This is an automatically translated article.
Article by Technician Nguyen Dinh Tuan - Medical Genetics Division, Vinmec High-Tech Center
One possible factor in 'unknown' infertility is oxidative stress (OS). High levels of oxidative stress impair sperm function and cause DNA damage, which in turn increases the risk of IVF failure. So what is oxidative stress and how does it affect male fertility?
About 1/6 couples have fertility problems, in which the male factor accounts for 50% of the cause. Although, semen analysis is still the 'gold standard' for assessing the quality of sperm (evaluating factors such as mass, quantity, motility, morphology, etc.). However, 25-40% of male infertility cases remain unexplained after semen analysis.
1. What is oxidative stress?
Oxidative stress is related to the excessive presence of ROS (Reactive Oxygen Species), ROS is defined as active oxidizing radicals derived from oxygen, including free radicals and some specific molecules are not free radicals and are able to participate in strong reactions. ROS usually exists in the form of free radicals such as superoxide, hydrogen peroxide, hydroxyl ion, peroxyl radical and hypochlorite ion. Antioxidants produced by the body fight these ROSs, keeping the system in balance, but when ROS production exceeds the body's ability to produce antioxidants, excess ROS can be damaging. to tissues such as proteins, cell membranes, and cell DNA, including sperm. This is called oxidative stress.
2. What causes oxidative stress in semen?
The ability to produce antioxidants is controlled by our gene function and can be influenced by lifestyle, such as a diet rich in antioxidants such as fruits and vegetables. The formation of free radicals is increased due to a variety of environmental factors including smoking, alcohol, and a poor-quality diet high in saturated fat, as well as the aging process and excess weight. The antioxidants inside our bodies must be made enough to balance the formation of free radicals, but for many people, there can be an excess of free radicals, leading to cell damage. cells and long-term health effects.
Tình trạng stress oxy hóa liên quan đến sự hiện diện quá mức của ROS
3. Oxidative stress and male fertility
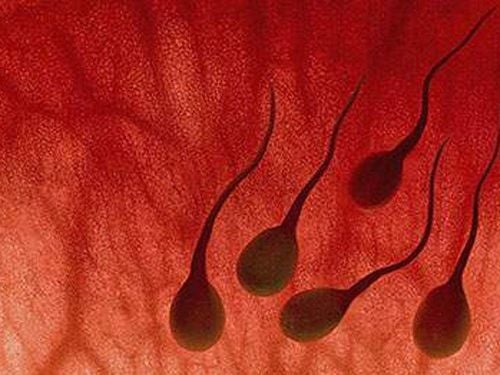
High levels of oxidative stress are associated with impaired sperm function and abnormal semen analysis results. There is ample evidence that high levels of oxidative stress can induce changes in sperm cell membranes, affecting their morphology and motility, as well as causing damage to their DNA. This DNA damage can lead to DNA abnormalities in the embryo, thereby causing a lower pregnancy rate and a higher risk of miscarriage.
Study of the authors Kuroda et al (2020) evaluated the correlation between ROS in semen with fertilization rate, embryo division rate and blastocyst rate after ICSI. The level of ROS in semen was compared between the fertilized and non-fertilized groups, the group of good quality split embryos and the group of undeveloped embryos, the group of good quality blastocysts and bad quality blastocysts. The results showed that the mean ROS concentration did not differ between the fertilized and non-fertilized groups. The concentration of ROS in the group of undeveloped embryos was significantly higher than in the group of good-quality dividing embryos (p = 0.0026) and significantly lower in the group of good quality blastocysts compared with the group of poor quality blastocysts ( p = 0.015).
Thus, the percentage of well-divided embryos and the percentage of good blastocysts in the group with high ROS concentration were lower than in the group with low ROS concentration. From that, the authors concluded that ROS in semen is believed to have an adverse effect on embryonic development in ICSI technique (Kuroda et al., 2020).

Mức độ stress oxy hóa cao có liên quan đến suy giảm chức năng tinh trùng
4. Method of assessing the level of oxidative stress
Although a semen analysis can show the effects of oxidative stress (such as reduced sperm quality or motility), it cannot indicate the reason behind it. The ROS level test helps to assess the level of oxygen stress. Currently, there are many methods of assessing ROS concentration being applied. Direct measurement of chemiluminescence such as nitrogen blue tetrazolium test, flourescein probe, electron spin resonance. The advantages of these methods are accurate measurement of free radicals, high accuracy, modern equipment. However, the cost is high and the threshold value is not standardized. Indirect methods such as total antioxidant capacity assay TAC, ROS-TAC lack specificity, low accuracy, and unstandardized cutoff values.
5. Who should be tested for oxidative stress?
Those who should be tested for oxidation are the following:
The wife's husband has a history of two or more miscarriages Men over 40 years of age Men with suboptimal semen analysis results preference (particularly low morphology or mobility) Men with unhealthy lifestyles, body mass index over 30, smoking, heavy drinking or poor diet.
6. Treat high levels of oxidative stress
If your ROS test shows high levels of oxidative stress, we may recommend lifestyle changes and antioxidant supplements, including vitamin C and specific minerals to help reduce these Free radicals can damage sperm. We may also recommend a more sophisticated test to assess the extent of DNA fragmentation in a sperm sample and may then suggest ICSI if the level of DNA fragmentation is high.
Follow Vinmec International General Hospital website to get more health, nutrition and beauty information to protect the health of yourself and your loved ones in your family.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.
References:
https://www.carefertility.com/blog/oxidative-stress-the-main-cause-of-sperm-dna-damage/ http://hosrem.org.vn/detailNews/thongtin/ ros-tinh-dich-5413