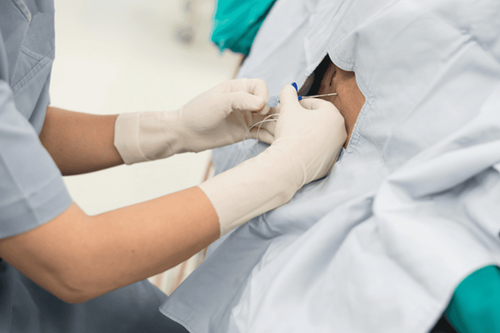
Nerve blockade is usually performed under imaging guidance such as ultrasound or computed tomography to assist physicians in placing the injection in the most appropriate position for maximum benefit. for the patient.
There are different methods of nerve blockade used for different purposes. People with acute or chronic pain may be given an injection of a nerve blocker for temporary pain relief. Usually, such pain originates in the spine, but other areas commonly affected include the neck, buttocks, legs, and arms. The injection of a nerve blocker allows the damaged nerve time to heal itself from the constant state of irritation. In addition, nerve block can provide diagnostic information to the physician. By performing a nerve block and then monitoring how the patient responds to the injection, the doctor can use this information to help determine the cause or source of the pain and the direction of further treatment. according to.
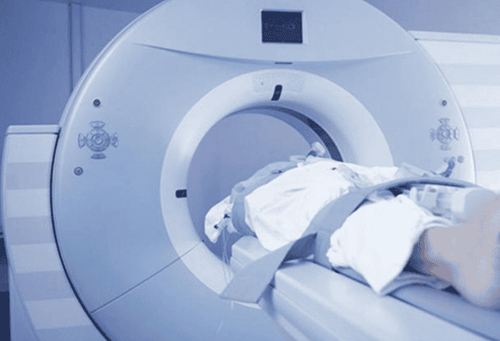
Phong bế thần kinh thường được thực hiện dưới hướng dẫn chẩn đoán hình ảnh như cắt lớp vi tính
2. Nerve Blocking Methods
Different pain sites require a different method of nerve block. Here are some common nerve block methods and locations.
Blockage of the trigeminal nerve (face) Blockage of the ophthalmic nerve (eyelids and scalp) Blockage of the supraorbital nerve (forehead) Blockage of the maxillary nerve (maxillary) Nerve blockade sphenoid-palatal (nose and palate) Epidural analgesia of cervical spine, thoracic spine, and lumbar spine (neck and back) Cervical and paravertebral nerve plexus block (shoulder and neck) high) Brachial, elbow, and wrist plexus block (shoulder/arm/hand, elbow and wrist) Subarachnoid and sciatic plexus block (abdomen and pelvis)
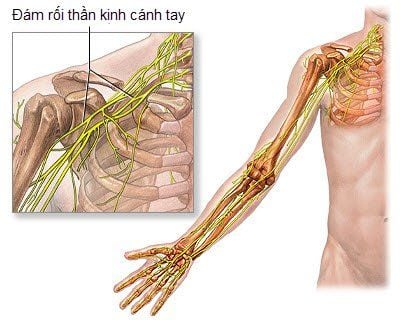
Đám rối thần kinh cánh tay là một vị trí có thể thực hiện phong bế thần kinh
In addition, there are a number of other methods including:
Sympathetic Nerve Blockade: The sympathetic nervous system is a network of nerves that extends the length of the spine. Sympathetic nerve blockade is performed to determine if sympathetic chain damage is present. These nerves control some of the body's involuntary functions, such as the dilation and narrowing of blood vessels. Star ganglion block: This is a method of sympathetic nerve blockade performed to determine if there is head, neck, chest, or arm sympathetic chain damage or whether it is the source of the pain in those areas does not. Although used primarily as a diagnostic method of blockade, stellate ganglion blockade may have an effect that extends beyond the duration of action of anesthetics. Posterior sagittal nerve block: Also known as anterior sagittal nerve block, posterior sacroiliac nerve block is indicated to determine whether the posterior sacroiliac joint is the cause of pain. The posterior interphalangeal joint is located at the back of the spine, right where the vertebrae rest slightly on the other vertebrae. These joints shape and limit spinal movement.
3. Side effects and risks
In general, nerve block is relatively safe, although there is always a risk, but it is very rare.
Increased blood sugar Rash, itching Weight gain Bleeding, soreness at the injection site, in addition to the risk of infection. Death (in rare cases)
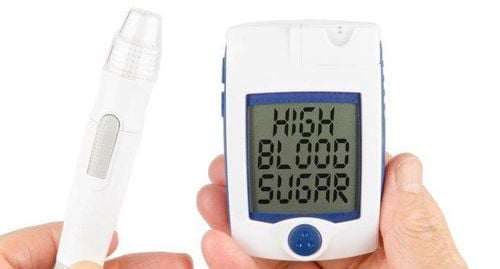
Phong bế thần kinh có nguy cơ làm tăng lượng đường trong máu
When 2 nerves are located close to each other, the doctor may have difficulty delineating the nerve to be affected. The drug can also enter the bloodstream. In very rare cases, nerve blockade can permanently destroy a nerve. The procedure can also destroy surrounding nerves. These risks are rare, and in general, nerve block is safe and effective.
4. How should the patient prepare before the procedure?
Usually no special preparation is needed before a nerve block procedure is performed. Patients should go to the toilet before the procedure.
The position for performing the procedure is that the patient can lie on his or her back, prone or on one side, depending on the position of the procedure, with supportive imaging facilities.
Although nerve block techniques are relatively diverse, they are not for everyone. If the patient has pain that is not caused by one or a small group of nerves, nerve block is not the correct choice. Depending on the pain condition, location, medical history, ... of each patient, the doctor will have a specific pain treatment method.
For examination, treatment and surgical pain relief of musculoskeletal diseases, customers can choose Vinmec International General Hospital. There is a full convergence of systems, modern medical equipment of standard standards, there are many methods of pain relief, minimizing complications for patients. Especially with a team of highly qualified and well-trained doctors and nurses, they will surely satisfy customers.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.
REFERENCES: webmd.com, radiologyinfo.org, medicalnewstoday