This is an automatically translated article.
Article by Pharmacist Nguyen Thi Thanh Nga - Clinical Pharmacist - Faculty of Pharmacy - Vinmec Times City International Hospital
Pharmacovigilance is defined as a science and professional practice concerned with the detection, evaluation, understanding and prevention of adverse events or any other drug-related problem, in order to ensure ensure safe drug use.
1. Concepts, goals and roles
What is Pharmacovigilance? Pharmacovigilance (Pharmacovigilance) according to the World Health Organization is defined as “the science and practice concerned with the detection, assessment, understanding and prevention of adverse events or any problem anything else related to drugs”[1], [5].
1.1. Objectives of pharmacovigilance [5]: Improve the quality of patient care and safety related to drug use and all medical interventions and medical support (paramedical). Improve the quality of public health and safety related to drug use. Detect drug-related problems and communicate promptly Evaluate benefits, harms, effectiveness and risks of drugs, guide to avoid risks and optimize effectiveness. Promote safe, rational and effective use of drugs (including cost-effectiveness) Promote clinical understanding, education and training on pharmacovigilance and effective communication to the community. 1.2. The Role of Pharmacovigilance Prior to market entry, the safety of a drug has been evaluated through several stages of drug research and development. However, after the drug is marketed, on the market, its use is no longer limited to a small number of patients and strict conditions like in clinical trials, but is expanded according to actual requirements. medical treatment. At this time, issues such as patient characteristics, comorbidities, concomitant medications, prolonged drug use, treatment adherence... are not quite the same as in clinical trials. In addition, some other problems related to drug safety such as counterfeit drugs, poor quality drugs or drug-related errors often appear only after the drug is licensed for circulation and put into use. Therefore, the safety of the drug still needs to continue to be monitored and evaluated after the drug is marketed in order to have timely intervention measures in case of necessity to ensure patient safety [1],[ 2].
For this reason, each country needs to develop its pharmacovigilance system to suit the characteristics of disease patterns, genetic factors, race and drug use [1].
2. Pharmacovigilance system in the world
The Global Drug Safety Monitoring Network was born after the Thalidomid disaster in 1961, when thousands of children were born with birth defects related to the mother's use of thalidomide during pregnancy. The 16th World Health Assembly affirmed the need to soon establish a system to help detect and fully and promptly disclose information about ADR [2]. Subsequently, the first national drug safety authorities were established in the UK (Commity on Safety of Drugs) [4]. Then, in 1968, WHO implemented a pilot project on global drug monitoring (WHO Pilot Research Project for International Drug Monitoring). Until now, the pharmacovigilance system in the world is developing strongly, with the UMC (Uppsala Monitoring Center) responsible for the activities of the global drug monitoring program (WHO). The most developed and influential reporting systems include The yellow card (UK), Medwatch (US) and CIOMS.
3. Pharmacovigilance system in Vietnam
Although pharmacovigilance was widely introduced in Europe in the 1960s, Vietnam started to become aware of pharmacovigilance in 1994, when the first ADR monitoring center was established. However, pharmacovigilance in Vietnam was still very simple until the establishment of the National Center for Drug Information and Adverse Reactions Reporting (DI&ADR) in 2009. Vietnam's pharmacovigilance system gradually complete with the operating structure shown as Figure 1 [3]
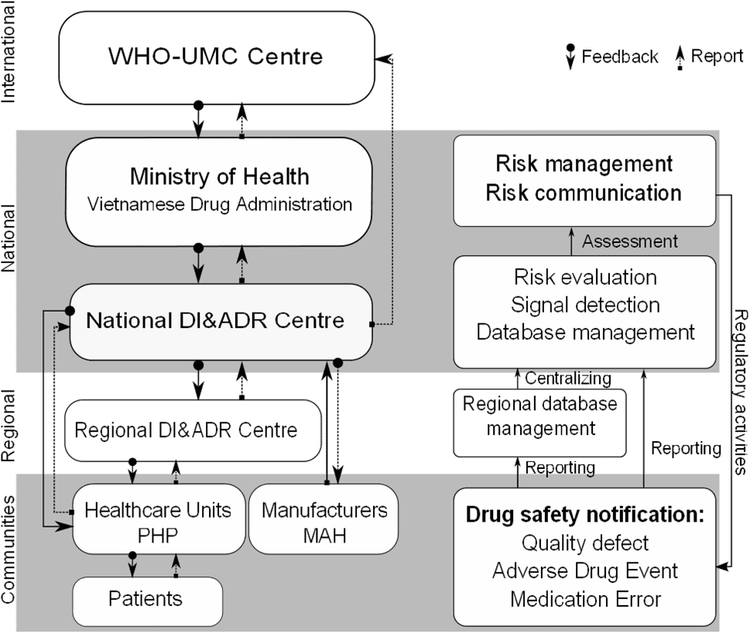
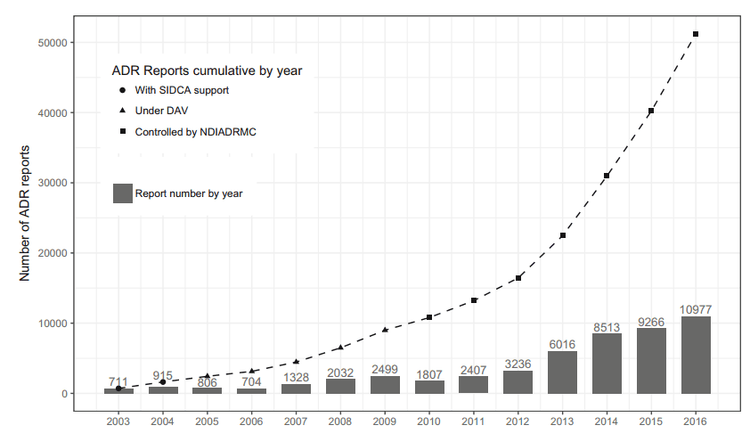
In recent years, under the coordination of the DI&ADR Center, the pharmacovigilance activity in Vietnam is growing rapidly, not only in terms of the number of reports (Figure 2) but also in the quality of reports[ 3].
The latest pharmacovigilance is always deployed and strongly promoted in countries. In our country, there has also been a marked improvement to ensure safe drug use.
References:
Ministry of Health (2015), National Guidelines for Pharmacovigilance, pp. 1-142. World Health Organization (2002), The importance of pharmacovigilance - Safety monitoring of medicinal products , pp. 48 p. Nguyen K. D., Nguyen P. T., et al. (2018), "Overview of Pharmacovigilance System in Vietnam: Lessons Learned in a Resource-Restricted Country", Drug Saf , 41(2), pp. 151-159. Wikipedia, "Committee on Safety of Medicines", Retrieved 05/07, 2020, from https://en.wikipedia.org/w/index.php?title=Committee_on_Safety_of_Medicines&oldid=944084091. World Health Organization (2006), The safety of medicins in public health programmes: Pharmacovigilance an essential tool , pp. 21-24.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.